Slide 1
... with some differences: • RNA molecule is single-stranded (rather than double stranded in DNA) • Uracil instead of Thymine. So in RNA Adenine binds with Uracil ...
... with some differences: • RNA molecule is single-stranded (rather than double stranded in DNA) • Uracil instead of Thymine. So in RNA Adenine binds with Uracil ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Enzymes act on specific substrates ◦ Substrate: substance that the enzyme breaks down Each substrate fits into the active site. (Like a lock & key) ...
... Enzymes act on specific substrates ◦ Substrate: substance that the enzyme breaks down Each substrate fits into the active site. (Like a lock & key) ...
chapter3_part2
... coiled (helical) or sheetlike array held in place by hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) between different parts of the polypeptide chain. ...
... coiled (helical) or sheetlike array held in place by hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) between different parts of the polypeptide chain. ...
Nonessential Amino Acid Metabolism in Healthy Adult Males Using
... Rose et al. (1948) showed increased growth by 7075% in rats fed essential amino acids (EAA) + NEAA Rechcigl et al. (1957) showed different growth rates in rats Glutamate gave the largest increase in growth Followed by Alanine, Aspartate, Asparagine, Proline, and Glutamine Smallest increase ...
... Rose et al. (1948) showed increased growth by 7075% in rats fed essential amino acids (EAA) + NEAA Rechcigl et al. (1957) showed different growth rates in rats Glutamate gave the largest increase in growth Followed by Alanine, Aspartate, Asparagine, Proline, and Glutamine Smallest increase ...
Chapter 25
... phosphorylated form, NRI-P • NRI is phosphorylated by NRII, a protein kinase • If NRII is complexed with PIIA it acts as a phosphatase, not a kinase ...
... phosphorylated form, NRI-P • NRI is phosphorylated by NRII, a protein kinase • If NRII is complexed with PIIA it acts as a phosphatase, not a kinase ...
Structural basis for the functional differences between ASCT1 and
... The alanine, serine and cysteine transporters (ASCT1 and 2) are electroneutral exchangers. They belong to the Solute Carrier Family 1, along with human glutamate transporters (Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters EAATs). Neutral amino acid exchange via ASCT1 is thought to be coupled to only one Na+ io ...
... The alanine, serine and cysteine transporters (ASCT1 and 2) are electroneutral exchangers. They belong to the Solute Carrier Family 1, along with human glutamate transporters (Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters EAATs). Neutral amino acid exchange via ASCT1 is thought to be coupled to only one Na+ io ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 Part A
... 11. Bring out the biochemistry of co-enzymes. 12. Explain the reaction characteristics of proteins. 13. Describe the process of catabolism of amino acids. 14. Bring out the biosynthetic pathways of cholesterol and bile. 15. Explain the process and importance of electron transport chain. 16. Describe ...
... 11. Bring out the biochemistry of co-enzymes. 12. Explain the reaction characteristics of proteins. 13. Describe the process of catabolism of amino acids. 14. Bring out the biosynthetic pathways of cholesterol and bile. 15. Explain the process and importance of electron transport chain. 16. Describe ...
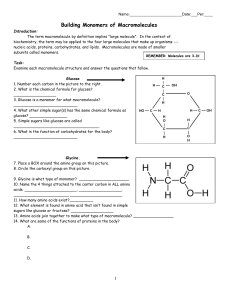
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... 12. What element is found in amino acid that isn’t found in simple sugars like glucose or fructose? __________________ 13. Amino acids join together to make what type of macromolecule? _________________ 14. What are some of the functions of proteins in the body? A. B. C. D. ...
... 12. What element is found in amino acid that isn’t found in simple sugars like glucose or fructose? __________________ 13. Amino acids join together to make what type of macromolecule? _________________ 14. What are some of the functions of proteins in the body? A. B. C. D. ...
Protein Synthesis
... hydrogen bonds by the enzyme Helicase. This occurs in the nucleus of the cell. Another enzyme, RNA polymerase, then binds to one unwound chain and the gene is transcribed into RNA (transcription). During transcription the triplet-codes of DNA, consisting of three nucleotides, are copied and correspo ...
... hydrogen bonds by the enzyme Helicase. This occurs in the nucleus of the cell. Another enzyme, RNA polymerase, then binds to one unwound chain and the gene is transcribed into RNA (transcription). During transcription the triplet-codes of DNA, consisting of three nucleotides, are copied and correspo ...
Biomolecules Fill in the crossword puzzle by using
... contains the elements carbon, hydrogen,oxygen and nitrogen and is composed of amino acids examples are insulin,hemglobin and enzymes. are the small building blocks of polymers ...
... contains the elements carbon, hydrogen,oxygen and nitrogen and is composed of amino acids examples are insulin,hemglobin and enzymes. are the small building blocks of polymers ...
NME2.35: amino acid and protein metabolism 13/03/08
... o Urea has the chemical structure H2N-C(=O)-NH2 o It is responsible for 90% of nitrogen excretion – 45g urea per day o It is water-soluble and an efficient nitrogen carrier (50% weight is nitrogen) o Its formation utilises both cytosolic and mitochondrial space The urea cycle consumes 3ATP and uses: ...
... o Urea has the chemical structure H2N-C(=O)-NH2 o It is responsible for 90% of nitrogen excretion – 45g urea per day o It is water-soluble and an efficient nitrogen carrier (50% weight is nitrogen) o Its formation utilises both cytosolic and mitochondrial space The urea cycle consumes 3ATP and uses: ...
Southern Blot
... CCU = proline PRO CCC = proline CCA = proline CCG = proline ACU = threonine THR ACC = threonine ACA = threonine ACG = threonine GCU = alanine ALA GCC = alanine GCA = alanine GCG = alanine UGU = cysteine UGC = cysteine UGA = stop UGG = tryptophan CGU = arginine CGC = arginine CGA = arginine CGG = arg ...
... CCU = proline PRO CCC = proline CCA = proline CCG = proline ACU = threonine THR ACC = threonine ACA = threonine ACG = threonine GCU = alanine ALA GCC = alanine GCA = alanine GCG = alanine UGU = cysteine UGC = cysteine UGA = stop UGG = tryptophan CGU = arginine CGC = arginine CGA = arginine CGG = arg ...
proteins - SD57 Mail
... • Ex. Keratin in hair and nails; collagen in skin; actin and myosin in muscle ...
... • Ex. Keratin in hair and nails; collagen in skin; actin and myosin in muscle ...
Southern Blot
... CCU = proline PRO CCC = proline CCA = proline CCG = proline ACU = threonine THR ACC = threonine ACA = threonine ACG = threonine GCU = alanine ALA GCC = alanine GCA = alanine GCG = alanine UGU = cysteine UGC = cysteine UGA = stop UGG = tryptophan CGU = arginine CGC = arginine CGA = arginine CGG = arg ...
... CCU = proline PRO CCC = proline CCA = proline CCG = proline ACU = threonine THR ACC = threonine ACA = threonine ACG = threonine GCU = alanine ALA GCC = alanine GCA = alanine GCG = alanine UGU = cysteine UGC = cysteine UGA = stop UGG = tryptophan CGU = arginine CGC = arginine CGA = arginine CGG = arg ...
Document
... Polymer: long chains of monomers Synthesizing and Digesting Polymers Dehydration Synthesis: removing a water molecule from 2 or more monomers to make a polymer Hydrolysis: adding water to a polymer to split it apart into ...
... Polymer: long chains of monomers Synthesizing and Digesting Polymers Dehydration Synthesis: removing a water molecule from 2 or more monomers to make a polymer Hydrolysis: adding water to a polymer to split it apart into ...
(C)
... 28. The term ketogenic amino acids refers to amino acids: (A) that are precursors for glucose synthesis, (B) degraded to yield acetyl CoA or acetoacetate, (C) that can not be converted to fatty acids or ketone bodies, (D) degraded to yield succinyl-CoA, pyruvate, a-ketoglutarate, fumarate and oxaloa ...
... 28. The term ketogenic amino acids refers to amino acids: (A) that are precursors for glucose synthesis, (B) degraded to yield acetyl CoA or acetoacetate, (C) that can not be converted to fatty acids or ketone bodies, (D) degraded to yield succinyl-CoA, pyruvate, a-ketoglutarate, fumarate and oxaloa ...
Ch 18
... ammonia is key—synthesis of most amino acids – Glutamine synthetase incorporates amino group – Coupled to glutamate synthase: reductive amination of ‐ketoglutarate to glutamate ...
... ammonia is key—synthesis of most amino acids – Glutamine synthetase incorporates amino group – Coupled to glutamate synthase: reductive amination of ‐ketoglutarate to glutamate ...
Ch.24Pt.7_000
... • Describe how a.a. Carbon Skeletons are processed • Define and explain Amino Acid Biosynthesis. • Describe the chemical composition of urine. • Explain the relationship and importance of Arginine, ...
... • Describe how a.a. Carbon Skeletons are processed • Define and explain Amino Acid Biosynthesis. • Describe the chemical composition of urine. • Explain the relationship and importance of Arginine, ...