Adrenergic receptor antagonists
... not obviously the result of β-receptor blockade. One is the occurrence of bad dreams, which occur mainly with highly lipid-soluble drugs such as propranolol, which enter the brain ...
... not obviously the result of β-receptor blockade. One is the occurrence of bad dreams, which occur mainly with highly lipid-soluble drugs such as propranolol, which enter the brain ...
The Nervous System : communication
... function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
... function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
Ch 09 Nervous System
... function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
... function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
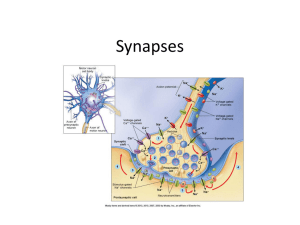
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
Document
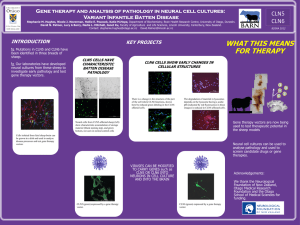
... Stephanie M. Hughes, Nicole J. Neverman, Hollie E. Peacock, Katie M.Hope, Department of Biochemistry, Brain Health Research Centre, University of Otago, Dunedin. David N. Palmer, Lucy A Barry, Nadia L. Mitchell, Janet Xu, Faculty of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Lincoln University, Canterbury, New ...
... Stephanie M. Hughes, Nicole J. Neverman, Hollie E. Peacock, Katie M.Hope, Department of Biochemistry, Brain Health Research Centre, University of Otago, Dunedin. David N. Palmer, Lucy A Barry, Nadia L. Mitchell, Janet Xu, Faculty of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Lincoln University, Canterbury, New ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... • One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons • Neural networks – Patterns of neural activity – Interconnected neurons that fire together or sequentially • Synaptic connections – Elimination and creation – Synaptic pruning ...
... • One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons • Neural networks – Patterns of neural activity – Interconnected neurons that fire together or sequentially • Synaptic connections – Elimination and creation – Synaptic pruning ...
Barry Jacobs presentation
... • There are times during development when conditions must be right or it may be difficult or impossible to correct them later. • A young child who is abused or neglected may have great difficulty in successfully navigating adult social life. • If not corrected early on in life an infant with catarac ...
... • There are times during development when conditions must be right or it may be difficult or impossible to correct them later. • A young child who is abused or neglected may have great difficulty in successfully navigating adult social life. • If not corrected early on in life an infant with catarac ...
Nervous System Study Guide
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
receptors
... Gave radioactively labeled nicotine to rats. Found > number of nicotinic receptors vs. controls. Unusual – receptors usually ↑ in numbers when there is a shortage of stimulation. Solution: nicotine initially exerts a stimulatory effect (agonist), and then desensitizes receptors to render them nonfun ...
... Gave radioactively labeled nicotine to rats. Found > number of nicotinic receptors vs. controls. Unusual – receptors usually ↑ in numbers when there is a shortage of stimulation. Solution: nicotine initially exerts a stimulatory effect (agonist), and then desensitizes receptors to render them nonfun ...
Chapter 11.1 Cell Communication
... movement of these receptors into the cell Ex: steroids – travel through the blood entering cells all over the body. - target cells only contain receptor molecule for that steroid in the cytoplasm, - binding occurs, then activation, in which receptor molecule enters nucleus to turn on specific genes ...
... movement of these receptors into the cell Ex: steroids – travel through the blood entering cells all over the body. - target cells only contain receptor molecule for that steroid in the cytoplasm, - binding occurs, then activation, in which receptor molecule enters nucleus to turn on specific genes ...
Structure of a Neuron
... electrical and chemical in nature Electrical Impulse: Action Potential ...
... electrical and chemical in nature Electrical Impulse: Action Potential ...
PSYC550 Psychopharmacology
... distribution within body, and drug elimination – Absorption depends on the route of administration – Drug distribution depends on how soluble the drug molecule is in fat (to pass through membranes) and on the extent to which the drug binds to blood proteins (albumin) – Drug elimination is accomplish ...
... distribution within body, and drug elimination – Absorption depends on the route of administration – Drug distribution depends on how soluble the drug molecule is in fat (to pass through membranes) and on the extent to which the drug binds to blood proteins (albumin) – Drug elimination is accomplish ...
Neuron and Brain Review Handout
... Myelin: Fatty substance on some axons--speeds up neural transmissions Terminal Branches of Axon: Form junctions with other cells and contain synaptic vesicles Synaptic vesicles: sac-like structures that contain neurotransmitters Synapse: The tiny gap between the sending and receiving neurons Neural ...
... Myelin: Fatty substance on some axons--speeds up neural transmissions Terminal Branches of Axon: Form junctions with other cells and contain synaptic vesicles Synaptic vesicles: sac-like structures that contain neurotransmitters Synapse: The tiny gap between the sending and receiving neurons Neural ...
Treatment Strategies for DWI Offenders
... Drug overdose was the leading cause of injury death in ...
... Drug overdose was the leading cause of injury death in ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... Synapse = minute fluid-filled gap between dendrites and axons (less than a millionth of an inch wide) called the “synaptic gap or cleft”; axons & dendrites don’t actually touch each other. (Synaptic) vesicles = house specific neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters = chemical messengers sent from the ve ...
... Synapse = minute fluid-filled gap between dendrites and axons (less than a millionth of an inch wide) called the “synaptic gap or cleft”; axons & dendrites don’t actually touch each other. (Synaptic) vesicles = house specific neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters = chemical messengers sent from the ve ...
Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now
... Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now: What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
... Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now: What is a stimulus? How do your senses work? Homework: 594-602 #1-5 ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...