* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Soon you will learn what HIV requires to come to life…
Survey
Document related concepts
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
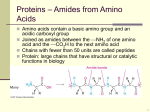
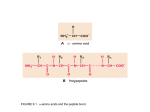
An arbitrary sub-grouping of the 20 natural amino acids Negatively-charted at pH 7 Aspartic Acid Asp D Glutamic Acid Glu E Polar Aspargine Asn N Nonpolar Alanine Ala A Glutamine Gln Q Important for Peptide Shape Valine Val V Glycine Gly G Threonine Thr T Serine Ser S Positively-charted at pH 7 Proline Pro P Histidine His H Methionine Met M Leucine Leu L Cysteine Cys C Lysine Lys K Arginine Arg R Cyclic Isoleucine Ile I Phenylalanine Phe F Tyrosine Tyr Y Tryptophan Trp W AA’s with polar or charged side chains can function as H-bond donors or acceptors Negatively-charted at pH 7 Aspartic Acid Asp D Glutamic Acid Glu E Polar Aspargine Asn N Nonpolar Alanine Ala A Glutamine Gln Q Important for Peptide Shape Valine Val V Glycine Gly G Threonine Thr T Serine Ser S Positively-charted at pH 7 Proline Pro P Histidine His H Methionine Met M Leucine Leu L Cysteine Cys C Lysine Lys K Arginine Arg R Cyclic Isoleucine Ile I Phenylalanine Phe F Tyrosine Tyr Y Tryptophan Trp W 1 All of the amino acids are special, and we will discuss some of their unique properties later Negatively-charted at pH 7 Aspartic Acid Asp D Polar Glutamic Acid Glu E Aspargine Asn N Nonpolar Alanine Ala A Glutamine Gln Q Important for Peptide Shape Valine Val V Glycine Gly G Threonine Thr T Serine Ser S Positively-charted at pH 7 Proline Pro P Histidine His H Methionine Met M Leucine Leu L Cysteine Cys C Lysine Lys K Arginine Arg R Cyclic Isoleucine Ile I AA’s with aromatic side chains have polar and nonpolar bits pKa values for AA’s (with ionizing side chains) Phenylalanine Phe F acid Tyrosine Tyr Y Tryptophan Trp W conjugate base pKa In general, if the pKa of an AA side chain is two log units from pH 7… … it exists entirely in one form. 2 Four “special” amino acids glycine proline cysteine histidine All amino acids are special, but these four amino acids will help us see how side chains might affect protein structure and function Glycine: the smallest amino acid and the only AA without an R group • First amino acid discovered (in 1820) from gelatin. • “R” = hydrogen • Reduced steric hindrance: can adopt a wider range of peptide conformations compared to other amino acids. Glycine is loose (accommodating) 3 For 19 amino acids, the trans geometry around the peptide bond is heavily favored Trans In proline, the trans isomer is only slightly favored over the cis isomer. Cis Heavily favored NOTE: proline also cannot be a hydrogen bond donor… Slightly favored Proline is the contrarian (while others zig, proline zags) Cysteine is the only amino acid that makes nonpeptidic bonds in proteins If there are multiple cysteines in a protein their side chains can form disulfide bonds cysteine cystine Disulfide bonds constrain protein conformation Cysteine is in love with itself... it’s the narcissist (generally unhealthy) 4 Your hair is made of protein that contains lots of disulfide bonds Chemicals (thioacetic acid) can break disulfide bonds. Other chemicals (hydrogen peroxide) can form disulfide bonds Chemicals can be bad for you… The pKa of the histidine side chain is between 6 and 7 (near physiological pH) Histidine can act as both an acid and a base at physiological pH (it can encompass being more than one thing at the same time -- a true intellectual) 5 Titration of L-Histidine pH 10 5 0 Side chains of the amino acids are often the functional components of proteins chymotrypsin acrosin Factor X Uncatalyzed rate 7-400 years Enzymes make the rate of reactions go faster 6 Amino acids cooperate in catalysis Asp 102 Ser 195 His 57 chymotrypsin The catalytic triad: serine, histidine, and aspartic acid work together to cleave amide bonds Protein structure and folding HUMPTY DUMPTY SAT ON A WALL. HUMPTY DUMPTY HAD A GREAT FALL. ALL THE KING’S HORSES AND ALL THE KING’S MEN, COULDN’T PUT HUMPTY TOGETHER AGAIN. What happens when you cook an egg? 7 Polypeptides interact in precisely defined ways to make distinct shapes Specific order of amino acids Regions of secondary structure stably interact Local structure of stretch of AA’s Higher order complex of polypeptide chains The folded structure of a protein determines its function. Proteins are composed of the two common secondary structures arranged in different ways Cytochrome b562 Lactic acid dehydrogenase Antibody We would like to understand the forces that stabilize secondary and tertiary structure (i.e. what determines a protein structure)? 8 Pauling showed that the dipoles of acetamide and polyglycine align in crystals (and that the peptide bond is flat) acetamide Pauling predicted that polypeptide chains in proteins would form helical chains that recapitulate this hydrogen bonding pattern… and he was right! In -helices, adjacent N-H groups (blue) point in the same direction… 9 C α8 C’8 8 7 C’7 C’6 C α7 - …and because of this arrangement of atoms, helices have a macrodipole 6 C α6 5 C’5 C α5 C’4 C α3 C α4 4 C’3 3 Cα 1 C’ 1 2 Cα 2 C’ 2 + Side chains of AA’s (R groups) point away from the helix 9 In -sheets, adjacent N-H groups point in opposite directions R R Cα N Cα C’ N C O C N R R In -sheets, there is no opportunity to form hydrogen bonds within one strand Why do some sequences form -helices and others form -sheets? Anfinsen proposed that the primary sequence determines protein conformation A thermodynamic hypothesis: The 3D structure of a protein represents the most stable folded conformation (favorable interactions are maximized and unfavorable interactions minimized)… If so… you should be able to put Humpty Dumpty back together again. Christian Anfinsen, Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1972 Egg test: Will a denatured protein (ribonuclease A) refold to its native conformation? 10