Page 50 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... while a protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains twisted and folded together into a specific shape. The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain determines the three-dimensional shape of the protein. 25. A protein is denatured if its three-dimensional shape is altered in any way (by temp ...
... while a protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains twisted and folded together into a specific shape. The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain determines the three-dimensional shape of the protein. 25. A protein is denatured if its three-dimensional shape is altered in any way (by temp ...
Cloze passage 4
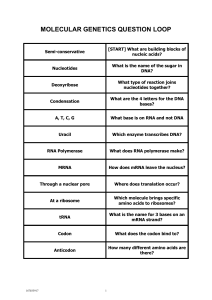
... CLOZE PASSAGE No 4 Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 ...
... CLOZE PASSAGE No 4 Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 ...
metabolism of amino acids
... amino nitrogen to αketoglutarate to produce glutamate- leaving behind the carbon skeleton • After removal of their amino groups, the carbon skeleton of aa undergo oxidation to compounds that can enter the TCA cycle ...
... amino nitrogen to αketoglutarate to produce glutamate- leaving behind the carbon skeleton • After removal of their amino groups, the carbon skeleton of aa undergo oxidation to compounds that can enter the TCA cycle ...
Chapter 3 - Proteins
... • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or greatest order) when it is completely stretched out like a string and when it is properly folded up. Explain. • (True/False) Loops of polypeptide that protrude from the surface of a protein often form the binding sit ...
... • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or greatest order) when it is completely stretched out like a string and when it is properly folded up. Explain. • (True/False) Loops of polypeptide that protrude from the surface of a protein often form the binding sit ...
Slide 12
... 17- which of the following amino acids are most likely to be found in the outside of the globular protein and which of them are more likely to be found in the inside of the protein : ( in globular protein , the outside is hydrophilic and the inside is hydrophobic ) Valine >> inside Aspartate >> outs ...
... 17- which of the following amino acids are most likely to be found in the outside of the globular protein and which of them are more likely to be found in the inside of the protein : ( in globular protein , the outside is hydrophilic and the inside is hydrophobic ) Valine >> inside Aspartate >> outs ...
amino acid , peptide and protein metabolism
... • Asparagine: Asparagine is synthesized by the transfer to the amide group of glutamine to the ß-carboxyl group of aspartate ...
... • Asparagine: Asparagine is synthesized by the transfer to the amide group of glutamine to the ß-carboxyl group of aspartate ...
syllabus - Wofford
... Section I – Course Introduction – Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins – Enzymes In this section, you will need to learn the structures of the amino acids. It isn’t so difficult, because you really only need to remember the R groups. Amino acid structures are important for your understanding protein stru ...
... Section I – Course Introduction – Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins – Enzymes In this section, you will need to learn the structures of the amino acids. It isn’t so difficult, because you really only need to remember the R groups. Amino acid structures are important for your understanding protein stru ...
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters
... serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs), like Prozac® inhibit the reuptake process resulting in prolonged serotonin presence in the synaptic cleft. ...
... serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs), like Prozac® inhibit the reuptake process resulting in prolonged serotonin presence in the synaptic cleft. ...
Organic Compounds
... R group makes each amino acid different There are 20 possible amino acids based off this one group The R group is = variable ...
... R group makes each amino acid different There are 20 possible amino acids based off this one group The R group is = variable ...
study guide section 3-1 carbon compounds
... a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ Most enzymes a. are changed by the reactions they catalyze. b. increase that activat ...
... a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ Most enzymes a. are changed by the reactions they catalyze. b. increase that activat ...
Physical properties of amino acids: Chemical properties of amino
... 2-Angiotensin II (8 amino acids) Asp.-Arg.-Val.-Tyr.-Ilu.-His.-Pro.-Phe. (vasoconstrictor) hormone. 3-Vasopressin (9 amino acids) Cys.-Tyr.-Phe.-Gln.-Asn.-Cys.-Pro.-Arg.-Gly. (antidiuretic hormone), acts on kidney tubules to prevent dieresis, secreted by the pituitary gland. ...
... 2-Angiotensin II (8 amino acids) Asp.-Arg.-Val.-Tyr.-Ilu.-His.-Pro.-Phe. (vasoconstrictor) hormone. 3-Vasopressin (9 amino acids) Cys.-Tyr.-Phe.-Gln.-Asn.-Cys.-Pro.-Arg.-Gly. (antidiuretic hormone), acts on kidney tubules to prevent dieresis, secreted by the pituitary gland. ...
A mutant defective in enzyme
... (c) Relatively high [K ] outside the cell and high [Na ] inside the cell, with greater permeability of the membrane to K+ than Na+. (d) Relatively high [K+] outside the cell and high [Na+] inside the cell, with greater permeability of the membrane to Na+ than K+. (e) Rubbing the cells together so th ...
... (c) Relatively high [K ] outside the cell and high [Na ] inside the cell, with greater permeability of the membrane to K+ than Na+. (d) Relatively high [K+] outside the cell and high [Na+] inside the cell, with greater permeability of the membrane to Na+ than K+. (e) Rubbing the cells together so th ...
serotoninSummary
... Tryptophan (Trp or W) is one of the 20 standard amino acids and is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the human body. Tryptophan is composed of the standard amino acid backbone with an indole ring side chain. Version 1.4 -11/2015 ...
... Tryptophan (Trp or W) is one of the 20 standard amino acids and is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the human body. Tryptophan is composed of the standard amino acid backbone with an indole ring side chain. Version 1.4 -11/2015 ...
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle
... • Glutamine is the major transport form of ammonia; it is present in blood in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. ...
... • Glutamine is the major transport form of ammonia; it is present in blood in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. ...
Protein Structure - Information technology
... structure, solution conditions (& history) and ingredient interactions ...
... structure, solution conditions (& history) and ingredient interactions ...
AMINO ACID: STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION.
... • Essential to be taken in diet. • Arginine and histidine are semi-essential • Non-essential • Can be synthesized in the body ...
... • Essential to be taken in diet. • Arginine and histidine are semi-essential • Non-essential • Can be synthesized in the body ...
Lecture 39 - Amino Acid Metabolism 2
... • Numerous genetic diseases are caused by defects in amino acid metabolic pathways; genetic diseases can be due to recessive or dominant mutations. ...
... • Numerous genetic diseases are caused by defects in amino acid metabolic pathways; genetic diseases can be due to recessive or dominant mutations. ...
A1983RT00700001
... unpleasant) method of phenollN 113 paper chromatography used so successfully by October 31, 1983 Fowden for the separation of nonprotein 1 amino acids. Using isolated intact pea “In the early 1960s, Sims and Folkes chloroplast and extracts derived from them clearly showed the role of the enzyme glu- ...
... unpleasant) method of phenollN 113 paper chromatography used so successfully by October 31, 1983 Fowden for the separation of nonprotein 1 amino acids. Using isolated intact pea “In the early 1960s, Sims and Folkes chloroplast and extracts derived from them clearly showed the role of the enzyme glu- ...
2.1 Molecules and metabolism
... • Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a diversity of stable compounds to exist. • Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. • Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme-catalysed reactions in a cell or organism. • Anabolism is the synt ...
... • Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a diversity of stable compounds to exist. • Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. • Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme-catalysed reactions in a cell or organism. • Anabolism is the synt ...
Macromolecules 9-3
... molecule joins monomers together to form polymers a. This process can reverse b. The adding of a water molecule to a polymer, which breaks the polymer into a monomer is called hydrolysis Lipids a. DO NOT FORM POLYMERS b. “Water-Fearing” i. HYDROPHOBIC c. Three classes of biologically important lipid ...
... molecule joins monomers together to form polymers a. This process can reverse b. The adding of a water molecule to a polymer, which breaks the polymer into a monomer is called hydrolysis Lipids a. DO NOT FORM POLYMERS b. “Water-Fearing” i. HYDROPHOBIC c. Three classes of biologically important lipid ...
Chapter 21 Biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and related
... compounds are generally scarce in the natural environments. • Free amino acids, pyrimidines and purines formed from metabolic turnover are often salvaged (reused). • Only certain bacteria are able to fix N2 into ammonia (NH3 or NH4+). ...
... compounds are generally scarce in the natural environments. • Free amino acids, pyrimidines and purines formed from metabolic turnover are often salvaged (reused). • Only certain bacteria are able to fix N2 into ammonia (NH3 or NH4+). ...