For the 5 W`s Flipbook you need to complete tRNA and rRNA (this is
... tRNA brings the corresponding amino acid based off of its anticodon recognizing mRNA’s codon. 10. What is this stage called, when mRNA gives the message to tRNA? Translation 11. If you want to know the name of the amino acid that a gene gives the instructions for, what trick can you use? (Without ev ...
... tRNA brings the corresponding amino acid based off of its anticodon recognizing mRNA’s codon. 10. What is this stage called, when mRNA gives the message to tRNA? Translation 11. If you want to know the name of the amino acid that a gene gives the instructions for, what trick can you use? (Without ev ...
From Genes to Proteins (11
... The _order____ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the __type amino acids______ in a protein. There are _64___ possible codons but only __20__ Possible Amino Acids Start codon = _AUG (Methionine or Met)___ Stop codons = _UAA UAG UGA_ ...
... The _order____ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the __type amino acids______ in a protein. There are _64___ possible codons but only __20__ Possible Amino Acids Start codon = _AUG (Methionine or Met)___ Stop codons = _UAA UAG UGA_ ...
P{11/27/11 PPPP RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Review DNA 1
... are edited out before the mRNA gets to the ribosomes. 47.The _______________are the parts that are not edited out and thus used to make the protein. Now that we have our message, The mRNA can move through the nuclear pores to go to ribosome’s Ribosomes will “read” the mRNA to build a protein mRNA mo ...
... are edited out before the mRNA gets to the ribosomes. 47.The _______________are the parts that are not edited out and thus used to make the protein. Now that we have our message, The mRNA can move through the nuclear pores to go to ribosome’s Ribosomes will “read” the mRNA to build a protein mRNA mo ...
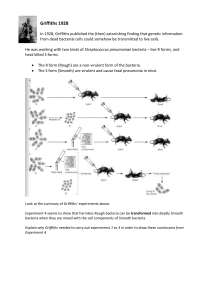
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Gene Isolation and Manipulation
... Conservatively, the amount of DNA necessary to encode this protein of 445 amino acids is 445 × 3 = 1335 base pairs. When compared with the actual amount of DNA used, 60 kb, the gene appears to be roughly 45 times larger than necessary. This “extra” DNA mostly represents the introns that must be corr ...
... Conservatively, the amount of DNA necessary to encode this protein of 445 amino acids is 445 × 3 = 1335 base pairs. When compared with the actual amount of DNA used, 60 kb, the gene appears to be roughly 45 times larger than necessary. This “extra” DNA mostly represents the introns that must be corr ...
DNA Structure and Function
... be a system to code for them using only 4 bases on DNA Codon: 3 consecutive bases on mRNA that code for a specific amino acid. Properties: Degenerate: Most amino acids have more than 1 codon Has a beginning and end ( 1 start codon; 3 stop codons) Unambiguous: 1 code = 1 meaning ...
... be a system to code for them using only 4 bases on DNA Codon: 3 consecutive bases on mRNA that code for a specific amino acid. Properties: Degenerate: Most amino acids have more than 1 codon Has a beginning and end ( 1 start codon; 3 stop codons) Unambiguous: 1 code = 1 meaning ...
DOC
... After a mismatch is identified and a nick introduced, EXO1 cuts out a section of the DNA strand containing the mismatched base. 7. How do E. coli distinguish between parental and newly replicated strands when performing DNA mismatch repair? For instance, if a T was wrongly paired with a G, how does ...
... After a mismatch is identified and a nick introduced, EXO1 cuts out a section of the DNA strand containing the mismatched base. 7. How do E. coli distinguish between parental and newly replicated strands when performing DNA mismatch repair? For instance, if a T was wrongly paired with a G, how does ...
Sunlight Water Entropy
... known about the need for an anti-entropic force that prevents dissipation of energy via amino acid substitutions that stabilize the organized genomes of all living genera. [1415]. For example, achiral glycine in position 6 of the GnRH decapeptide is linked to the stability of all organized genome in ...
... known about the need for an anti-entropic force that prevents dissipation of energy via amino acid substitutions that stabilize the organized genomes of all living genera. [1415]. For example, achiral glycine in position 6 of the GnRH decapeptide is linked to the stability of all organized genome in ...
Microbes in Medicine and Research
... RNA. This RNA is formally called messenger RNA (mRNA). • RNA differs from DNA in that it is single stranded, and does not contain the nucleotide Thymine (T), but instead contains Uracil (U). ...
... RNA. This RNA is formally called messenger RNA (mRNA). • RNA differs from DNA in that it is single stranded, and does not contain the nucleotide Thymine (T), but instead contains Uracil (U). ...
Topic 11 DNA intro - Manhasset Public Schools
... of the ladder are made of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules. The sugar is deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are pairs of 4 types of nitrogen bases: Adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. The bases are known by their coded letters A, G, T, C. These bases always bond in a certain way as a ...
... of the ladder are made of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules. The sugar is deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are pairs of 4 types of nitrogen bases: Adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. The bases are known by their coded letters A, G, T, C. These bases always bond in a certain way as a ...
Chapter 3 The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... Storage fats are all one kind of lipid. Oils, waxes, and some vitamins are also lipids Fats are complex polymers of fatty acids attached to glycerol A fat molecule is a triglyceride, containing three fatty acids. Saturated fats have all carbon atoms in the fatty acid chains bonded to at least two hy ...
... Storage fats are all one kind of lipid. Oils, waxes, and some vitamins are also lipids Fats are complex polymers of fatty acids attached to glycerol A fat molecule is a triglyceride, containing three fatty acids. Saturated fats have all carbon atoms in the fatty acid chains bonded to at least two hy ...
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology states that
... The RNAP will keep slipping, producing truncated transcripts and elongation will not occur ...
... The RNAP will keep slipping, producing truncated transcripts and elongation will not occur ...
Lecture #7 Date - Woodland Hills School District
... √ DNA, not protein, is the hereditary material √ Expt: sulfur(S) is in protein, phosphorus (P) is in DNA; only P was found in host cell ...
... √ DNA, not protein, is the hereditary material √ Expt: sulfur(S) is in protein, phosphorus (P) is in DNA; only P was found in host cell ...
Chapter 13: Carbohydrates
... compact and round shape. The non-polar R groups point inward and the polar R groups point outward and this makes these proteins soluble in water. Fibrous proteins, like keratin (hair, skin), consist of long, thin, fibrous shapes. Cross-linking is an important aspect ...
... compact and round shape. The non-polar R groups point inward and the polar R groups point outward and this makes these proteins soluble in water. Fibrous proteins, like keratin (hair, skin), consist of long, thin, fibrous shapes. Cross-linking is an important aspect ...
Human Genetics
... As the complementary strand is formed, the DNA and the new strand are “zipped” together, creating two separate strands of the same DNA. ...
... As the complementary strand is formed, the DNA and the new strand are “zipped” together, creating two separate strands of the same DNA. ...
chapter 4 pptol
... Two polynucleotide chains – double-stranded Hydrogen bonds hold nitrogenous bases together Bases pair specifically (A-T and C-G) Forms a helix DNA wrapped about histones forms chromatin Chromosomes are condensed chromatin ...
... Two polynucleotide chains – double-stranded Hydrogen bonds hold nitrogenous bases together Bases pair specifically (A-T and C-G) Forms a helix DNA wrapped about histones forms chromatin Chromosomes are condensed chromatin ...
File
... 20. Explain the relationship between monomers and polymers, using polysaccharides as an example. ...
... 20. Explain the relationship between monomers and polymers, using polysaccharides as an example. ...
Molecular Structure of DNA and RNA part 1 powerpoint
... 4. The double helix folds, bends and interacts with proteins resulting in 3-D structures in the form of chromosomes ...
... 4. The double helix folds, bends and interacts with proteins resulting in 3-D structures in the form of chromosomes ...
Biochemistry Notes 2012
... • Atoms - basic building blocks of all matter. • Elements – pure substances that can’t be broken down into other substances. (atoms) • Molecules – two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds. (smallest combination that can’t be divided without changing its chemical and physical properties) • ...
... • Atoms - basic building blocks of all matter. • Elements – pure substances that can’t be broken down into other substances. (atoms) • Molecules – two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds. (smallest combination that can’t be divided without changing its chemical and physical properties) • ...
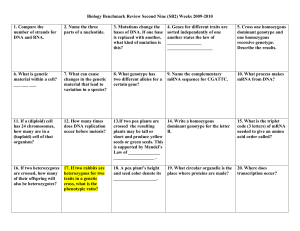
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... 15. What is the triplet code (3 letters) of mRNA needed to give an amino acid order called? ...
... 15. What is the triplet code (3 letters) of mRNA needed to give an amino acid order called? ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.