Bio 17 – Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
Nervous System
... Ionic differences of intra- and extracellular fluid produce electrical differences or voltage Potassium (K+) is high inside, sodium (Na+) is high outside cell K+ diffuses out readily through K+ channels, leaving a ...
... Ionic differences of intra- and extracellular fluid produce electrical differences or voltage Potassium (K+) is high inside, sodium (Na+) is high outside cell K+ diffuses out readily through K+ channels, leaving a ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM Bachelor
... Pharmacokinetic processes govern the absorption, distribution, and elimination of drugs and are of great practical importance in the choice and administration of a particular drug for a particular patient, e.g., one with impaired renal function. In practical therapeutics, a drug should be able to re ...
... Pharmacokinetic processes govern the absorption, distribution, and elimination of drugs and are of great practical importance in the choice and administration of a particular drug for a particular patient, e.g., one with impaired renal function. In practical therapeutics, a drug should be able to re ...
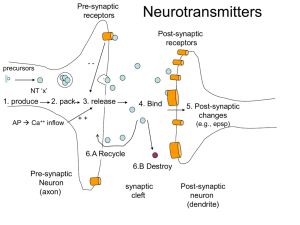
1. Neurotransmitter released from the pre
... Is found at the neuromuscular junction Is a metabotropic receptor Is blocked by Ca++ in the pore when the membrane is within 20 mV of resting potential e. is ligand- and voltage- gated f. Is found at synapses that have AMPA receptors. ...
... Is found at the neuromuscular junction Is a metabotropic receptor Is blocked by Ca++ in the pore when the membrane is within 20 mV of resting potential e. is ligand- and voltage- gated f. Is found at synapses that have AMPA receptors. ...
Specific NT systems
... • A drug can do only two things, either: – Increase the effect of neurotransmitter X (agonist) – Decrease the effect of neurotransmitter X (antagonist) Thus, in order to understand the action of a ‘drug Y’, we need to understand the neurochemical system it interacts with. In other words, we need to ...
... • A drug can do only two things, either: – Increase the effect of neurotransmitter X (agonist) – Decrease the effect of neurotransmitter X (antagonist) Thus, in order to understand the action of a ‘drug Y’, we need to understand the neurochemical system it interacts with. In other words, we need to ...
Unit 3A Notes
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. 2. Neurons 1. ...
... 2. Biological psychologists study the linkage and interplay between the body and the mind. 3. Even more broadly, there is a biopsychosocial component. This concept believes we do the things we do because of (1) our bodies, (2) our minds or thinking, and (3) the culture that we live in. 2. Neurons 1. ...
教案- Pharmacologic Management of Parkinsonism
... and presynaptically on striatal axons coming from cortical neurons and from dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra. The D2 receptors are located postsynaptically on striatal neurons and presynaptically on axons in the substantia nigra belonging to neurons in the basal ganglia. The benefits of do ...
... and presynaptically on striatal axons coming from cortical neurons and from dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra. The D2 receptors are located postsynaptically on striatal neurons and presynaptically on axons in the substantia nigra belonging to neurons in the basal ganglia. The benefits of do ...
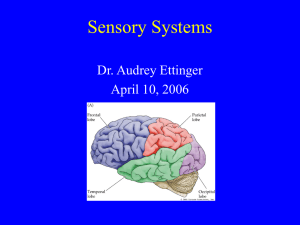
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
... 2. Drugs acting on catecholamine metabolism... Not discussed 3. Drugs acting on catecholamine storage... Probably the most important and most widely studied of these drugs is (+)-amphetamine. Understanding the mechanism of action of this drug allows for interpretation of an array of analogs. AMPHETA ...
... 2. Drugs acting on catecholamine metabolism... Not discussed 3. Drugs acting on catecholamine storage... Probably the most important and most widely studied of these drugs is (+)-amphetamine. Understanding the mechanism of action of this drug allows for interpretation of an array of analogs. AMPHETA ...
INC-IEM Neuroengineering Seminar - 13-11-04
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
Nervous System
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
Learning Objectives
... By contrast, inhibitory neurotransmitters (GABA and glycine) allow Cl– to flow in. This increases the membrane’s negative resting potential and hinders the action of stimulatory transmitters (hyperpolarization) ...
... By contrast, inhibitory neurotransmitters (GABA and glycine) allow Cl– to flow in. This increases the membrane’s negative resting potential and hinders the action of stimulatory transmitters (hyperpolarization) ...
ANP 214 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1
... 4. Which type of parasympathetic receptor relies upon G-protein activity? Several different types of toxins are agonists for these types of receptors, and will therefore bind to the receptor. What types of symptoms might be observed in a patient suffering from poisoning by such a toxin? 5. Given you ...
... 4. Which type of parasympathetic receptor relies upon G-protein activity? Several different types of toxins are agonists for these types of receptors, and will therefore bind to the receptor. What types of symptoms might be observed in a patient suffering from poisoning by such a toxin? 5. Given you ...
General Issues
... 2. Rank those sources based on how fast they reach blood & thus the brain 3. List the factors that determine the effect of a drug on an individual. (In other words, what makes a psychoactive drug be more effective in one person than another) ...
... 2. Rank those sources based on how fast they reach blood & thus the brain 3. List the factors that determine the effect of a drug on an individual. (In other words, what makes a psychoactive drug be more effective in one person than another) ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
Neurons
... information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks called SYNAPTIC VESICLES Vesicles fuse together with the membrane and spill contents into the synaptic gap They may bind to certain areas at various receptor sites ...
... information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks called SYNAPTIC VESICLES Vesicles fuse together with the membrane and spill contents into the synaptic gap They may bind to certain areas at various receptor sites ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... • Efferent neurons (motor), send information from the central nervous system to the glands and muscles, enabling the body to move. • Interneurons carry information between neurons in the Central Nervous System. ...
... • Efferent neurons (motor), send information from the central nervous system to the glands and muscles, enabling the body to move. • Interneurons carry information between neurons in the Central Nervous System. ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems
... likely generates an action potential Inhibitory effect – neurotransmitter that likely does not generate an action potential Sensory nerves – carry info to central nervous system Motor nerves – carry info from central nervous system to muscles and glands ...
... likely generates an action potential Inhibitory effect – neurotransmitter that likely does not generate an action potential Sensory nerves – carry info to central nervous system Motor nerves – carry info from central nervous system to muscles and glands ...
Lesson 1 - UCLA Brain Research Institute
... Oxycodone is currently legal in the U.S. However it is intended to be controlled Schedule II ...
... Oxycodone is currently legal in the U.S. However it is intended to be controlled Schedule II ...
Psych B – Module 22
... • Found in beer, wine, and liquor • The second most used psychoactive drug (caffeine first) • Slows thinking, and impairs physical activity ...
... • Found in beer, wine, and liquor • The second most used psychoactive drug (caffeine first) • Slows thinking, and impairs physical activity ...
Peripheral nervous system
... memory/learning - doesn’t take place in any specific part • short-term memory - temporary memory ...
... memory/learning - doesn’t take place in any specific part • short-term memory - temporary memory ...
Nerve Pathways Practice Sheet
... Fill-in-the-Blanks The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) ___________________ ...
... Fill-in-the-Blanks The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) ___________________ ...