MODULE 2
... A. Prions contains proteins and nucleic acids B. BSE and Mad-Cow disease are caused by prions C. AOTA D. NOTA ...
... A. Prions contains proteins and nucleic acids B. BSE and Mad-Cow disease are caused by prions C. AOTA D. NOTA ...
Slide 1
... For example, most of us have a protein enzyme that can create melanin, the main pigment that gives color to our skin and hair. In contrast, albino people make a defective version of this protein enzyme, so they are unable to make melanin and they have very pale skin and hair. What is a protein? Prob ...
... For example, most of us have a protein enzyme that can create melanin, the main pigment that gives color to our skin and hair. In contrast, albino people make a defective version of this protein enzyme, so they are unable to make melanin and they have very pale skin and hair. What is a protein? Prob ...
DNA Review - East Pennsboro High School
... segment of DNA synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3’-5’ direction by DNA polymerase. Okazaki Fragments ...
... segment of DNA synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3’-5’ direction by DNA polymerase. Okazaki Fragments ...
What does DNA stand for?
... segment of DNA synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3’-5’ direction by DNA polymerase. Okazaki Fragments ...
... segment of DNA synthesized discontinuously in small segments in the 3’-5’ direction by DNA polymerase. Okazaki Fragments ...
Definitions
... characteristics that allow them to be well adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation The study of fossils Inherited factors are controlled by pairs of factors. These factors separate from each other at gamete formation with only one member ...
... characteristics that allow them to be well adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation The study of fossils Inherited factors are controlled by pairs of factors. These factors separate from each other at gamete formation with only one member ...
Translation Worksheet and Key File
... If the sequence on the DNA molecule calls for a protein with the following DNA codons: 1) What would be the base sequence on mRNA? 2) What would be the base sequence on tRNA? 3) Wh ...
... If the sequence on the DNA molecule calls for a protein with the following DNA codons: 1) What would be the base sequence on mRNA? 2) What would be the base sequence on tRNA? 3) Wh ...
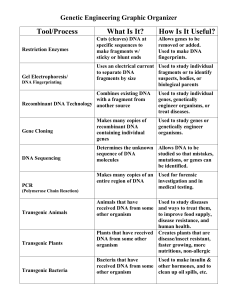
DNA Technology Tools Graphic Organizer KEY
... Makes many copies of an Used for forensic entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates ...
... Makes many copies of an Used for forensic entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates ...
Ch. 17: From Gene to Protein
... 3) RNA splicing: exons (expressed sequences) kept introns (intervening sequences) are spliced out forming a spliceosome ...
... 3) RNA splicing: exons (expressed sequences) kept introns (intervening sequences) are spliced out forming a spliceosome ...
... dna replication is necessary for the transmission of genetic information and thus such a process must achieve accurate copying of the genome. Since the last century the replicon model has been proposed in order to explain the general mechanism of genome duplication in bacteria. Later work in yeast l ...
GENE EXPRESSION CH 17
... • RNA is the bridge between proteins and genes that code for them • The concept of gene is universal to all domains of life • The general process of gene expression is also universal • The genetic code is also universal ...
... • RNA is the bridge between proteins and genes that code for them • The concept of gene is universal to all domains of life • The general process of gene expression is also universal • The genetic code is also universal ...
DNA Transcription / Translation
... B. unwinds a strand of DNA. C. binds to a strand of RNA. D. attaches to the promoter sequence of a gene. ...
... B. unwinds a strand of DNA. C. binds to a strand of RNA. D. attaches to the promoter sequence of a gene. ...
Sections 5.3-5.5 - BridgesToLiteracy.com
... 50% of dry mass of most cells All proteins are polymers with the same set of 20 amino acids ...
... 50% of dry mass of most cells All proteins are polymers with the same set of 20 amino acids ...
Mendelism
... the uncharged phosphate groups were not incidental features. The hydrogens were part of the hydrogen bonds that held together the three intertwined chains. Without the hydrogen atoms, the chains would immediately fly apart and the structure vanish. “Everything I knew about nucleic-acid chemistry ind ...
... the uncharged phosphate groups were not incidental features. The hydrogens were part of the hydrogen bonds that held together the three intertwined chains. Without the hydrogen atoms, the chains would immediately fly apart and the structure vanish. “Everything I knew about nucleic-acid chemistry ind ...
iitrtildna
... In the 1950 four scientists (James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins and Franklin) determined the true structure of DNA from data and X-ray pictures of the molecule. In 1953, Watson and Crick published this research. The true structure of the DNA molecule is a double helix, as shown at right. S ...
... In the 1950 four scientists (James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins and Franklin) determined the true structure of DNA from data and X-ray pictures of the molecule. In 1953, Watson and Crick published this research. The true structure of the DNA molecule is a double helix, as shown at right. S ...
2-BuildingBlocks
... these study questions by referencing the relevant sections of the textbook. The written explanations are the most important part of your answers and key to learning of concepts. 1. As part of an ambitious student research project you create a short synthetic peptide consisting of 4 amino acids. Howe ...
... these study questions by referencing the relevant sections of the textbook. The written explanations are the most important part of your answers and key to learning of concepts. 1. As part of an ambitious student research project you create a short synthetic peptide consisting of 4 amino acids. Howe ...
C - NCSU Bioinformatics Research Center
... to be taken at the ribosome • Start transcription (begin a protein) • Add one of twenty amino acids (extend a protein) • Stop transcription (end a protein) ...
... to be taken at the ribosome • Start transcription (begin a protein) • Add one of twenty amino acids (extend a protein) • Stop transcription (end a protein) ...
document
... • Although genes were known to exist on chromosomes, chromosomes are composed of both protein and DNA—scientists did not know which of these is responsible for inheritance. In 1928, Frederick Griffith discovered the phenomenon of transformation: dead bacteria could transfer genetic material to "tran ...
... • Although genes were known to exist on chromosomes, chromosomes are composed of both protein and DNA—scientists did not know which of these is responsible for inheritance. In 1928, Frederick Griffith discovered the phenomenon of transformation: dead bacteria could transfer genetic material to "tran ...
Open File
... Chromosomes are composed of genes, which is a segment of DNA that codes for a particular protein, which in turn codes for a trait. Hence you hear it commonly referred to as the gene for blue eyes. Meanwhile, DNA is the chemical that genes and chromosomes are made of. DNA is a nucleic acid found not ...
... Chromosomes are composed of genes, which is a segment of DNA that codes for a particular protein, which in turn codes for a trait. Hence you hear it commonly referred to as the gene for blue eyes. Meanwhile, DNA is the chemical that genes and chromosomes are made of. DNA is a nucleic acid found not ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.