AP Macromolecule Notes 09
... o Defensive: protection against diseases; antibodies o Signal: detect stimuli, communicate between cells, hormones; Insulin o Transport: carry nutrients in the blood, sugar to cells; Hemoglobin o Storage: store amino acid; Ovalbumin o Enzymes:* catalyze reactions; Amylase o Milk: amino acids in babi ...
... o Defensive: protection against diseases; antibodies o Signal: detect stimuli, communicate between cells, hormones; Insulin o Transport: carry nutrients in the blood, sugar to cells; Hemoglobin o Storage: store amino acid; Ovalbumin o Enzymes:* catalyze reactions; Amylase o Milk: amino acids in babi ...
Microsoft Word
... (GFAT) Targeted Inhibitors which has been divided into five sections. Section A provides a brief introduction about Glutamine-Fructose 6-Phosphate Amidotransferse (GFAT) enzyme. Section B deals with asymmetric synthesis of non-proteinogenic amino acids with enzyme L-Amino Acid Transaminase. ...
... (GFAT) Targeted Inhibitors which has been divided into five sections. Section A provides a brief introduction about Glutamine-Fructose 6-Phosphate Amidotransferse (GFAT) enzyme. Section B deals with asymmetric synthesis of non-proteinogenic amino acids with enzyme L-Amino Acid Transaminase. ...
Protein Similarities II
... The "lighter" amino acids aren't necessary to the electron-carrying function; at least, they don't have to be precisely the same for the protein to work. This isn't at all unlikely. For instance, there is an alpha helix going up the left side of the image above. It probably has to be an alpha helix ...
... The "lighter" amino acids aren't necessary to the electron-carrying function; at least, they don't have to be precisely the same for the protein to work. This isn't at all unlikely. For instance, there is an alpha helix going up the left side of the image above. It probably has to be an alpha helix ...
Technical Data Sheet Yeast Extract 19512
... is based on our own research and development work and is to the best of our knowledge true and accurate. Users should, however, conduct their own tests to determine the suitability of our products for their own specific purposes. Statements contained herein should not be considered as a warranty of ...
... is based on our own research and development work and is to the best of our knowledge true and accurate. Users should, however, conduct their own tests to determine the suitability of our products for their own specific purposes. Statements contained herein should not be considered as a warranty of ...
pptx
... TCA cycle intermediates are made and used in additional metabolic pathways • Cataplerotic reactions use cycle intermediates to make: ...
... TCA cycle intermediates are made and used in additional metabolic pathways • Cataplerotic reactions use cycle intermediates to make: ...
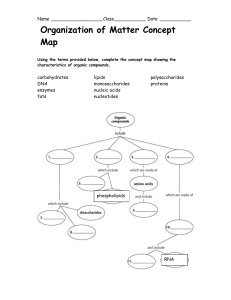
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
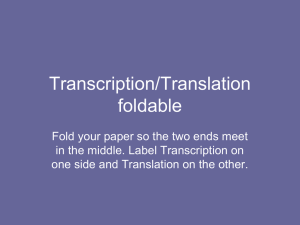
Transcription/Translation foldable
... acid sequence to make a protein. How? - tRNA brings an amino acid with an anticodon to the rRNA - tRNA binds to a codon in mRNA and releases a amino acid - a chain of amino acids is formed = PROTEIN! ...
... acid sequence to make a protein. How? - tRNA brings an amino acid with an anticodon to the rRNA - tRNA binds to a codon in mRNA and releases a amino acid - a chain of amino acids is formed = PROTEIN! ...
Biochemistry Practice Questions
... 1. Which are the four most abundant elements in living cells? a. Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur b. Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen c. Carbon, oxygen, sulfur, phosphorus d. Carbon, sulfur, hydrogen, magnesium 2. Which pair of compounds can be classified as inorganic? a. Nucleic acids and mineral ...
... 1. Which are the four most abundant elements in living cells? a. Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur b. Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen c. Carbon, oxygen, sulfur, phosphorus d. Carbon, sulfur, hydrogen, magnesium 2. Which pair of compounds can be classified as inorganic? a. Nucleic acids and mineral ...
pro amino crème
... pro amino crème for younger, healthier skin pro amino crème has the ability to boost the skin’s natural moisture levels, restoring free water levels and natural lipids to enhance barrier function and maintain a balanced, youthful complexion. pro amino is a crème that is formulated with the eight ess ...
... pro amino crème for younger, healthier skin pro amino crème has the ability to boost the skin’s natural moisture levels, restoring free water levels and natural lipids to enhance barrier function and maintain a balanced, youthful complexion. pro amino is a crème that is formulated with the eight ess ...
Worksheet – Proteins Proteins are polymers of amino acids, joined
... is governed by the IMF of the side chains. The non-polar side chains will interact via LDF. These are also called hydrophobic interactions, since these groups can not interact with water. For this reason, they are usually buried in the interior of proteins, away from water. They can be disrupted by ...
... is governed by the IMF of the side chains. The non-polar side chains will interact via LDF. These are also called hydrophobic interactions, since these groups can not interact with water. For this reason, they are usually buried in the interior of proteins, away from water. They can be disrupted by ...
Nadine Noelting
... Eukaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (eu_PheOH); a member of the biopterindependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family of non-heme, iron(II)-dependent enzymes that also includes prokaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (pro_PheOH), eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase (TyrOH) and eukaryotic tryptoph ...
... Eukaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (eu_PheOH); a member of the biopterindependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family of non-heme, iron(II)-dependent enzymes that also includes prokaryotic phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (pro_PheOH), eukaryotic tyrosine hydroxylase (TyrOH) and eukaryotic tryptoph ...
Atom - TeacherWeb
... Definition only for Dehydration synthesis and Hydrolysis Read molecular formulas with coefficients and subscripts ...
... Definition only for Dehydration synthesis and Hydrolysis Read molecular formulas with coefficients and subscripts ...
Review Sheet Exam 1 C483 Spring 2014
... of the twenty common amino acids, as well as a number of modified amino acids and some amino acids that do not occur in proteins. You must know the structures of all these amino acids, as well as associated nomenclature (one and three letter, as well as full names). You should be familiar with the p ...
... of the twenty common amino acids, as well as a number of modified amino acids and some amino acids that do not occur in proteins. You must know the structures of all these amino acids, as well as associated nomenclature (one and three letter, as well as full names). You should be familiar with the p ...
Review 3
... Structures to know • All amino acids • (deoxy)ribonucleosides and (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
... Structures to know • All amino acids • (deoxy)ribonucleosides and (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
d) a and b
... c) a hydrogen atom b) an amine group d) a carboxylic acid group e) all of these are attached to the central carbon of an amino acid 8. Which of the following is found in membranes and also serves as an energy reserve source? a) DNA b) RNA ...
... c) a hydrogen atom b) an amine group d) a carboxylic acid group e) all of these are attached to the central carbon of an amino acid 8. Which of the following is found in membranes and also serves as an energy reserve source? a) DNA b) RNA ...
Topic 2.4 Proteins Study Guide Amino acids are linked together by
... Topic 2.4 Proteins Study Guide Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. The amino acid sequence o ...
... Topic 2.4 Proteins Study Guide Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. The amino acid sequence o ...
Chapter 20-Amino Acid Metabolism
... → The major source of amino acids is the diet. Humans can only synthesize 11 of the 20 common amino acids. The other 9 (H I L K M F T W V) are essential. Arginine is essential only during growth. Tyr is not essential, but only because it can be readily synthesized from the essential Phe. → No specia ...
... → The major source of amino acids is the diet. Humans can only synthesize 11 of the 20 common amino acids. The other 9 (H I L K M F T W V) are essential. Arginine is essential only during growth. Tyr is not essential, but only because it can be readily synthesized from the essential Phe. → No specia ...
C - Eric Hamber Secondary
... - heavy metals (mercury, lead etc.) bind preferentially with specific R group bonds (the S in Cystine), breaking the tertiary structure. C11. FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS - polymers of amino acids - have 2 major functions I) Structural - large proteins are important - muscle, tendon, cartilage, hair etc. K ...
... - heavy metals (mercury, lead etc.) bind preferentially with specific R group bonds (the S in Cystine), breaking the tertiary structure. C11. FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS - polymers of amino acids - have 2 major functions I) Structural - large proteins are important - muscle, tendon, cartilage, hair etc. K ...
AMINO ACIDS COMPLEX Factsheet
... nutrients, sugars and fatty acids, which do not contain nitrogen. Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins are not obtained directly from human diet, instead they are broken down from dietary protein into the constituent amino acid, which the body uses to build the specif ...
... nutrients, sugars and fatty acids, which do not contain nitrogen. Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Proteins are not obtained directly from human diet, instead they are broken down from dietary protein into the constituent amino acid, which the body uses to build the specif ...
3.2 Proteins - Biology with Radjewski
... • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed ...
... • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed ...