What is the Nervous System?
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
Respiratory Drugs
... stimulation pathways; work slowly and are better at preventing attacks, however if pt doesn’t respond to bronchodilators with acute attack, must give high dose corticosteroids ...
... stimulation pathways; work slowly and are better at preventing attacks, however if pt doesn’t respond to bronchodilators with acute attack, must give high dose corticosteroids ...
The Brain for Not-So
... Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
... Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
Model organisms with simple nervous systems: lamprey, crabs
... well understood motor system that regulates swimming behavior and a nervous system in which axons can regenerate after injury. ...
... well understood motor system that regulates swimming behavior and a nervous system in which axons can regenerate after injury. ...
Name
... Neurons Matching A. Afferent Neuron B. Association Neuron C. Cutaneous Sense Organs D. Efferent Neuron E. Ganglion ...
... Neurons Matching A. Afferent Neuron B. Association Neuron C. Cutaneous Sense Organs D. Efferent Neuron E. Ganglion ...
solutions - Berkeley MCB
... This is where the retinal ganglion cell axons leave the retina and therefore there are no photoreceptors (and thus no response to light) at this location. 3) The fovea allows for increase visual acuity by which of the following specializations: a. high ratio of photoreceptors to ganglion cells b. la ...
... This is where the retinal ganglion cell axons leave the retina and therefore there are no photoreceptors (and thus no response to light) at this location. 3) The fovea allows for increase visual acuity by which of the following specializations: a. high ratio of photoreceptors to ganglion cells b. la ...
Neuro-fatigue
... tiredness, and lack of energy. Neuro-fatigue is somewhat different in that it involves mental fatigue caused by the alterations of chemicals in different parts of the brain, or chemical imbalances within the brain caused by the injury. Individuals with a brain injury describe neuro-fatigue as comple ...
... tiredness, and lack of energy. Neuro-fatigue is somewhat different in that it involves mental fatigue caused by the alterations of chemicals in different parts of the brain, or chemical imbalances within the brain caused by the injury. Individuals with a brain injury describe neuro-fatigue as comple ...
Psych B – Module 22
... • Leaves, stems, resin, and flowers form the hemp plant that, when smoked, lower inhibitions and produce feelings of relaxation and mild euphoria • THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the active ingredient • Disrupts memory; lung damage from ...
... • Leaves, stems, resin, and flowers form the hemp plant that, when smoked, lower inhibitions and produce feelings of relaxation and mild euphoria • THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the active ingredient • Disrupts memory; lung damage from ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
Addiction Power Point (Didn`t use)
... emotions 3- Cerebral Cortex: Controls specific functions. It enables us to see, feel, hear, and taste. The frontal cortex is the reasoning center of the brain. ...
... emotions 3- Cerebral Cortex: Controls specific functions. It enables us to see, feel, hear, and taste. The frontal cortex is the reasoning center of the brain. ...
Spatial Memory - American Psychological Association
... Neuroscience: Psychologists can study which brain areas are activated when spatial tasks are solved. In laboratory animals, they may record electrical signals from neurons or measure the release of chemicals in the brain. In humans, brain activity can be measured through or scalp or with imaging dev ...
... Neuroscience: Psychologists can study which brain areas are activated when spatial tasks are solved. In laboratory animals, they may record electrical signals from neurons or measure the release of chemicals in the brain. In humans, brain activity can be measured through or scalp or with imaging dev ...
210_Blanks_lecture3_drugs
... Raises the voltage for the NMDA receptors ___________responsible for blocking the NMDA receptors until high enough voltage NMDA allows both ______________________to enter Ca2+ causes long term changes in the cell Thought to be involved in long term memory GABA Synthesized from ___________ Two differ ...
... Raises the voltage for the NMDA receptors ___________responsible for blocking the NMDA receptors until high enough voltage NMDA allows both ______________________to enter Ca2+ causes long term changes in the cell Thought to be involved in long term memory GABA Synthesized from ___________ Two differ ...
Lecture 5 Transmitters and receptors lecture 2015
... Unusual neurotransmitters: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ATP is made from adenosine and packed into large dense core or small synaptic type vesicles. ATP is released along with another transmitter, or by itself. After release, ATPase and other enzymes break it down and adenosine can be taken up agai ...
... Unusual neurotransmitters: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ATP is made from adenosine and packed into large dense core or small synaptic type vesicles. ATP is released along with another transmitter, or by itself. After release, ATPase and other enzymes break it down and adenosine can be taken up agai ...
MS Word - Graphic Science
... concentration. However, taken at high dose, the drugs can give users a high. This, combined with dopamine’s involvement in pleasure and reward pathways, means the drugs also have potential for abuse and addiction. ...
... concentration. However, taken at high dose, the drugs can give users a high. This, combined with dopamine’s involvement in pleasure and reward pathways, means the drugs also have potential for abuse and addiction. ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Notes
... Amphetamines ("speed") work by causing the release of norepinephrine, as well as other neurotransmitters called dopamine and serotonin Dopamine (excitatory and inhibitory) Another relative of norepinephrine and epinephrine is dopamine It can be both excitatory and inhibitory depending on the recepto ...
... Amphetamines ("speed") work by causing the release of norepinephrine, as well as other neurotransmitters called dopamine and serotonin Dopamine (excitatory and inhibitory) Another relative of norepinephrine and epinephrine is dopamine It can be both excitatory and inhibitory depending on the recepto ...
Slide ()
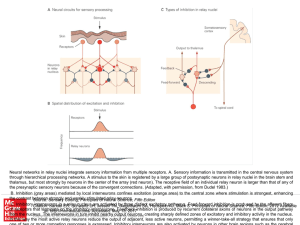
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
Ch.02 - Neuroscience
... Links central nervous system (spinal cord) to sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
... Links central nervous system (spinal cord) to sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
11/19/2014 Sedative‐Hypnotic and Anxiolytic Medications
... Most are orally bioavailable, with good absorption Several generate active metabolites in vivo – Valium®, Librium® and thus have longer activities Half‐lives range from 2 hours to 80 hours Elderly patients metabolize more slowly – half‐lives may reach 7‐10 days for diazepam (Valium®) ...
... Most are orally bioavailable, with good absorption Several generate active metabolites in vivo – Valium®, Librium® and thus have longer activities Half‐lives range from 2 hours to 80 hours Elderly patients metabolize more slowly – half‐lives may reach 7‐10 days for diazepam (Valium®) ...
notes - Other Places you want to go
... Colorless fluid that contains chemicals that have many functions Includes lymphocytes to fight infection Main function is to protect brain and spinal cord ***Know Figure 16.5 (see Brain handout to study)*** Functions of some parts of the brain: Cerebrum – deals with “higher-level” brain func ...
... Colorless fluid that contains chemicals that have many functions Includes lymphocytes to fight infection Main function is to protect brain and spinal cord ***Know Figure 16.5 (see Brain handout to study)*** Functions of some parts of the brain: Cerebrum – deals with “higher-level” brain func ...
29.5 Brain Function and Chemistry
... 29.5 Brain Function and Chemistry • There are three common technologies. – CT uses x-rays to view structure. – MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to view structure. – PET detects activity, where glucose is used, in the brain. ...
... 29.5 Brain Function and Chemistry • There are three common technologies. – CT uses x-rays to view structure. – MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to view structure. – PET detects activity, where glucose is used, in the brain. ...
29.5 Brain Function and Chemistry KEY CONCEPT brain.
... 29.5 Brain Function and Chemistry • There are three common technologies. – CT uses x-rays to view structure. – MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to view structure. – PET detects activity, where glucose is used, in the brain. ...
... 29.5 Brain Function and Chemistry • There are three common technologies. – CT uses x-rays to view structure. – MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to view structure. – PET detects activity, where glucose is used, in the brain. ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
abstract english
... brain functions such as attention consciousness and working memory. Although brain activity correlates with behavior there are large differences between individuals in the shape of brain waves. Twin studies showed that the variation between individuals is highly heritable. Yet it is unknown how indi ...
... brain functions such as attention consciousness and working memory. Although brain activity correlates with behavior there are large differences between individuals in the shape of brain waves. Twin studies showed that the variation between individuals is highly heritable. Yet it is unknown how indi ...