TEACHER`S GUIDE
... After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send information to each other usi ...
... After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send information to each other usi ...
Neuron
... that makes it more likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” •Inhibitory - neurotransmitter effect that makes it less likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” ...
... that makes it more likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” •Inhibitory - neurotransmitter effect that makes it less likely that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential or “fire” ...
The Brain and Nervous System - Mr. Conzen
... How do we function? People are made up of billions of cells - in Psychology we focus on the nervous system. Nervous system sends messages throughout the body that encompass thought, perception, emotion, etc. ...
... How do we function? People are made up of billions of cells - in Psychology we focus on the nervous system. Nervous system sends messages throughout the body that encompass thought, perception, emotion, etc. ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint notes
... = an area at the read of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. ...
... = an area at the read of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. ...
I am part of an organization called Rutgers BRAIN. Our mission is to
... for research and awareness of neurological and psychological diseases/disorders. We are hosting various events during the week of March 20th which is called “Brain Awareness Week.” One of our events is “BRAIN Blast” which will be on Wednesday, March 22nd at 7:30 pm in the Busch Campus Center Interna ...
... for research and awareness of neurological and psychological diseases/disorders. We are hosting various events during the week of March 20th which is called “Brain Awareness Week.” One of our events is “BRAIN Blast” which will be on Wednesday, March 22nd at 7:30 pm in the Busch Campus Center Interna ...
Students know
... What are stimulants? • Drugs change how the brain works, by changing the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the syna ...
... What are stimulants? • Drugs change how the brain works, by changing the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the syna ...
The synapse.
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
CH 8 Nervous part 1
... The name “endorphin” comes from endo- and -orphin; intended to mean "a morphine-like substance originating from within the body. ...
... The name “endorphin” comes from endo- and -orphin; intended to mean "a morphine-like substance originating from within the body. ...
Airgas template - Morgan Community College
... The parasympathetic nervous system functions in maintaining vital functions and responding when there is a critical threat to the integrity of the individual—the “fight-or-flight” response. ...
... The parasympathetic nervous system functions in maintaining vital functions and responding when there is a critical threat to the integrity of the individual—the “fight-or-flight” response. ...
Adenosine - Wellington ICU
... Class - short acting anti-arrhythmic - naturally occurring purine nucleoside ...
... Class - short acting anti-arrhythmic - naturally occurring purine nucleoside ...
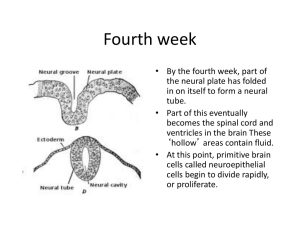
Fourth week
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
The nervous system
... for reasoning, thought, memory, speech, sensation, etc. Divided into two halves. ...
... for reasoning, thought, memory, speech, sensation, etc. Divided into two halves. ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach) transmitter plays a role in
... *A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often…But it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed* ...
... *A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often…But it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed* ...
The Nervous System
... Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morphine mimics endorphins Antagonist – block neurotransmitters Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory * ...
... Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons Agonist – mimic neurotransmitters Example: Morphine mimics endorphins Antagonist – block neurotransmitters Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory * ...
neuron and nervous system
... Nervous System – body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network consisting of nerve cells Central Nervous System (CNS) – brain and spinal cord **Neural networks – interconnected neural cells; more connections made as experience gained Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – sensory and motor neuron ...
... Nervous System – body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network consisting of nerve cells Central Nervous System (CNS) – brain and spinal cord **Neural networks – interconnected neural cells; more connections made as experience gained Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – sensory and motor neuron ...
Psychology - Cobb Learning
... • Found in beer, wine, and liquor • The second most used psychoactive drug (caffeine first) • Slows thinking, and impairs physical activity ...
... • Found in beer, wine, and liquor • The second most used psychoactive drug (caffeine first) • Slows thinking, and impairs physical activity ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) Neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap and binds to the receptor sites on the receiving neuron. Neural Networks and learning a song (singing OR playing an instrument). Patterns are created and strengthened the more we use the ...
... axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) Neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap and binds to the receptor sites on the receiving neuron. Neural Networks and learning a song (singing OR playing an instrument). Patterns are created and strengthened the more we use the ...
Unit 3 Biology of Behavior The Neuron Dendrites: Tree
... branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. b. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotransmitters are excitatory (create a new action potential) while others are inhibitory (s ...
... branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. b. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotransmitters are excitatory (create a new action potential) while others are inhibitory (s ...
镇静催眠药sedative-hypnotic drugs
... 苯二氮卓类Benzodiazepines 【Mechanism of action】 On the GABA neuron ending there are specific points with high affinity to BDZ . The binding point exists in the cortex , mid brain ,cornu ammonis , spinal cord and so on , consistent with the distribution of GABAA receptors . Recent years studies ind ...
... 苯二氮卓类Benzodiazepines 【Mechanism of action】 On the GABA neuron ending there are specific points with high affinity to BDZ . The binding point exists in the cortex , mid brain ,cornu ammonis , spinal cord and so on , consistent with the distribution of GABAA receptors . Recent years studies ind ...
How Opioid Drugs Bind to Receptors
... may not apply uniformly to all opioid ligands. actions and/or crystallization conditions. in complex with different signalling proteins The transmembrane structures of the four In other words, the unusual conformation could provide necessary — although not ORs are very similar to each other, as expe ...
... may not apply uniformly to all opioid ligands. actions and/or crystallization conditions. in complex with different signalling proteins The transmembrane structures of the four In other words, the unusual conformation could provide necessary — although not ORs are very similar to each other, as expe ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... scales ranging from milliseconds to months. ...
... scales ranging from milliseconds to months. ...