Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life - wfs
... to the formation of polypeptides, proteins. 7. In the cytoplasm tRNA molecules contain anticodons. The tRNA anticodons pair with the mRNA codons through base pairing. Because each tRNA with a particular anticodon carries a specific amino acid, the codon – anticodon match allows a very specific prote ...
... to the formation of polypeptides, proteins. 7. In the cytoplasm tRNA molecules contain anticodons. The tRNA anticodons pair with the mRNA codons through base pairing. Because each tRNA with a particular anticodon carries a specific amino acid, the codon – anticodon match allows a very specific prote ...
Differences between DNA and RNA • Ribonucleic acid is similar to
... DNA consists of 2 complementary strands, whereas RNA generally exists as a single strand. ...
... DNA consists of 2 complementary strands, whereas RNA generally exists as a single strand. ...
Ecology Pre
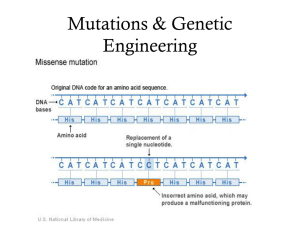
... SC.912.L.16.4 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence may or may not result in phenotypic change. Explain how mutations in gametes may result in phenotypic changes in offspring. SC.912.L.16.9 Explain how and why the genetic code is universal and is common to almost all organisms ...
... SC.912.L.16.4 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence may or may not result in phenotypic change. Explain how mutations in gametes may result in phenotypic changes in offspring. SC.912.L.16.9 Explain how and why the genetic code is universal and is common to almost all organisms ...
Study Guide
... protein - a caloric nutrient that can be structural (materials) or functional (machines) and is made of amino acids. fat - a slippery molecule used for the body to store energy. carbohydrate - a carbon, hydrogen and oxygen molecule that includes sugar and starch. sugar - a ring-base molecule that ta ...
... protein - a caloric nutrient that can be structural (materials) or functional (machines) and is made of amino acids. fat - a slippery molecule used for the body to store energy. carbohydrate - a carbon, hydrogen and oxygen molecule that includes sugar and starch. sugar - a ring-base molecule that ta ...
Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation)
... Do you remember who manufactured proteins? Can you remember of what proteins are composed? Who contains the “code” to make proteins? ...
... Do you remember who manufactured proteins? Can you remember of what proteins are composed? Who contains the “code” to make proteins? ...
Mutations that happen during Transcription and
... pass to separate cells during the first meiotic division ...
... pass to separate cells during the first meiotic division ...
Why is DNA called the "blueprint of life"?
... Key Learning: DNA segments contain information for the production of proteins necessary for growth and ...
... Key Learning: DNA segments contain information for the production of proteins necessary for growth and ...
Transcription and Translation
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
3.2.1: Transcription and Translation
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
... ◊This process is similar to DNA replication except that the result is one single stranded RNA molecule. ...
Bio 262- Genetics Study Guide
... double- base pairs of nucleotides. the four nucleotides in dna contain the bases" stranded molecule held together by weak bonds between base pairs of nucleotides. The four nucleotides in DNA contain the bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In nature, base pairs form only b ...
... double- base pairs of nucleotides. the four nucleotides in dna contain the bases" stranded molecule held together by weak bonds between base pairs of nucleotides. The four nucleotides in DNA contain the bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In nature, base pairs form only b ...
Life Substances
... f. What structures can Carbon form, based on its bonding capacities? g. What is meant by the term "isomers?" f What is meant by the term "Carbon compounds vary in size?" i. What are macromolecutes? j. What is a polymer? ...
... f. What structures can Carbon form, based on its bonding capacities? g. What is meant by the term "isomers?" f What is meant by the term "Carbon compounds vary in size?" i. What are macromolecutes? j. What is a polymer? ...
BINF 730 Biological Sequence Analysis Lecture 1 Biological
... • RNA does not form a double helix • RNA may have a complex three-dimensional structure ...
... • RNA does not form a double helix • RNA may have a complex three-dimensional structure ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... RNA carries copies of genes – acts as “messengers” ◦ Messenger RNA or mRNA ...
... RNA carries copies of genes – acts as “messengers” ◦ Messenger RNA or mRNA ...
DNA Basics - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... repel each other, just like the identical poles of two magnets will repel each other. An A won’t pair with a C, and a T won’t pair with a G. So if there’s even a single base that’s not complementary to its partner, it could keep a single strand from sticking to another single strand. What’s a gene a ...
... repel each other, just like the identical poles of two magnets will repel each other. An A won’t pair with a C, and a T won’t pair with a G. So if there’s even a single base that’s not complementary to its partner, it could keep a single strand from sticking to another single strand. What’s a gene a ...
Central Dogma of Biology Nucleic Acids
... DNA double helix: Many weak (H-bonds), makes for very stable structure. If you have many weak bonds (e.g. each bond only few kT) you can get a biomolecule that will not fall apart. ...
... DNA double helix: Many weak (H-bonds), makes for very stable structure. If you have many weak bonds (e.g. each bond only few kT) you can get a biomolecule that will not fall apart. ...
Recombinant DNA
... Cut DNA into pieces Insert DNA into vectors that can replicate in bacteria Transform (introduce) DNA into host cell Plate cells and select those with vectors Each colony has one chunk of DNA The whole set is a library of human DNA ...
... Cut DNA into pieces Insert DNA into vectors that can replicate in bacteria Transform (introduce) DNA into host cell Plate cells and select those with vectors Each colony has one chunk of DNA The whole set is a library of human DNA ...
Practice Science Olympiad Exam: Designer Genes
... In a gene where both alleles code for part of a trait and phenotypes can be a mixture of two traits, this phenomenon is called? Name an example of a human gene which shows incomplete dominance. What disease does the sickle cell anemia disorder prevent if both alleles are present (Ss) or the person h ...
... In a gene where both alleles code for part of a trait and phenotypes can be a mixture of two traits, this phenomenon is called? Name an example of a human gene which shows incomplete dominance. What disease does the sickle cell anemia disorder prevent if both alleles are present (Ss) or the person h ...
Biology Study Guide 10 p
... E. organelles that position tRNA and mRNA to make proteins _____rRNA F. triplet loop of bases on tRNA _____codon G. triplet of bases on mRNA _____anti-codon H. non-coding regions of RNA that are removed _____RNA polymerase I. coding regions of RNA that are expressed and leave nucleus _____ribosomes ...
... E. organelles that position tRNA and mRNA to make proteins _____rRNA F. triplet loop of bases on tRNA _____codon G. triplet of bases on mRNA _____anti-codon H. non-coding regions of RNA that are removed _____RNA polymerase I. coding regions of RNA that are expressed and leave nucleus _____ribosomes ...
Glossary
... of small RNAs, ranging from 18 to 23 nucleotides in length. Approximately 2,000 human miRNAs have been identified and numbered in the order they were found (i.e.; miR-376). miRNAs are generated from long transcripts, termed primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), that are cleaved by the nuclear Drosha-DGCR8 co ...
... of small RNAs, ranging from 18 to 23 nucleotides in length. Approximately 2,000 human miRNAs have been identified and numbered in the order they were found (i.e.; miR-376). miRNAs are generated from long transcripts, termed primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), that are cleaved by the nuclear Drosha-DGCR8 co ...
Biology Today is Monday Aug 31, 2015
... • There are 20 different types of amino acids • Change based on the “R” Group ...
... • There are 20 different types of amino acids • Change based on the “R” Group ...
Chapter Outline - Ltcconline.net
... I. Biology and Society: Mix-and-Match Viruses A. DNA: Structure and Replication 1. DNA 2. The discovery of DNA B. DNA and RNA Structure 1. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids a. They consist of chemical units called: b. A nucleotide polymer is a: c. Nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds between the sug ...
... I. Biology and Society: Mix-and-Match Viruses A. DNA: Structure and Replication 1. DNA 2. The discovery of DNA B. DNA and RNA Structure 1. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids a. They consist of chemical units called: b. A nucleotide polymer is a: c. Nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds between the sug ...
Requirements for Test Review-Solutions-Acid-Base-Grade 11-2015
... • Electrolytes: Strong and Weak Definitions, (ex: have 0.1M of acetic acid and 0.1M of HCl, how do you know experimentally which is the stronger electrolyte) (answer: light bulb experiment (which is brighter, more dim), rate of reaction with metal and metal carbonate for acids, measurement of pH) ...
... • Electrolytes: Strong and Weak Definitions, (ex: have 0.1M of acetic acid and 0.1M of HCl, how do you know experimentally which is the stronger electrolyte) (answer: light bulb experiment (which is brighter, more dim), rate of reaction with metal and metal carbonate for acids, measurement of pH) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.