Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... Abbreviations for the 20 different amino acids: Phenylalanine-Phe, Leucine-Leu, Isoleucine-Ile, Methionine-Met, Valine-Val, Serine-Ser, Proline-Pro, Threonine-Thr, Alanine-Ala, Tyrosine-Tyr, Histidine-His, Glutamine-Gin, Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptop ...
... Abbreviations for the 20 different amino acids: Phenylalanine-Phe, Leucine-Leu, Isoleucine-Ile, Methionine-Met, Valine-Val, Serine-Ser, Proline-Pro, Threonine-Thr, Alanine-Ala, Tyrosine-Tyr, Histidine-His, Glutamine-Gin, Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptop ...
Wheel of Amino Acids Wheel of Amino Acids
... In this activity you will use your knowledge of protein synthesis to decode the DNA strand and build a partial chain of amino acids (protein). ...
... In this activity you will use your knowledge of protein synthesis to decode the DNA strand and build a partial chain of amino acids (protein). ...
a sample task
... amino acids in a polypeptide chain. For example, the pancreatic hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, A and B, shown in the diagram below. Each chain has its own set of amino acids, assembled in a particular order. For instance, the sequence of the A chain starts with glycine at the N-terminus ...
... amino acids in a polypeptide chain. For example, the pancreatic hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, A and B, shown in the diagram below. Each chain has its own set of amino acids, assembled in a particular order. For instance, the sequence of the A chain starts with glycine at the N-terminus ...
Lab 1 activity, AMINO ACIDS - Cal State LA
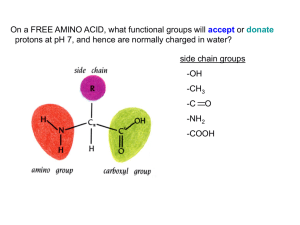
... On a FREE AMINO ACID, what functional groups will accept or donate protons at pH 7, and hence are normally charged in water? ...
... On a FREE AMINO ACID, what functional groups will accept or donate protons at pH 7, and hence are normally charged in water? ...
Polymers and Amino Acids
... Proteins and amino acids Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. Amino acids contain both amine (NH2) and carboxyl (COOH) functional groups. In alpha amino acids, these groups are attached to the same carbon atom. ...
... Proteins and amino acids Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. Amino acids contain both amine (NH2) and carboxyl (COOH) functional groups. In alpha amino acids, these groups are attached to the same carbon atom. ...
Biochemistry PPT
... Plants make their energy from the sun, animals get their energy from foods eaten ...
... Plants make their energy from the sun, animals get their energy from foods eaten ...
practice exam
... 20. ______ The net effect of the eight steps of the citric acid cycle is to A. completely oxidize an acetyl group to carbon dioxide. B. convert pyruvate to acetyl CoA. C. produce a citrate molecule D. produce 2 ATP for every pass through the cycle. E. More than one of the above 21. ______ The standa ...
... 20. ______ The net effect of the eight steps of the citric acid cycle is to A. completely oxidize an acetyl group to carbon dioxide. B. convert pyruvate to acetyl CoA. C. produce a citrate molecule D. produce 2 ATP for every pass through the cycle. E. More than one of the above 21. ______ The standa ...
Review - Columbus Labs
... pKa Values of the Amino Acid Side Chains • Arginine, Arg, R: pKa(guanidino group) = 12.5 • Lysine, Lys, K: pKa = 10.5 ...
... pKa Values of the Amino Acid Side Chains • Arginine, Arg, R: pKa(guanidino group) = 12.5 • Lysine, Lys, K: pKa = 10.5 ...
First cells ppt The first cells ppt
... • Most early scientists believed that the atmosphere was “reducing” (electron adding) made up of: – Very little O2 – Thick water vapor – Volcanic gases such as methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH4) ...
... • Most early scientists believed that the atmosphere was “reducing” (electron adding) made up of: – Very little O2 – Thick water vapor – Volcanic gases such as methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH4) ...
Name
... c. May have evolved from gibbons but not rats d. Is more closely related to humans than to rats e. May have evolved from rats but not from humans and gibbons 8. Proteins like hemoglobin and insulin have different structures because they have different ______________________, which is also known as t ...
... c. May have evolved from gibbons but not rats d. Is more closely related to humans than to rats e. May have evolved from rats but not from humans and gibbons 8. Proteins like hemoglobin and insulin have different structures because they have different ______________________, which is also known as t ...
Mechanisms of hormonal regulation and pathologies of protein
... Maple syrup urine disease - the disorder of the oxidative decarboxylation of -ketoacids derived from valine, isoleucine, and leucine caused by the missing or defect of branched-chain dehydrogenase. The levels of branched-chain amino acids and corresponding -ketoacids are markedly elevated in both ...
... Maple syrup urine disease - the disorder of the oxidative decarboxylation of -ketoacids derived from valine, isoleucine, and leucine caused by the missing or defect of branched-chain dehydrogenase. The levels of branched-chain amino acids and corresponding -ketoacids are markedly elevated in both ...
Protein Synthesis
... Importance of Proteins & DNA D. Proteins perform the following important functions: – Enzymes, which speed up chemical reaction sin the body. – Keratin, which makes up our hair and nails. – Collagen, which makes up our skin. – Hemoglobin, which transports O2 in our body E. There are 20 different am ...
... Importance of Proteins & DNA D. Proteins perform the following important functions: – Enzymes, which speed up chemical reaction sin the body. – Keratin, which makes up our hair and nails. – Collagen, which makes up our skin. – Hemoglobin, which transports O2 in our body E. There are 20 different am ...
http://www - bu people
... 6. Draw the ionized and nonionized forms of acidic and basic residues and note the approximate pH range in which these forms exist. 6. In nonionized histidine, the imidazole ring can exist as two tautomers, with the hydrogen atom on either nitrogen atom. The ring is readily protonated, with a pKa va ...
... 6. Draw the ionized and nonionized forms of acidic and basic residues and note the approximate pH range in which these forms exist. 6. In nonionized histidine, the imidazole ring can exist as two tautomers, with the hydrogen atom on either nitrogen atom. The ring is readily protonated, with a pKa va ...
C483 Practice Final Exam
... Part A. (2 points each) Questions 1-8 focus on the most recent material. 1. ______ Which statement concerning nitrogen metabolism reactions in humans is FALSE? A. Ammonia is released in the liver mitochondria when glutamate is oxidized to ketoglutarate. B. Glutamate synthetase is a “mop up” enzyme ...
... Part A. (2 points each) Questions 1-8 focus on the most recent material. 1. ______ Which statement concerning nitrogen metabolism reactions in humans is FALSE? A. Ammonia is released in the liver mitochondria when glutamate is oxidized to ketoglutarate. B. Glutamate synthetase is a “mop up” enzyme ...
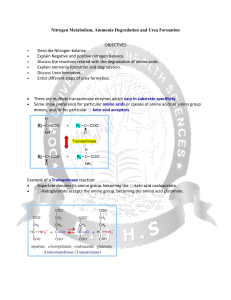
Nitrogen Metabolism, Ammonia Degradation and Urea Formation
... Hereditary deficiency of any of the Urea Cycle enzymes leads to hyperammonemia elevated [ammonia] in blood. Total lack of any Urea Cycle enzyme is lethal. Elevated ammonia is toxic, especially to the brain. ...
... Hereditary deficiency of any of the Urea Cycle enzymes leads to hyperammonemia elevated [ammonia] in blood. Total lack of any Urea Cycle enzyme is lethal. Elevated ammonia is toxic, especially to the brain. ...
Proteins
... Proteins fold in << 1 second Bigger proteins don’t take much longer to fold, but are much harder to simulate So… ...
... Proteins fold in << 1 second Bigger proteins don’t take much longer to fold, but are much harder to simulate So… ...
The test will be a mixture of MCQs related to basic cell biology
... 4. Lysosomes are spherical or oval vesicles derived from the Golgi apparatus. They are membranebound organelles of varying sizes containing hydrolase enzymes capable of digesting most biological molecules. What is the function of lysosomes? a) They manufacture membrane phospholipids and make cholest ...
... 4. Lysosomes are spherical or oval vesicles derived from the Golgi apparatus. They are membranebound organelles of varying sizes containing hydrolase enzymes capable of digesting most biological molecules. What is the function of lysosomes? a) They manufacture membrane phospholipids and make cholest ...
Lecture Topic: Fatty Acid Synthesis
... Nitrogen is an essential element found in proteins, nucleic acids and many other molecules Biologically available nitrogen is scarce Nitrogen incorporation begins with fixation (reduction) of N2 by prokaryotic microorganisms to form ammonia (NH3) Nitrogen supply is often the rate-limiting factor in ...
... Nitrogen is an essential element found in proteins, nucleic acids and many other molecules Biologically available nitrogen is scarce Nitrogen incorporation begins with fixation (reduction) of N2 by prokaryotic microorganisms to form ammonia (NH3) Nitrogen supply is often the rate-limiting factor in ...
Biological Catalysts
... *In some cases, plants or animals are used for the isolation of enzymes, but industrial enzymes are produced mostly using microorganisms in fermenter vessels. *Production of enzymes of choice can be increased to high levels by mutation and selection techniques. *Often, the microorganism excretes the ...
... *In some cases, plants or animals are used for the isolation of enzymes, but industrial enzymes are produced mostly using microorganisms in fermenter vessels. *Production of enzymes of choice can be increased to high levels by mutation and selection techniques. *Often, the microorganism excretes the ...
Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide
... “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called? Activation Energy (EA) 4. How do enzymes increase the rate or speed ...
... “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called? Activation Energy (EA) 4. How do enzymes increase the rate or speed ...
Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide
... “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called? Activation Energy (EA) 4. How do enzymes increase the rate or speed ...
... “Reusable” proteins that put together or break down substrates to form products 2. Since enzymes are proteins they are made of ……what? Amino acids joined by peptide bonds 3. The energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called? Activation Energy (EA) 4. How do enzymes increase the rate or speed ...
File - Wk 1-2
... nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) can serve as a co-substrate, but NAD+ is mainly used as for glutamate degradation and NADPH is used for its synthesis. The glutamate dehydrogenase reaction implies that glutamate is both nonessential and gl ...
... nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) can serve as a co-substrate, but NAD+ is mainly used as for glutamate degradation and NADPH is used for its synthesis. The glutamate dehydrogenase reaction implies that glutamate is both nonessential and gl ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... 4. Explain how functional groups allow organic molecules to be linked together. 5. Identify the sugars Glucose, Galactose and Fructose when the structure is given. 6. Be able to draw the ringed structure of glucose and show how two glucose units can join together to form maltose. Name the kind of re ...
... 4. Explain how functional groups allow organic molecules to be linked together. 5. Identify the sugars Glucose, Galactose and Fructose when the structure is given. 6. Be able to draw the ringed structure of glucose and show how two glucose units can join together to form maltose. Name the kind of re ...