Plasmid Miniprep - California State University
... cDNA (complementary DNA) DNA copy of a gene that lacks introns and therefore consists solely of the coding sequence. Made by reverse transcription. ...
... cDNA (complementary DNA) DNA copy of a gene that lacks introns and therefore consists solely of the coding sequence. Made by reverse transcription. ...
Organic Chemistry - Biology Junction
... • Each "Rung" of the DNA "staircase" is formed by the linking of 2 Nucleotides through Hydrogen Bonds. • These Hydrogen bonds form only between specific Nucleotides. This is known as Base Pairing. The rules are as follows: – Adenine (A) will ONLY bond to Thymine (T) – Cytosine (C) will ONLY bond to ...
... • Each "Rung" of the DNA "staircase" is formed by the linking of 2 Nucleotides through Hydrogen Bonds. • These Hydrogen bonds form only between specific Nucleotides. This is known as Base Pairing. The rules are as follows: – Adenine (A) will ONLY bond to Thymine (T) – Cytosine (C) will ONLY bond to ...
Organic Chemistry - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... • Each "Rung" of the DNA "staircase" is formed by the linking of 2 Nucleotides through Hydrogen Bonds. • These Hydrogen bonds form only between specific Nucleotides. This is known as Base Pairing. The rules are as follows: – Adenine (A) will ONLY bond to Thymine (T) – Cytosine (C) will ONLY bond to ...
... • Each "Rung" of the DNA "staircase" is formed by the linking of 2 Nucleotides through Hydrogen Bonds. • These Hydrogen bonds form only between specific Nucleotides. This is known as Base Pairing. The rules are as follows: – Adenine (A) will ONLY bond to Thymine (T) – Cytosine (C) will ONLY bond to ...
DNA - NylandBiology2012-2013
... 9. In DNA, thymine is complementary to ________________ ; cytosine is complementary to _____________ 10. In a strand of DNA, the percentage of thymine is 30 %. What is the percentage of cytosine in the same DNA strand? _________________ 11. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1 ...
... 9. In DNA, thymine is complementary to ________________ ; cytosine is complementary to _____________ 10. In a strand of DNA, the percentage of thymine is 30 %. What is the percentage of cytosine in the same DNA strand? _________________ 11. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1 ...
Introduction
... DNA The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid, which is the basic hereditary unit of life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determinin ...
... DNA The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid, which is the basic hereditary unit of life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determinin ...
There are three parts in this exam (50% +20% +30%)
... phosphoryl group transfer scale, which makes it a universal donor of the phosphoryl group; (D) ATP has a position roughly at the bottom of the phosphoryl group transfer scale, which allows it to serve as a pipeline to transfer energy from catabolism to anabolism; (E) None of the above. 14. Please c ...
... phosphoryl group transfer scale, which makes it a universal donor of the phosphoryl group; (D) ATP has a position roughly at the bottom of the phosphoryl group transfer scale, which allows it to serve as a pipeline to transfer energy from catabolism to anabolism; (E) None of the above. 14. Please c ...
Fill in the blank 12-2 and 12
... In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the _____________________________. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly all of the cell’s genetic information. Many eukaryotes have __________ times the amount of DNA as prokaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA is located in the cell ______ ...
... In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the _____________________________. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly all of the cell’s genetic information. Many eukaryotes have __________ times the amount of DNA as prokaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA is located in the cell ______ ...
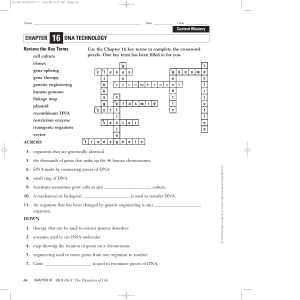
chapter dna technology - Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
1 - contentextra
... Because of the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases of the two DNA chains, the DNA can be opened down the middle thus exposing the bases on both chains. ...
... Because of the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases of the two DNA chains, the DNA can be opened down the middle thus exposing the bases on both chains. ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription & Translation
... bases called the anticodon that is complementary to one mRNA codon. ...
... bases called the anticodon that is complementary to one mRNA codon. ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... was the genetic material when they performed an experiment with a T2 virus. By using different radioactively labeled components, they demonstrated that only the virus DNA entered a bacterium to take over the cell and produce new viruses. ...
... was the genetic material when they performed an experiment with a T2 virus. By using different radioactively labeled components, they demonstrated that only the virus DNA entered a bacterium to take over the cell and produce new viruses. ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... the production of proteins within the cell. These proteins in turn, form the structural units of cells and control all chemical processes within the cell. Think of proteins as the building blocks for an organism, proteins make up your skin, your hair, parts of individual cells. How you look is large ...
... the production of proteins within the cell. These proteins in turn, form the structural units of cells and control all chemical processes within the cell. Think of proteins as the building blocks for an organism, proteins make up your skin, your hair, parts of individual cells. How you look is large ...
Transcription 12.06.21 lec
... There's this relationship: thymine with adenine, guanine to cytosine – or vice versa; whichever strand has one, the other strand has the other. This is because these two pairings of adenine-‐thymin ...
... There's this relationship: thymine with adenine, guanine to cytosine – or vice versa; whichever strand has one, the other strand has the other. This is because these two pairings of adenine-‐thymin ...
DNAandProteinSynthesis
... • mRNA is read and the tRNA bring amino acids in order to it build proteins! ...
... • mRNA is read and the tRNA bring amino acids in order to it build proteins! ...
Molecular Genetics
... • The mRNA attaches to one of three binding sites on the ribosome. • As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, each mRNA codon is paired with the correct tRNA anticodon. • The pairing of the next amino acid creates a bond between the two amino acids called a peptide bond. • In this way, the entire mRNA ...
... • The mRNA attaches to one of three binding sites on the ribosome. • As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, each mRNA codon is paired with the correct tRNA anticodon. • The pairing of the next amino acid creates a bond between the two amino acids called a peptide bond. • In this way, the entire mRNA ...
Major Functions
... A gene is a stretch of DNA that contains the information to produce a particular product (usually a protein). ...
... A gene is a stretch of DNA that contains the information to produce a particular product (usually a protein). ...
Chapter 3,
... continuous transcription of the lac operon genes. The enzymes are continuously present and the bacterium is able to catabolize lactose normally. A bacterium continuously producing the lac enzymes is at a disadvantage relative to wild type cells because producing the enzymes when no lactose is availa ...
... continuous transcription of the lac operon genes. The enzymes are continuously present and the bacterium is able to catabolize lactose normally. A bacterium continuously producing the lac enzymes is at a disadvantage relative to wild type cells because producing the enzymes when no lactose is availa ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.