The simplest enzyme revisited: The chicken and
... the chicken and egg argument between proteins and nucleic acid polymers disappears. The answer to “which came first, protein or nucleic acid” is: “metabolism.” They grew up together by catalyzing each other’s reactions. In this context sugars and amino sugars may also play a significant role. All of t ...
... the chicken and egg argument between proteins and nucleic acid polymers disappears. The answer to “which came first, protein or nucleic acid” is: “metabolism.” They grew up together by catalyzing each other’s reactions. In this context sugars and amino sugars may also play a significant role. All of t ...
Amino Acid Metabolism 1. Explain the role of glutamate in amino
... transferred to alpha-ketoglutarate to form glutamate. Glutamate is converted to alphaketoglutarate and ammonia, and this ammonia then enters the urea cycle. 2. The amino group can be transferred to glutamate which in turn can be the source of nitrogen for the formation of aspartate from OAA. The ami ...
... transferred to alpha-ketoglutarate to form glutamate. Glutamate is converted to alphaketoglutarate and ammonia, and this ammonia then enters the urea cycle. 2. The amino group can be transferred to glutamate which in turn can be the source of nitrogen for the formation of aspartate from OAA. The ami ...
Food Biotechnology Dr. Tarek Elbashiti
... increasing the availability of erythrose 4phosphate (strategy 1, Figure 5.1), phosphoenolpyruvate (strategies 2, 3, and 4, Figure 5.1), and ribose-5-P (strategy 1 Figure 5.1) by inactivating the enzymes involved in their consumption and/or amplifying the enzymes involved in their production. ...
... increasing the availability of erythrose 4phosphate (strategy 1, Figure 5.1), phosphoenolpyruvate (strategies 2, 3, and 4, Figure 5.1), and ribose-5-P (strategy 1 Figure 5.1) by inactivating the enzymes involved in their consumption and/or amplifying the enzymes involved in their production. ...
Food Biotechnology Dr. Tarek Elbashiti 7. Metabolic Engineering of
... increasing the availability of erythrose 4phosphate (strategy 1, Figure 5.1), phosphoenolpyruvate (strategies 2, 3, and 4, Figure 5.1), and ribose-5-P (strategy 1 Figure 5.1) by inactivating the enzymes involved in their consumption and/or amplifying the enzymes involved in their production. ...
... increasing the availability of erythrose 4phosphate (strategy 1, Figure 5.1), phosphoenolpyruvate (strategies 2, 3, and 4, Figure 5.1), and ribose-5-P (strategy 1 Figure 5.1) by inactivating the enzymes involved in their consumption and/or amplifying the enzymes involved in their production. ...
Amino Acid Analysis Please follow the guidelines below for
... Please clearly label your tubes, and include printed information about your samples, including weights. We will keep the samples stored at -80o C prior to analysis For HAA, we have a method calibrated from 5pmol-50pmol of each of the following amino acids: Cya**, His, Ser, Arg, Gly, Asp, MetS02**, G ...
... Please clearly label your tubes, and include printed information about your samples, including weights. We will keep the samples stored at -80o C prior to analysis For HAA, we have a method calibrated from 5pmol-50pmol of each of the following amino acids: Cya**, His, Ser, Arg, Gly, Asp, MetS02**, G ...
Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
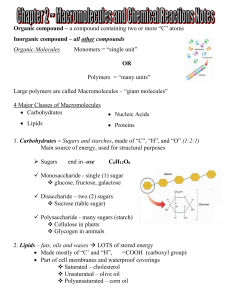
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
“Translation” means : Ribosomes in the cell cytoplasm read the
... will match up with a new molecule : tRNA (transfer RNA). Each transfer RNA can attach to one kind of amino acid. The bottom 3 bases (the tRNA’s “anticodon”) make sure it can only attach to one specific codon. Most amino acids have more than one possible codon (they have the first two bases the same ...
... will match up with a new molecule : tRNA (transfer RNA). Each transfer RNA can attach to one kind of amino acid. The bottom 3 bases (the tRNA’s “anticodon”) make sure it can only attach to one specific codon. Most amino acids have more than one possible codon (they have the first two bases the same ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer
... o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein Structure Description of level Identify chemical bonds responsible for each level Relationship between protein structure and function Effect of environment on shape and function of proteins Nucleic Acids (pp. 49-50) Mo ...
... o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein Structure Description of level Identify chemical bonds responsible for each level Relationship between protein structure and function Effect of environment on shape and function of proteins Nucleic Acids (pp. 49-50) Mo ...
Quiz Chapter 5 Organic Molecules
... 19. A particular polypeptide contains 90 amino acids. When the polypeptide is completely hydrolyzed, how many water molecules are formed during this process? a. 2 d. 89 b. 30 e 90 c. 45 20. All of the following qualities contribute to capillary action EXCEPT: a. cohesion d. hydrogen bonding b. adhes ...
... 19. A particular polypeptide contains 90 amino acids. When the polypeptide is completely hydrolyzed, how many water molecules are formed during this process? a. 2 d. 89 b. 30 e 90 c. 45 20. All of the following qualities contribute to capillary action EXCEPT: a. cohesion d. hydrogen bonding b. adhes ...
Ch20.2 Amino-acids-degradation and synthesis
... A. Synthesis from α-keto acids Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate are synthesized by transfer of an amino group to the α-keto acids pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and α-ketoglutarate, respectively. These transamination reactions (Figure 20.12, and see p. 250) are the most direct of the biosynthetic pat ...
... A. Synthesis from α-keto acids Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate are synthesized by transfer of an amino group to the α-keto acids pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and α-ketoglutarate, respectively. These transamination reactions (Figure 20.12, and see p. 250) are the most direct of the biosynthetic pat ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • First Step: Copying of genetic information from DNA to RNA called Transcription Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), b ...
... • First Step: Copying of genetic information from DNA to RNA called Transcription Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), b ...
pro amino crème
... pro amino crème for younger, healthier looking skin Designed to enhance barrier function by restoring free water levels and natural lipids, pro amino crème aims to maintain a balanced, youthful complexion. pro amino crème has been formulated with the eight essential amino acids, proteins and vitamin ...
... pro amino crème for younger, healthier looking skin Designed to enhance barrier function by restoring free water levels and natural lipids, pro amino crème aims to maintain a balanced, youthful complexion. pro amino crème has been formulated with the eight essential amino acids, proteins and vitamin ...
Lh6Ch18AAOxid
... Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Amino acids from protein are an important energy source in carnivorous animals and during starvation. 2. The first step of AA catabolism is transfer of the NH3 via PLP-dependent aminotransferase usually to ketoglutarate to yield L-glutamate. 3. In most mammal ...
... Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Amino acids from protein are an important energy source in carnivorous animals and during starvation. 2. The first step of AA catabolism is transfer of the NH3 via PLP-dependent aminotransferase usually to ketoglutarate to yield L-glutamate. 3. In most mammal ...
Table 1 The Essential Amino Acids and Their Plant Sources
... into its amino acid subunits. acids legumes grains Isoleucine Then, in the body cells, the X Lysine amino acids are linked in X Valine specific sequences to form X X Histidine new proteins. People can X X Threonine synthesize 11 of the 20 X X Phenylalanine different amino acids by X X Leucine conver ...
... into its amino acid subunits. acids legumes grains Isoleucine Then, in the body cells, the X Lysine amino acids are linked in X Valine specific sequences to form X X Histidine new proteins. People can X X Threonine synthesize 11 of the 20 X X Phenylalanine different amino acids by X X Leucine conver ...
Protein mteabolism
... Conversion of aromatic acids into specialized products 1- Phenylalanine amino acid Essential amino acid Converted into tyrosine (major pathway ) ...
... Conversion of aromatic acids into specialized products 1- Phenylalanine amino acid Essential amino acid Converted into tyrosine (major pathway ) ...
Chapter 22 Biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides and related
... transamination reaction. • Asn is synthesized from Asp by an amidation (酰胺 化) reaction with Gln donating the NH4+(catalyzed by an amidotransferase). • Thr and Met are all derived from Asp, branching off after Asp is converted to aspartate b-semialdehyde (in a way similar to Glu to glutamate gsemiald ...
... transamination reaction. • Asn is synthesized from Asp by an amidation (酰胺 化) reaction with Gln donating the NH4+(catalyzed by an amidotransferase). • Thr and Met are all derived from Asp, branching off after Asp is converted to aspartate b-semialdehyde (in a way similar to Glu to glutamate gsemiald ...
Choosing Healthful Foods
... • You need 20 amino acids for your body to function properly. The body makes 11 of those amino acids. The 9 you need from food are known as essential amino acids. • Example of complete protein: meat, fish, poultry, milk, yogurt, and eggs • Example of incomplete protein: grains, legumes, nuts, seeds ...
... • You need 20 amino acids for your body to function properly. The body makes 11 of those amino acids. The 9 you need from food are known as essential amino acids. • Example of complete protein: meat, fish, poultry, milk, yogurt, and eggs • Example of incomplete protein: grains, legumes, nuts, seeds ...
Protein - manorhousehomeeconomics
... Proteins are made up of atoms of: Carbon C Hydrogen H Oxygen O Nitrogen N and sometimes small amounts of Phosphorus (P), Sulphur (S) and Iron (Fe) Nitrogen is needed for growth. Proteins are the only nutrients that contain the element nitrogen. These elements are bonded together in s ...
... Proteins are made up of atoms of: Carbon C Hydrogen H Oxygen O Nitrogen N and sometimes small amounts of Phosphorus (P), Sulphur (S) and Iron (Fe) Nitrogen is needed for growth. Proteins are the only nutrients that contain the element nitrogen. These elements are bonded together in s ...
Chemistry of Proteins Model Making
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...