Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) functions as an amino group carrier in aminotransferases ...
... Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) functions as an amino group carrier in aminotransferases ...
Amino Acids
... reorders them, re-folds them, and turns them into whatever is needed by the body at that time. From only 20 amino acids, the body is able to make thousands of unique proteins with different functions. ...
... reorders them, re-folds them, and turns them into whatever is needed by the body at that time. From only 20 amino acids, the body is able to make thousands of unique proteins with different functions. ...
Chemical Compounds in Cells and in Our Food
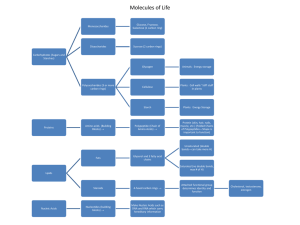
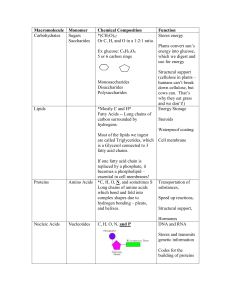
... Complex carbohydrates – made up of many simple sugars attached to each other – Starch – Cellulose – make up plant cell walls Found in cell membranes, other cell parts, and ...
... Complex carbohydrates – made up of many simple sugars attached to each other – Starch – Cellulose – make up plant cell walls Found in cell membranes, other cell parts, and ...
Protein Digestion and Absorption
... phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are essential because the body can’t synthesize them. They must be present in the diet or they will be deficient. Four amino acids are considered conditionally essential including arginine, ...
... phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are essential because the body can’t synthesize them. They must be present in the diet or they will be deficient. Four amino acids are considered conditionally essential including arginine, ...
2.3 Biomolecules Hon
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Inborn error in metabolism of amino acids
... inability of the body to metabolize phenylalanine, caused by a deficiency in Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH) enzyme or The defect is due to deficiency of dihydrobiopterin reductase.an enzyme that catalyzes the regeneration of tetrahydrobiopterin (cofactor of PAH) ...
... inability of the body to metabolize phenylalanine, caused by a deficiency in Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH) enzyme or The defect is due to deficiency of dihydrobiopterin reductase.an enzyme that catalyzes the regeneration of tetrahydrobiopterin (cofactor of PAH) ...
1 - edl.io
... 18. Define the following terms: solution, solvent, solute, concentration 19. Describe what the pH scale tells us about H+ concentration & how to use it. 20. What is an acid? What is a base? 21. What is an organic compound? 22. What are the four main organic molecules found in organism? 23. List the ...
... 18. Define the following terms: solution, solvent, solute, concentration 19. Describe what the pH scale tells us about H+ concentration & how to use it. 20. What is an acid? What is a base? 21. What is an organic compound? 22. What are the four main organic molecules found in organism? 23. List the ...
Solvil - Vitaflo UK
... Indications Solvil is for use in the dietary management of urea cycle disorders or other inborn errors of metabolism requiring branched chain amino acid (BCAA) supplementation. Dosage and Administration To be determined by the clinician or dietitian and is dependent on the age, bodyweight and medica ...
... Indications Solvil is for use in the dietary management of urea cycle disorders or other inborn errors of metabolism requiring branched chain amino acid (BCAA) supplementation. Dosage and Administration To be determined by the clinician or dietitian and is dependent on the age, bodyweight and medica ...
ap biology review guide big idea #2
... 1. If the following molecules were to undergo a dehydration synthesis reaction, what molecules would result? Circle the parts of each amino acid that will interact and draw the resulting molecule. ...
... 1. If the following molecules were to undergo a dehydration synthesis reaction, what molecules would result? Circle the parts of each amino acid that will interact and draw the resulting molecule. ...
practice making a protein from dna
... Look up each 3 letter codon on the table of amino acids and write down the three letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Do this next to the word "Protein" (Amino acids can be written as words or abbreviations like this: Arginine or Arg or R) It should look like MET - ARG - ... - ... - GLN STOP (bu ...
... Look up each 3 letter codon on the table of amino acids and write down the three letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Do this next to the word "Protein" (Amino acids can be written as words or abbreviations like this: Arginine or Arg or R) It should look like MET - ARG - ... - ... - GLN STOP (bu ...
Biomolecules Worksheet
... 5). All enzymes and proteins are chains of specific amino acids, but in order for them to perform their specific tasks, they must also have the correct 3D shape. a) There are a number of structural levels in a protein, describe what is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. ...
... 5). All enzymes and proteins are chains of specific amino acids, but in order for them to perform their specific tasks, they must also have the correct 3D shape. a) There are a number of structural levels in a protein, describe what is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. ...
File
... • All the protein amino acids except lysine, threonine, proline, and hydroxyproline participate in transamination. • Transamination is readily reversible, and aminotransferases also function in amino acid biosynthesis. • The coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is present at the catalytic site of ami ...
... • All the protein amino acids except lysine, threonine, proline, and hydroxyproline participate in transamination. • Transamination is readily reversible, and aminotransferases also function in amino acid biosynthesis. • The coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is present at the catalytic site of ami ...
Bi 12 Biological Molecules Current.pptx
... ¨ occurs when two or more proteins are joined together to form a protein complex. ¨ Held together by hydrogen bonds or disulphide bridges ...
... ¨ occurs when two or more proteins are joined together to form a protein complex. ¨ Held together by hydrogen bonds or disulphide bridges ...
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
... Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
1-1 Amino Acids
... peptide backbone, to polar organic molecules, and to water. This tendency dominates the interactions in which they participate. Some of them can change their charge state depending on their pH or the microenvironment. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid have pKa values near 5 in aqueous solution, so the ...
... peptide backbone, to polar organic molecules, and to water. This tendency dominates the interactions in which they participate. Some of them can change their charge state depending on their pH or the microenvironment. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid have pKa values near 5 in aqueous solution, so the ...
Lecture 27
... Spontaneous cyclization is prevented by acetylation of amino group by Nacetylglutamate synthase. N-acetylglutamate-5-semialdehyde is converted to amine by transamination. Hydrolysis of protecting group yields ornithine which can be converted to arginine. In humans it is direct from glutamate-5-semia ...
... Spontaneous cyclization is prevented by acetylation of amino group by Nacetylglutamate synthase. N-acetylglutamate-5-semialdehyde is converted to amine by transamination. Hydrolysis of protecting group yields ornithine which can be converted to arginine. In humans it is direct from glutamate-5-semia ...
Protein Synthesis - Los Gatos High School
... proteins that control the functioning of the cell • There are two main types of RNA used: mRNA (messenger RNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA) ...
... proteins that control the functioning of the cell • There are two main types of RNA used: mRNA (messenger RNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA) ...
Document
... 30. Attracted to water molecules, "Water Loving" _________________________________ 31. Large carbon compounds are built from smaller molecules called ______________________________. 32. The main difference among the ________ different amino acids is found in their ______________________________. 33 ...
... 30. Attracted to water molecules, "Water Loving" _________________________________ 31. Large carbon compounds are built from smaller molecules called ______________________________. 32. The main difference among the ________ different amino acids is found in their ______________________________. 33 ...
QUIZ #1 - Introduction, Water, pH, buffers, Amino Acids, Proteins
... 13. Which of the following is NOT true about the pI of a tri-protic amino acid? a. When the pH = pI, the amino acid has no net charge b. When the pH = pI, the amino acid will not migrate in an electric field c. When the pH = pI, the amino acid is at its greatest buffering capacity d. When the pH = ...
... 13. Which of the following is NOT true about the pI of a tri-protic amino acid? a. When the pH = pI, the amino acid has no net charge b. When the pH = pI, the amino acid will not migrate in an electric field c. When the pH = pI, the amino acid is at its greatest buffering capacity d. When the pH = ...
03 - summer worksheet
... compounds suggested in the “types” column (choose from car4bohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). ...
... compounds suggested in the “types” column (choose from car4bohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Enzymes act on specific substrates ◦ Substrate: substance that the enzyme breaks down Each substrate fits into the active site. (Like a lock & key) ...
... Enzymes act on specific substrates ◦ Substrate: substance that the enzyme breaks down Each substrate fits into the active site. (Like a lock & key) ...