Slide 1
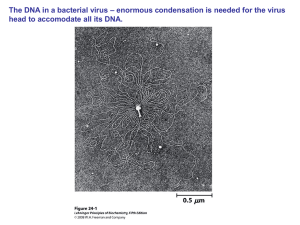
... The DNA in a bacterial virus – enormous condensation is needed for the virus head to accomodate all its DNA. ...
... The DNA in a bacterial virus – enormous condensation is needed for the virus head to accomodate all its DNA. ...
Submission to IP Australia re Myriad Proposal
... medical research. Nonetheless I support the High Court's interpretation in this case, believing that it is important to find a balance between incentives to develop diagnostic testing on the one hand, and on the other, the social implications for the health needs of individuals when it comes to main ...
... medical research. Nonetheless I support the High Court's interpretation in this case, believing that it is important to find a balance between incentives to develop diagnostic testing on the one hand, and on the other, the social implications for the health needs of individuals when it comes to main ...
Notes handout for Basic Biochemistry
... Nucleotides are composed of _______-containing base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group ...
... Nucleotides are composed of _______-containing base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group ...
Section 3.3: Carbon Compounds Building Blocks of Cells • The parts
... In a complex organism, cells recognize neighboring cells by the short, branched chains of varying sugar units on their outer surface. ...
... In a complex organism, cells recognize neighboring cells by the short, branched chains of varying sugar units on their outer surface. ...
Print › Benchmark Second Nine Weeks | Quizlet | Quizlet
... If two pea plants are crossed the resulting plants may be tall or short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel's Law of ...
... If two pea plants are crossed the resulting plants may be tall or short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel's Law of ...
Measuring forces in the DNA molecule
... These have been modified such that each end carries one base pair. Two of these microscopic beams are connected with a flexible polymer. On the other side, the beams are coupled to microscopic spheres which can be pulled apart using optical laser tweezers. In solution, the base pairs on the end of o ...
... These have been modified such that each end carries one base pair. Two of these microscopic beams are connected with a flexible polymer. On the other side, the beams are coupled to microscopic spheres which can be pulled apart using optical laser tweezers. In solution, the base pairs on the end of o ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... makes RNA from a DNA template, uses a process that resembles the synthesis of a DNA strand during DNA replication, and substitutes uracil (U) for thymine (T). RNA nucleotides are linked by the transcription enzyme RNA polymerase. ...
... makes RNA from a DNA template, uses a process that resembles the synthesis of a DNA strand during DNA replication, and substitutes uracil (U) for thymine (T). RNA nucleotides are linked by the transcription enzyme RNA polymerase. ...
Chapter 18 – Gene Mutations and DNA Repair
... • One purine replaced by another purine; one pyrimidine replace by another pyrimidine ...
... • One purine replaced by another purine; one pyrimidine replace by another pyrimidine ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... – Nitrogenous bases include • Purines: adenine and guanine • Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine, uracil ...
... – Nitrogenous bases include • Purines: adenine and guanine • Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine, uracil ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... DNA vs.RNA: differences • DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) and RNA (ribose nucleic acid) are both nucleotide polymers. These molecules are very similar but there are some distinct differences between them. ...
... DNA vs.RNA: differences • DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) and RNA (ribose nucleic acid) are both nucleotide polymers. These molecules are very similar but there are some distinct differences between them. ...
Chapter 18 – Gene Mutations and DNA Repair
... – One base is replaced by another – Transition • One purine replaced by another purine; one pyrimidine replace by another pyrimidine ...
... – One base is replaced by another – Transition • One purine replaced by another purine; one pyrimidine replace by another pyrimidine ...
biomolecule notes
... a. Made of amino acids b. There are 20 different amino acids c. The sequence of amino acids determines the proteins shape & function d. Polypeptide = long chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds e. provide structure for tissues & organs f. carry out cell metabolism g. examples: egg whites, enzy ...
... a. Made of amino acids b. There are 20 different amino acids c. The sequence of amino acids determines the proteins shape & function d. Polypeptide = long chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds e. provide structure for tissues & organs f. carry out cell metabolism g. examples: egg whites, enzy ...
Document
... could provide genetic information to another bacteria by a process known as transformation ...
... could provide genetic information to another bacteria by a process known as transformation ...
RNA and Protein
... What is the function of each? mRNA – messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to direct protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. ...
... What is the function of each? mRNA – messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to direct protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. ...
Toward detection of DNA-bound proteins using solid-state
... Movie showing a MD simulation of the nanopore-induced rupture of a protein-DNA complex. First, a cross section of the nanopore is shown. Next, ions moving in the electric field transverse to the membrane are shown. Although ions and water are not shown during the whole video, they were always presen ...
... Movie showing a MD simulation of the nanopore-induced rupture of a protein-DNA complex. First, a cross section of the nanopore is shown. Next, ions moving in the electric field transverse to the membrane are shown. Although ions and water are not shown during the whole video, they were always presen ...
MolecularBiology1APLab6
... • Lower case letters are the species • Next capital letter is the strain • The number is the order of discovery within the particular bacteria ...
... • Lower case letters are the species • Next capital letter is the strain • The number is the order of discovery within the particular bacteria ...
DNA Mutations
... A synonym is a word having the same or nearly the same meaning as another; so a synonym mutation is a different codon that still codes for the same amino acid. Example: ...
... A synonym is a word having the same or nearly the same meaning as another; so a synonym mutation is a different codon that still codes for the same amino acid. Example: ...
Macromolecule Review
... 2. Which of the molecules listed above can often be composed of C, H, and O alone? 3. Which of the compounds can be identified by looking at the C:H:O ratios alone? 4. What other elements are commonly associated with each of these four types of macromolecules? ...
... 2. Which of the molecules listed above can often be composed of C, H, and O alone? 3. Which of the compounds can be identified by looking at the C:H:O ratios alone? 4. What other elements are commonly associated with each of these four types of macromolecules? ...
transcription and translation
... Add5’ cap- protects mRNA and allows it to leave nucleus/find a ribosome Poly (A) tailThey are added to: protect mRNA and allow it to leave nucleus/find a ribosome Introns (non-coding sequences between exons) are removed and exons (amino acid coding sequences) are spliced together ...
... Add5’ cap- protects mRNA and allows it to leave nucleus/find a ribosome Poly (A) tailThey are added to: protect mRNA and allow it to leave nucleus/find a ribosome Introns (non-coding sequences between exons) are removed and exons (amino acid coding sequences) are spliced together ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.