Protein Sequence WKS - Kenton County Schools
... If this protein is made it causes the organism to be very sarcastic and sing Happy Birthday in a high pitch squeaky voice. This organism eats chocolate chip cookies uncontrollably and enjoys making fun of 15-16 year olds. methionine – glycine – lysine – tryptophan – asparagines – proline – alanine – ...
... If this protein is made it causes the organism to be very sarcastic and sing Happy Birthday in a high pitch squeaky voice. This organism eats chocolate chip cookies uncontrollably and enjoys making fun of 15-16 year olds. methionine – glycine – lysine – tryptophan – asparagines – proline – alanine – ...
General pathways of amino acids transformation
... active dehydrogenase Present in both the cytosol and mitochondria of the liver ...
... active dehydrogenase Present in both the cytosol and mitochondria of the liver ...
2770 October 2007 Mid-Term Test
... All of the following functions of an enzyme are true EXCEPT: A) Enzymes help to catalyze nearly all metabolic reactions. B) Enzyme activity is sensitive to enzyme and substrate concentration. C) Enzymes are sensitive to temperature and pH changes. D. An increased activity of an enzyme increases the ...
... All of the following functions of an enzyme are true EXCEPT: A) Enzymes help to catalyze nearly all metabolic reactions. B) Enzyme activity is sensitive to enzyme and substrate concentration. C) Enzymes are sensitive to temperature and pH changes. D. An increased activity of an enzyme increases the ...
Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids and are
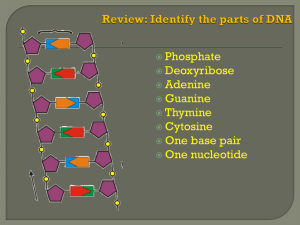
... COLOR and LABEL the parts of a nucleotide --- sugar (5-sided)-green, phosphate group (round)yellow, and nitrogen base (6-sided)-blue. ATP used for cellular energy is a high energy nucleotide with three phosphate groups. Color code the ATP and LABEL THE PHOSPHATES. ...
... COLOR and LABEL the parts of a nucleotide --- sugar (5-sided)-green, phosphate group (round)yellow, and nitrogen base (6-sided)-blue. ATP used for cellular energy is a high energy nucleotide with three phosphate groups. Color code the ATP and LABEL THE PHOSPHATES. ...
ATP
... from PRPP, Gln, Gly, N10-formyl H4 folate, HCO3-, Asp through the de novo pathway. • Pyrimidine nucleotides are synthesized using HCO3-, Gln, Asp, and PRPP. • De novo synthesis of nucleotides are regulated via feedback inhibition. ...
... from PRPP, Gln, Gly, N10-formyl H4 folate, HCO3-, Asp through the de novo pathway. • Pyrimidine nucleotides are synthesized using HCO3-, Gln, Asp, and PRPP. • De novo synthesis of nucleotides are regulated via feedback inhibition. ...
mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart
... • Transcribe the DNA into mRNA codons by writing the complementary bases. • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that ...
... • Transcribe the DNA into mRNA codons by writing the complementary bases. • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that ...
Nucleic Acids - Spring Branch ISD
... another monomer and creates water as a byproduct. The remaining “loose ends of the two monomer join together) Molecule- a chemically bonded combination of 2 or more atoms Ex: O2, H2O, C6H12O6 Compound- a chemically bonded combination of 2 or more DIFFERENT atoms Ex: H2O, C6H12O6 Biomolecule- a molec ...
... another monomer and creates water as a byproduct. The remaining “loose ends of the two monomer join together) Molecule- a chemically bonded combination of 2 or more atoms Ex: O2, H2O, C6H12O6 Compound- a chemically bonded combination of 2 or more DIFFERENT atoms Ex: H2O, C6H12O6 Biomolecule- a molec ...
Mic 428 Lecture 11
... product of gene C can be prevented by control at the level of translation. The synthesis of the product of gene D can be prevented by control at the level of transcription. ...
... product of gene C can be prevented by control at the level of translation. The synthesis of the product of gene D can be prevented by control at the level of transcription. ...
A1985ASW1100001
... reversibly and at a separate site. The clincher as to its role in protein synthesis was that after it was charged with amino acids and reisolated, its bound amino acids were rapidly and quantitatively transferred to peptide linkages in protein on ribosomes~And that reaction was dependent on GTP. Pre ...
... reversibly and at a separate site. The clincher as to its role in protein synthesis was that after it was charged with amino acids and reisolated, its bound amino acids were rapidly and quantitatively transferred to peptide linkages in protein on ribosomes~And that reaction was dependent on GTP. Pre ...
Lecture#20
... in the figure: one of these is serine that can be changed to a selenocysteine and a second is methionine that can be formylated (cofactor is N-10 formyl tetrafolate) A 22nd amino acid was recently found in archae and is pyrrolysine ...
... in the figure: one of these is serine that can be changed to a selenocysteine and a second is methionine that can be formylated (cofactor is N-10 formyl tetrafolate) A 22nd amino acid was recently found in archae and is pyrrolysine ...
Lecture 40
... Amino acids are precursors of numerous biomolecules A variety of biomolecules are derived from amino acids ...
... Amino acids are precursors of numerous biomolecules A variety of biomolecules are derived from amino acids ...
Enzyme Shape
... a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. Different types of enzymes have different shapes and functions because ...
... a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. Different types of enzymes have different shapes and functions because ...
Covalent Reactions Atoms SHARE electrons
... • Secondary: polypeptides take on a certain orientation in space (alpha helix or pleated sheet) due to hydrogen bonding between peptides • Tertiary: final 3D shape maintained by various bonding (covalent, ionic and hydrogen) • Quaternary: only in some protein, due to polypeptide arrangements ...
... • Secondary: polypeptides take on a certain orientation in space (alpha helix or pleated sheet) due to hydrogen bonding between peptides • Tertiary: final 3D shape maintained by various bonding (covalent, ionic and hydrogen) • Quaternary: only in some protein, due to polypeptide arrangements ...
Regulation on Cellular respiration
... intermediates. High concentrations of citrate indicate a plentiful supply of intermediates for energy production; therefore, high activity of the glycolytic pathway is not required. • This allows regulation between glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle. ...
... intermediates. High concentrations of citrate indicate a plentiful supply of intermediates for energy production; therefore, high activity of the glycolytic pathway is not required. • This allows regulation between glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle. ...
amino acids
... thousands of proteins ● amino acids differ from each other at their “side” or “R” chains ● because they are so different, and can be put together in almost infinite combinations, proteins are among the most diverse macromolecules. ...
... thousands of proteins ● amino acids differ from each other at their “side” or “R” chains ● because they are so different, and can be put together in almost infinite combinations, proteins are among the most diverse macromolecules. ...
A plant has stunted growth and yellowing leaves because it is
... The diagram below shows an endergonic reaction in which a dipeptide is formed from two amino acids in a cell. ...
... The diagram below shows an endergonic reaction in which a dipeptide is formed from two amino acids in a cell. ...
bonds form when water is removed to hold acids together.
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of _____________ in a process called __________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make ________________________ which can join together to make a ...
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of _____________ in a process called __________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make ________________________ which can join together to make a ...























