DNA Replication • DNA strands separate and the nucleotides in the
... o It can actually make 64 combinations but we only need 20 A codon is the name for 3 nucleotides in a row o AUG codon is the “start codon” o “stop codon” is the termination codon Start codon As seen to the in the above diagram, most amino acids have 2 different codons to use except the beginner codo ...
... o It can actually make 64 combinations but we only need 20 A codon is the name for 3 nucleotides in a row o AUG codon is the “start codon” o “stop codon” is the termination codon Start codon As seen to the in the above diagram, most amino acids have 2 different codons to use except the beginner codo ...
OCR Biology B - Centre of the Cell
... 2.1.4 Nucleic acids 3.1.2 The developing individual: meiosis, growth and development 5.1.1 Patterns of inheritance 5.1.2 Population genetics and epigenetics 2.1.4 Nucleic acids (a) the structure of a nucleotide as the monomer from which nucleic acids are made (c) (i) the structure of the DNA molecul ...
... 2.1.4 Nucleic acids 3.1.2 The developing individual: meiosis, growth and development 5.1.1 Patterns of inheritance 5.1.2 Population genetics and epigenetics 2.1.4 Nucleic acids (a) the structure of a nucleotide as the monomer from which nucleic acids are made (c) (i) the structure of the DNA molecul ...
review sheet
... a. Label the diagram with the following terms: hydrogen bond, phosphodiester bond, deoxyribose, phosphate group. (Use each term only once) b. Label ALL the nitrogenous bases present with the appropriate letter (A,C,G,T). c. What part of the DNA molecule actually contains the hereditary information? ...
... a. Label the diagram with the following terms: hydrogen bond, phosphodiester bond, deoxyribose, phosphate group. (Use each term only once) b. Label ALL the nitrogenous bases present with the appropriate letter (A,C,G,T). c. What part of the DNA molecule actually contains the hereditary information? ...
I. Biology (35 points total) The following questions cover some of the
... DNA transfers information to mRNA in the form of a code defined by a sequence of nucleotides bases. During protein synthesis, ribosomes move along the mRNA molecule and "read" its sequence three nucleotides at a time (codon) from the 5' end to the 3' end. Each amino acid is specified by the mRNA's c ...
... DNA transfers information to mRNA in the form of a code defined by a sequence of nucleotides bases. During protein synthesis, ribosomes move along the mRNA molecule and "read" its sequence three nucleotides at a time (codon) from the 5' end to the 3' end. Each amino acid is specified by the mRNA's c ...
DNA Structure, Replication, and Repair
... A DNA segment has information for making the protein hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in your red blood cells One allele will give information for producing normal hemoglobin -Another allele (ONLY 1 base different) produces hemoglobin with 1 different amino acid This difference makes the hemoglobin ...
... A DNA segment has information for making the protein hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in your red blood cells One allele will give information for producing normal hemoglobin -Another allele (ONLY 1 base different) produces hemoglobin with 1 different amino acid This difference makes the hemoglobin ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA ANSWER KEY
... 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less genetic material. It also makes it possible for ...
... 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less genetic material. It also makes it possible for ...
Lesson 1 DNA and proteins
... Transcription • The part of the DNA molecule to be transcribed unwinds and ‘unzips’ as DNA helicase breaks the H bonds between the bases • RNA polymerase catalyses the binding of activated free RNA nucleotides to the template • Uracil binds to adenine NOT thymine • The nucleotides condense together ...
... Transcription • The part of the DNA molecule to be transcribed unwinds and ‘unzips’ as DNA helicase breaks the H bonds between the bases • RNA polymerase catalyses the binding of activated free RNA nucleotides to the template • Uracil binds to adenine NOT thymine • The nucleotides condense together ...
The Bioinformatics Institute
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contains the information prescribing the amino acid sequence of proteins. This information is arranged in units termed genes. A GENE is the entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide Ribonucleic acid (RNA) serves i ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contains the information prescribing the amino acid sequence of proteins. This information is arranged in units termed genes. A GENE is the entire nucleic acid sequence that is necessary for the synthesis of a functional polypeptide Ribonucleic acid (RNA) serves i ...
chromosome2
... 3. Necessary for chromosomal replication B. Structure 1. TTAGGG repeated 250 - 1000 times 2. This sequence can form a hairpin terminus C. Problems replicated ends of a linear chromosome 1. DNA is replicated only 5' to 3' 2. G-rich strand ends up as single stranded a) 12 - 16 base overhang D. Telomer ...
... 3. Necessary for chromosomal replication B. Structure 1. TTAGGG repeated 250 - 1000 times 2. This sequence can form a hairpin terminus C. Problems replicated ends of a linear chromosome 1. DNA is replicated only 5' to 3' 2. G-rich strand ends up as single stranded a) 12 - 16 base overhang D. Telomer ...
Things to Cover for Exam 1
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
Chapter 18-20 review
... skull with a small dried fragment of the scalp still attached. They extracted a tiny amount of DNA from the scalp tissue. How could they obtain sufficient DNA for an analysis of the ancient human's genes? a. subject the DNA to electrophoresis b. use a nucleic acid probe c. subject the specimen to am ...
... skull with a small dried fragment of the scalp still attached. They extracted a tiny amount of DNA from the scalp tissue. How could they obtain sufficient DNA for an analysis of the ancient human's genes? a. subject the DNA to electrophoresis b. use a nucleic acid probe c. subject the specimen to am ...
Macromolecules 2: Proteins and Nucleic Acids Amino Acids differ
... Secondary structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonding of peptide bonds ...
... Secondary structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonding of peptide bonds ...
DNA - eduBuzz.org
... The function of DNA The genetic information contained within the DNA can be thought of as a list of genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between prote ...
... The function of DNA The genetic information contained within the DNA can be thought of as a list of genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between prote ...
AP-ppt-PCR
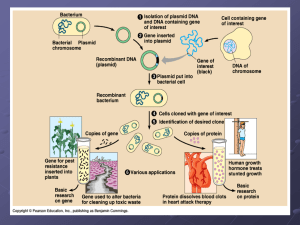
... Not all bacteria pick up plasmid-how do we distinguish? Annealing of human DNA to plasmid is random-how do we distinguish which plasmids have human DNA? ...
... Not all bacteria pick up plasmid-how do we distinguish? Annealing of human DNA to plasmid is random-how do we distinguish which plasmids have human DNA? ...
Chapter 3 – Carbon Compounds in Cells
... unique shape Shape is extremely important for the enzyme to recognize and attach to its target Denaturation: the process of changing a protein’s shape so it can no longer function properly Ex. Cooking egg whites or meats Caused by heat, pH change, salt concentration change, or chemical balance chang ...
... unique shape Shape is extremely important for the enzyme to recognize and attach to its target Denaturation: the process of changing a protein’s shape so it can no longer function properly Ex. Cooking egg whites or meats Caused by heat, pH change, salt concentration change, or chemical balance chang ...
Mutation and Recombination
... Natural mutation is a very rare event and can only be studied in organisms with very high division rates (such as bacteria). A spontaneous mutation may be detected by using selective media. For example, the antibiotic penicillin, could be added to the culture media. If some of the aseptically transf ...
... Natural mutation is a very rare event and can only be studied in organisms with very high division rates (such as bacteria). A spontaneous mutation may be detected by using selective media. For example, the antibiotic penicillin, could be added to the culture media. If some of the aseptically transf ...
Stg Chp 11 - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mamre organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring. d. all of the above. 6. When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromoso ...
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mamre organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring. d. all of the above. 6. When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromoso ...
Vocab table - Genetics and variation teacher
... A mutation in a chromosome where a section is removed, or in a gene, where one of the bases is removed from the sequence ...
... A mutation in a chromosome where a section is removed, or in a gene, where one of the bases is removed from the sequence ...
Organic molecules
... **can bond to many different elements **can bond to other C atoms **form covalent bonds **can form single, double, triple bonds **can form a chain or ring • Carbon compounds: 4 found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins ...
... **can bond to many different elements **can bond to other C atoms **form covalent bonds **can form single, double, triple bonds **can form a chain or ring • Carbon compounds: 4 found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins ...
00_BioBackground
... • In plants and animals, individual cells cooperate to form multicellular tissues and organ systems that meet the biological needs of the organism • We are interested in biological sequences that regulate all biological processes in cells and organisms • Our primary concern are the instructions for ...
... • In plants and animals, individual cells cooperate to form multicellular tissues and organ systems that meet the biological needs of the organism • We are interested in biological sequences that regulate all biological processes in cells and organisms • Our primary concern are the instructions for ...
DNA Control (Protein Synthesis)
... •the nucleus is considered the control center of the cell because it tells the cell when to make proteins and which type of proteins to make •Every cell has a complete set of instructions in the DNA but different parts of the DNA are read in different types of cells...thus making different proteins ...
... •the nucleus is considered the control center of the cell because it tells the cell when to make proteins and which type of proteins to make •Every cell has a complete set of instructions in the DNA but different parts of the DNA are read in different types of cells...thus making different proteins ...
242140_Fx_DNA-RNA
... 4. After transcription is complete, what happens to the newly constructed mRNA strand? Go back to Mr. Mason’s website and click on the link labeled “Genetics – Translation” 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details ...
... 4. After transcription is complete, what happens to the newly constructed mRNA strand? Go back to Mr. Mason’s website and click on the link labeled “Genetics – Translation” 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details ...
Ch. 10- Structure and Analysis of DNA and RNA p. 262-288
... Replication: one facet of the cell cycle, a fundamental property of all living organisms. Once genetic material is replicated, it is divided equally into daughter cells. During gamete formation, the genetic material is also replicated, but each cell only gets half the original genetic material. Expr ...
... Replication: one facet of the cell cycle, a fundamental property of all living organisms. Once genetic material is replicated, it is divided equally into daughter cells. During gamete formation, the genetic material is also replicated, but each cell only gets half the original genetic material. Expr ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.