Amino Acids and Healthy Muscle - SEA
... Amino acid intake through meals and supplements has a great influence on the maintenance and promotion of our body muscles. In particular, the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) which cannot be produced in our living body are called “essential amino acids”. Human beings should take BCAAs (valine, le ...
... Amino acid intake through meals and supplements has a great influence on the maintenance and promotion of our body muscles. In particular, the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) which cannot be produced in our living body are called “essential amino acids”. Human beings should take BCAAs (valine, le ...
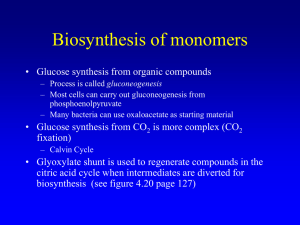
Biosynthesis of monomers
... – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
... – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
Protein Folding Lab with Balloons
... DNA codes for RNA which codes for the order of amino acids to make specific proteins. A protein’s structure determines its function. Since different amino acids have different properties, they influence the folding of the protein. Some amino acids are hydrophobic, some polar, and others ionic ( + or ...
... DNA codes for RNA which codes for the order of amino acids to make specific proteins. A protein’s structure determines its function. Since different amino acids have different properties, they influence the folding of the protein. Some amino acids are hydrophobic, some polar, and others ionic ( + or ...
Ch 30 reading guide
... 1.Degradation of amino acids is primarily in the _________________, with the first step being removal of ______________________. 2. The a-amino group of many amino acids if transferred to a-ketogluterate to make _________________________, which is then oxidativley deaminated to yiled _______________ ...
... 1.Degradation of amino acids is primarily in the _________________, with the first step being removal of ______________________. 2. The a-amino group of many amino acids if transferred to a-ketogluterate to make _________________________, which is then oxidativley deaminated to yiled _______________ ...
File
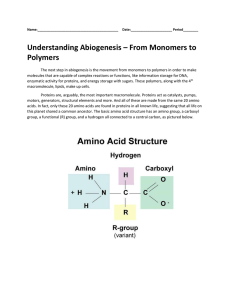
... The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromolecule, l ...
... The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromolecule, l ...
Catabolism of Carbon Skeletons of AAs1.06 MB
... • The pathways of amino acid catabolism normally accounts for only 10-15% of human body's energy production. • 20 catabolic pathways converge to form only 6 major products, all of which enter citric acid cycle. • From there, C skeletons are diverted to gluconeogenesis or ketogenesis or are complete ...
... • The pathways of amino acid catabolism normally accounts for only 10-15% of human body's energy production. • 20 catabolic pathways converge to form only 6 major products, all of which enter citric acid cycle. • From there, C skeletons are diverted to gluconeogenesis or ketogenesis or are complete ...
CLINICAL CASE (UREA CYCLE)
... Urinary orotic acid excretion was 285 g/mg creatinine (normal: 0.3 – 10 g/mg creatinine). Oral therapy was started by administering a combination of essential amino acids (including arginine) at a dose of 1.1g/kg/d. By the seventh day, his plasma NH4+ level was 40 uM, and he appeared clinically we ...
... Urinary orotic acid excretion was 285 g/mg creatinine (normal: 0.3 – 10 g/mg creatinine). Oral therapy was started by administering a combination of essential amino acids (including arginine) at a dose of 1.1g/kg/d. By the seventh day, his plasma NH4+ level was 40 uM, and he appeared clinically we ...
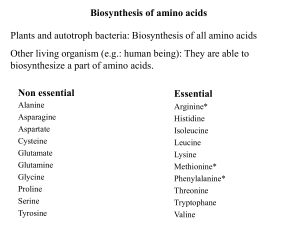
Biosynthesis of the nutritionally nonessential amino acids
... misleading since all 20 common amino acids are essential to ensure health. ...
... misleading since all 20 common amino acids are essential to ensure health. ...
CHAP Twenty-Five - Foothill College
... 1) Amino Acid Structure A) Stereochemistry B) Acid/Base properties C) Zwitterion D) pI definition and calculations E) Gel electrophoresis 2) Synthesis of Amino Acids A) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky: Carboxylic acid to α-haloacid then SN2 reaction w excess ammonia B) Streker Synthesis: Aldehyde with NH4Cl a ...
... 1) Amino Acid Structure A) Stereochemistry B) Acid/Base properties C) Zwitterion D) pI definition and calculations E) Gel electrophoresis 2) Synthesis of Amino Acids A) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky: Carboxylic acid to α-haloacid then SN2 reaction w excess ammonia B) Streker Synthesis: Aldehyde with NH4Cl a ...
Biology Section 2 Molecules of Life Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
... o Polypeptides- long string of amino acids o Protein shape influenced by bonding, solvent, temperature Enzymes o Enzymes- RNA or protein catalysts o Physical fit between enzyme and substrate (substance being catalyzed) o Active site- folds o Slight change in shape weakens chemical bonds o Enzymes ...
... o Polypeptides- long string of amino acids o Protein shape influenced by bonding, solvent, temperature Enzymes o Enzymes- RNA or protein catalysts o Physical fit between enzyme and substrate (substance being catalyzed) o Active site- folds o Slight change in shape weakens chemical bonds o Enzymes ...
FCH 532 Lecture 27
... Reaction 2: displacement of the acetate by sulfide. Sulfide is derived fro man 8-electron reduction reaction. ...
... Reaction 2: displacement of the acetate by sulfide. Sulfide is derived fro man 8-electron reduction reaction. ...
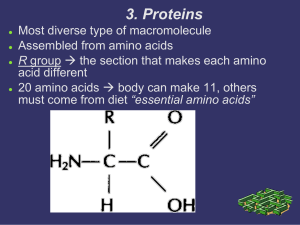
3. Proteins
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
... R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
4.1_Proteins_Amino_Acids_2011
... chain (green circles). (B) The conformation of the main-chain atoms in a protein is determined by one pair of ϕ and ψ angles for each amino acid; because of steric collisions between atoms within each amino acid, most pairs of ϕ and ψ angles do not occur. In this so-called Ramachandran plot, each do ...
... chain (green circles). (B) The conformation of the main-chain atoms in a protein is determined by one pair of ϕ and ψ angles for each amino acid; because of steric collisions between atoms within each amino acid, most pairs of ϕ and ψ angles do not occur. In this so-called Ramachandran plot, each do ...
Competition
... small units called amino acids bonded together There are only 20 types of amino acids, but there are millions of proteins. Therefore the number of amino acids, and their sequence determine the protein. Only 12 of the amino acids can be made by our body, the rest have to come from our food (meat, n ...
... small units called amino acids bonded together There are only 20 types of amino acids, but there are millions of proteins. Therefore the number of amino acids, and their sequence determine the protein. Only 12 of the amino acids can be made by our body, the rest have to come from our food (meat, n ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... _____ 1. Choose the nucleotide sequence of the RNA strand that would be complementary to the following DNA strand: GTAGTCA a. UATUAGA. b. ACGACTG. c. CAUCAGU. d. CATCAGT. _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes ...
... _____ 1. Choose the nucleotide sequence of the RNA strand that would be complementary to the following DNA strand: GTAGTCA a. UATUAGA. b. ACGACTG. c. CAUCAGU. d. CATCAGT. _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes ...
Biosynthesis of amino acids
... Nitrogenase complexes of different species are highly conservative. Subunits of different nitrogenases are compatible. ...
... Nitrogenase complexes of different species are highly conservative. Subunits of different nitrogenases are compatible. ...
Amino acids catabolism
... Glutamate is formed from NH4+ and α-ketoglutarate in a reductive amination that requires NADPH. This reaction is catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) The conversion of Glutamate to Glutamine is catalyzed by glutamine synthetase (GS) that requires ATP Combination of GDH and GS is responsible fo ...
... Glutamate is formed from NH4+ and α-ketoglutarate in a reductive amination that requires NADPH. This reaction is catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) The conversion of Glutamate to Glutamine is catalyzed by glutamine synthetase (GS) that requires ATP Combination of GDH and GS is responsible fo ...
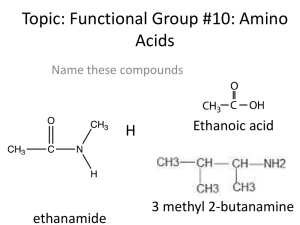
Topic: Functional Group #10: Amino Acids
... Topic: Functional Group #10: Amino Acids Name these compounds ...
... Topic: Functional Group #10: Amino Acids Name these compounds ...
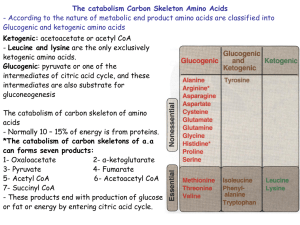
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
MECHANISTIC INVESTIGATION OF D-ARGININE DEHYDROGENASE FROM PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA
... D-‐arginine dehydrogenase (DADH) catalyzes the oxidation of D-‐amino acids to the corresponding iminoacids, which are non-‐enzymatically hydrolyzed in solution to α-‐ ketoacids and ammonia. The enzyme ...
... D-‐arginine dehydrogenase (DADH) catalyzes the oxidation of D-‐amino acids to the corresponding iminoacids, which are non-‐enzymatically hydrolyzed in solution to α-‐ ketoacids and ammonia. The enzyme ...