Slide ()
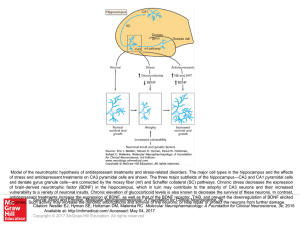
... and dentate gyrus granule cells—are connected by the mossy fiber (mf) and Schaffer collateral (SC) pathways. Chronic stress decreases the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus, which in turn may contribute to the atrophy of CA3 neurons and their increased vulnerab ...
... and dentate gyrus granule cells—are connected by the mossy fiber (mf) and Schaffer collateral (SC) pathways. Chronic stress decreases the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus, which in turn may contribute to the atrophy of CA3 neurons and their increased vulnerab ...
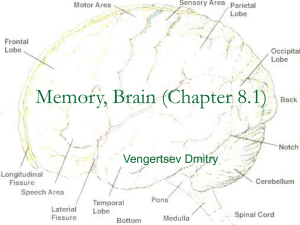
Nervous System
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
Advanced Medicinal Chemistry
... window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in homo- or heteropolymer arrays. Almost no channels ...
... window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in homo- or heteropolymer arrays. Almost no channels ...
Advanced Medicinal Chemistry
... window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in homo- or heteropolymer arrays. Almost no channels ...
... window of less than one volt The membrane potential of most cells is 60-70mV Ion channels regulate passive ion flow through membranes in an electric or concentration gradient Channels are ion selective and comprise groups of glycoprotein subunits in homo- or heteropolymer arrays. Almost no channels ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... that cause a change in neural plasma membrane permeability. This change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the axon. Electrical condition of resting state are restored by the diffusion of ...
... that cause a change in neural plasma membrane permeability. This change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the axon. Electrical condition of resting state are restored by the diffusion of ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors of the receiving neuron in a key-lock ...
... Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors of the receiving neuron in a key-lock ...
Abstract
... 1. Introduction We spend almost one third of our life time just to sleep. Sleep/wakefulness cycle is a very intriguing physiological phenomenon. We fall asleep at least once per day. After sleeping for a while, we can wake up naturally. However, the mechanism regulating sleep/wakefulness cycle has n ...
... 1. Introduction We spend almost one third of our life time just to sleep. Sleep/wakefulness cycle is a very intriguing physiological phenomenon. We fall asleep at least once per day. After sleeping for a while, we can wake up naturally. However, the mechanism regulating sleep/wakefulness cycle has n ...
Mechanisms of drug action
... β1 receptors are a sub group of adrenoceptors. Endogenous adrenaline and nor adrenaline act on these receptors in heart and increase heart rate and cardiac contractility there by increasing the cardiac work load and the blood pressure. Propranolol is a β receptor antagonist. It binds to β1 receptors ...
... β1 receptors are a sub group of adrenoceptors. Endogenous adrenaline and nor adrenaline act on these receptors in heart and increase heart rate and cardiac contractility there by increasing the cardiac work load and the blood pressure. Propranolol is a β receptor antagonist. It binds to β1 receptors ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
FOUNDATION MODULE 2012 SELF ASSESMENT BCQs 6TH
... b. Beta-blockers block beta receptors causing decrease in heart rate*** ...
... b. Beta-blockers block beta receptors causing decrease in heart rate*** ...
to read the full article
... under control. At its most basic level, when neurons are in their excitatory state they are 'firing' to carry electrical and chemical messages which fulfill designated functions. However, when neurons are in their inhibitory state, they are actively supressed so that they do not 'fire'. This natural ...
... under control. At its most basic level, when neurons are in their excitatory state they are 'firing' to carry electrical and chemical messages which fulfill designated functions. However, when neurons are in their inhibitory state, they are actively supressed so that they do not 'fire'. This natural ...
Psychology
... • The discomfort and distress that follow when a person who is dependent on a drug discontinues the use of the drug • Withdrawal symptoms are usually the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
... • The discomfort and distress that follow when a person who is dependent on a drug discontinues the use of the drug • Withdrawal symptoms are usually the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
The Brain`s Response to Hallucinogens
... Scientists have recently found that the damaged serotonin neurons can regrow their fibers, but the fibers don't grow back normally. The fibers may regrow into brain areas where they don't normally grow, but not into other brain areas where they should be located. The new growth patterns may cause ch ...
... Scientists have recently found that the damaged serotonin neurons can regrow their fibers, but the fibers don't grow back normally. The fibers may regrow into brain areas where they don't normally grow, but not into other brain areas where they should be located. The new growth patterns may cause ch ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... the opening of channels that allow ions (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage pulse that propagates along it (see arrow). ...
... the opening of channels that allow ions (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage pulse that propagates along it (see arrow). ...
Zilles, Karl, Neurotransmitter Receptor Distribution
... Director of the Vogt Instit of Brain Research at Heinrich Heine Univ Dusseldorf; pronounced ZILL is... 550 journal articles and 60 book chapters; grad from med school in 1971... he jokes: colleagues were jealous of this trip... thought he might be tempted to come to California and never leave! he st ...
... Director of the Vogt Instit of Brain Research at Heinrich Heine Univ Dusseldorf; pronounced ZILL is... 550 journal articles and 60 book chapters; grad from med school in 1971... he jokes: colleagues were jealous of this trip... thought he might be tempted to come to California and never leave! he st ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... 30) With regard to mental processes, some behaviorists (such as Skinner) suggested that a. Mental processes play no role in behavior b. Mental processes were the most important aspects of behavior c. Behaviors could not be understood without also studying mental processes d. Mental processes were wh ...
... 30) With regard to mental processes, some behaviorists (such as Skinner) suggested that a. Mental processes play no role in behavior b. Mental processes were the most important aspects of behavior c. Behaviors could not be understood without also studying mental processes d. Mental processes were wh ...
Puzzle 2A: The Neuron and Nervous System
... potential, a neuron is said to be this 6. Type of reflex that does not involve the brain 9. These neurons carry information from the specialized receptor cells in the sense organs 10. Designates the messagesending neuron at the synaptic gap ...
... potential, a neuron is said to be this 6. Type of reflex that does not involve the brain 9. These neurons carry information from the specialized receptor cells in the sense organs 10. Designates the messagesending neuron at the synaptic gap ...
Chapter 3 – The nerve cell Study Guide Describe an integrate
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
Neurotransmitter release in the brain
... connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmitter fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the synaptic cleft. The transmitter molecules (typically 10,000-100,000 molecules pe ...
... connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmitter fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the synaptic cleft. The transmitter molecules (typically 10,000-100,000 molecules pe ...
Neurons
... the neural impulse over synapse PSP – postsynaptic potential – change in membrane potential: ...
... the neural impulse over synapse PSP – postsynaptic potential – change in membrane potential: ...
Brain-Computer Interface
... NASA is researching a similar system that reads electric signals from the nerves in the mouth and throat area, rather than directly from the brain. Neural Signals is developing technology to restore speech to disabled people. An implant in an area of the brain associated with speech (Broca's area) w ...
... NASA is researching a similar system that reads electric signals from the nerves in the mouth and throat area, rather than directly from the brain. Neural Signals is developing technology to restore speech to disabled people. An implant in an area of the brain associated with speech (Broca's area) w ...