Proteins
... 1. Amino group NH2 2. Carboxyl group –COOH 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
... 1. Amino group NH2 2. Carboxyl group –COOH 3. R group -different for every AA -determines the properties of AA Joined together by peptide bonds ...
(key)
... ~ U..tvA #V\I~c ... l,,t or~ ~.It fv-'-"1 OJ.J.P.{~,....,f'lA~)sJrt.r/- fk.._ tn f4v.A h.~$ "' 'c dfl~' ti-u... AA ~l..t.l.nu ev,"jt, ,,... fu l>Jv.4 ...
... ~ U..tvA #V\I~c ... l,,t or~ ~.It fv-'-"1 OJ.J.P.{~,....,f'lA~)sJrt.r/- fk.._ tn f4v.A h.~$ "' 'c dfl~' ti-u... AA ~l..t.l.nu ev,"jt, ,,... fu l>Jv.4 ...
SAMPLE ABSTRACT
... This laboratory has recently cloned and functionally identified cDNAs encoding SAT1 and SAT2, the first members of the system A family of Na+-coupled glutamine transporters. Since glutamine is a critical precursor for neurotransmitter glutamate via the glutamate/glutamine cycle, we propose that SAT ...
... This laboratory has recently cloned and functionally identified cDNAs encoding SAT1 and SAT2, the first members of the system A family of Na+-coupled glutamine transporters. Since glutamine is a critical precursor for neurotransmitter glutamate via the glutamate/glutamine cycle, we propose that SAT ...
Final Review - Chemistry Courses: About: Department of
... 16. energetics of FA synthesis and degradation 17. nitrogen processing, catabolism of AA 18. medical applications of nucleotide metabolism 19. nucleic acid structure on atomic level ...
... 16. energetics of FA synthesis and degradation 17. nitrogen processing, catabolism of AA 18. medical applications of nucleotide metabolism 19. nucleic acid structure on atomic level ...
Document
... • Functionally related genes co-induced: – evidence for induction of specific biological pathways ...
... • Functionally related genes co-induced: – evidence for induction of specific biological pathways ...
Exercise 3
... 721 shows the mechanism for stage I of this reaction; the transformation of the amino acid to the keto acid (we also did this in lecture). A Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for stage II of this reaction which transforms a-Ketoglutarate to glutamate. Be sure to use an arrow pushing mechanism as done ...
... 721 shows the mechanism for stage I of this reaction; the transformation of the amino acid to the keto acid (we also did this in lecture). A Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for stage II of this reaction which transforms a-Ketoglutarate to glutamate. Be sure to use an arrow pushing mechanism as done ...
removal of amino gp from glutamate to release ammonia Other
... 3. Metabolic break down of carbon skeleton to generate common intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
... 3. Metabolic break down of carbon skeleton to generate common intermediates that can be catabolized to CO2 or used in anabolic pathways to be stored as glucose or fat. ...
Amino acids
... • made by bonding amino acids together is specific orders • Amino acids • monomers (building blocks) of proteins • over 500 different AA are known • 20 AA are standard and make many different kinds of proteins • 9 are considered essential (must get from the diet) our body can’t make them • the shape ...
... • made by bonding amino acids together is specific orders • Amino acids • monomers (building blocks) of proteins • over 500 different AA are known • 20 AA are standard and make many different kinds of proteins • 9 are considered essential (must get from the diet) our body can’t make them • the shape ...
BIO 101 Exam 2 Practice Quiz Name
... You will be able to use a periodic table for your exam. Multiple Choice 1. What is the weakest type of chemical bond? a. Covalent b. Ionic ...
... You will be able to use a periodic table for your exam. Multiple Choice 1. What is the weakest type of chemical bond? a. Covalent b. Ionic ...
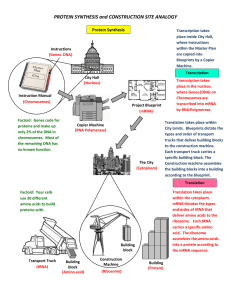
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
FALSE degradation also needs to be considered. A change in
... 5. Ketone bodies are synthesized in the adipose tissue from dietary fatty acids. FALSE KB’s are synthesized primarily in liver, not in adipose. KB are synthesized when acetyl CoA supply in mitochondria exceeds the energy need of that cell. While dietary fatty acids might be used to synthesize KB by ...
... 5. Ketone bodies are synthesized in the adipose tissue from dietary fatty acids. FALSE KB’s are synthesized primarily in liver, not in adipose. KB are synthesized when acetyl CoA supply in mitochondria exceeds the energy need of that cell. While dietary fatty acids might be used to synthesize KB by ...
Proteins
... Aminoacids are called as Magic 20 because they form the basic components of life Amino acids are Mono or Di carboxylic acids with one or two amino groups (NH2). Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized in the body Essential amino acids are 1 to 8 in adults and 1 to 10 in children The 10 essential ...
... Aminoacids are called as Magic 20 because they form the basic components of life Amino acids are Mono or Di carboxylic acids with one or two amino groups (NH2). Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized in the body Essential amino acids are 1 to 8 in adults and 1 to 10 in children The 10 essential ...
+ E A.
... Genetic defects for both the synthase and the lyase. Missing or impaired cystathionine synthase leads to homocystinuria. High concentration of homocysteine and methionine in the urine. Homocysteine is highly reactive molecule. Disease is often associated with mental retardation, multisystemic disord ...
... Genetic defects for both the synthase and the lyase. Missing or impaired cystathionine synthase leads to homocystinuria. High concentration of homocysteine and methionine in the urine. Homocysteine is highly reactive molecule. Disease is often associated with mental retardation, multisystemic disord ...
RESEARCH NOTES
... - al. - ( 1951 J. Biol. Chem. l88:397) has revealed that all enzymes of the tryptophan biosynthetic pathway are decreased two- to five-fold when zinc is omitted from the growth medium (Vogel’s Medium N). The effect is mare marked in a histidine mutant than in the wild type. An explanation of this ef ...
... - al. - ( 1951 J. Biol. Chem. l88:397) has revealed that all enzymes of the tryptophan biosynthetic pathway are decreased two- to five-fold when zinc is omitted from the growth medium (Vogel’s Medium N). The effect is mare marked in a histidine mutant than in the wild type. An explanation of this ef ...
biomolecule notes
... a. Made of amino acids b. There are 20 different amino acids c. The sequence of amino acids determines the proteins shape & function d. Polypeptide = long chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds e. provide structure for tissues & organs f. carry out cell metabolism g. examples: egg whites, enzy ...
... a. Made of amino acids b. There are 20 different amino acids c. The sequence of amino acids determines the proteins shape & function d. Polypeptide = long chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds e. provide structure for tissues & organs f. carry out cell metabolism g. examples: egg whites, enzy ...
5.Amino acids
... • Flavor enhancers, MSG, glycine, alanine. Tryptophan and histidine act as antioxidants to preserve milk powder. For fruit juices cysteine is used as an antioxidant. • Aspartame, dipeptide (aspartyl-phenylalanine-methyl ester) produced by combination of asp and Phe is 200 sweeter than sucrose. Used ...
... • Flavor enhancers, MSG, glycine, alanine. Tryptophan and histidine act as antioxidants to preserve milk powder. For fruit juices cysteine is used as an antioxidant. • Aspartame, dipeptide (aspartyl-phenylalanine-methyl ester) produced by combination of asp and Phe is 200 sweeter than sucrose. Used ...
Amino acids introduction
... Cysteine Aspartic acid (Aspartate) Glutamic acid (Glutamate) Phenylalanine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Lysine Leucine Methionine Asparagine Proline Glutamine Arginine Serine Threonine Valine Tryptophan Tyrosine ©CMBI 2001 ...
... Cysteine Aspartic acid (Aspartate) Glutamic acid (Glutamate) Phenylalanine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Lysine Leucine Methionine Asparagine Proline Glutamine Arginine Serine Threonine Valine Tryptophan Tyrosine ©CMBI 2001 ...
1 - UCSB CLAS
... 3. (Ch 24, #17) Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an amino acid transformation is greatly reduced if a PLP-requiring enzymatic reaction is carried out at a pH at which the pyridine nitrogen is not protonated. 4. (Ch 24, #18) Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an amino acid transform ...
... 3. (Ch 24, #17) Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an amino acid transformation is greatly reduced if a PLP-requiring enzymatic reaction is carried out at a pH at which the pyridine nitrogen is not protonated. 4. (Ch 24, #18) Explain why the ability of PLP to catalyze an amino acid transform ...