Chapter 11 Vocabulary and Objectives
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
WS 12 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with ____, and C bonds with _____. This is due to ___________________ bonding. A and T form ______ hydrogen bonds, C and G form ______ hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and __________. ...
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with ____, and C bonds with _____. This is due to ___________________ bonding. A and T form ______ hydrogen bonds, C and G form ______ hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and __________. ...
DNA and RNA Review
... Define: transcription, translation, replication, and transformation (**BE SURE to specify and describe what happens in each process**) ...
... Define: transcription, translation, replication, and transformation (**BE SURE to specify and describe what happens in each process**) ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... ____, and G always pairs with ______ a. C, U b. U, T c. C, T d. T, C 4. During DNA replication, what pulls apart DNA? a. Protease b. Helicase c. Primase d. Ligase 5. The amino acid’s ____________ determines what protein is created: a. size b. order c. color d. ribosome e. ribosomal RNA ...
... ____, and G always pairs with ______ a. C, U b. U, T c. C, T d. T, C 4. During DNA replication, what pulls apart DNA? a. Protease b. Helicase c. Primase d. Ligase 5. The amino acid’s ____________ determines what protein is created: a. size b. order c. color d. ribosome e. ribosomal RNA ...
CentralDogmaNotes
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
... • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation ...
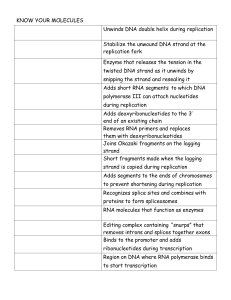
Know your molecules organizer
... Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ ...
... Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ ...
Nucleic Acids Powerpoint
... • Nucleic acids are large biomolecules (polymers) – essential for all known forms of life • Include DNA and RNA • Made from long strands of nucleotides (monomers) – A nucleotide contains a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base – The nitrogeneous bases are connected by the sugar ...
... • Nucleic acids are large biomolecules (polymers) – essential for all known forms of life • Include DNA and RNA • Made from long strands of nucleotides (monomers) – A nucleotide contains a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base – The nitrogeneous bases are connected by the sugar ...
The Story of DNA vs. RNA
... § Proteins help to determine the size, shape and many other traits of an organism. ...
... § Proteins help to determine the size, shape and many other traits of an organism. ...
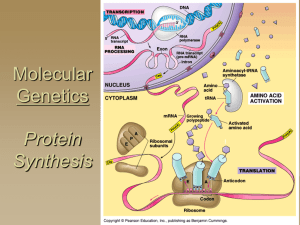
Molecular Genetics
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
... A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA ...
RNA
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
Presentation title: Introduction to RNA
... sequence in parallel to give millions of short “reads”, each between approximately 50‐200 bases in length. With this data comes a computational and statistical challenge because the biology must be inferred from millions of short sequences. Along with technical biases, there is ...
... sequence in parallel to give millions of short “reads”, each between approximately 50‐200 bases in length. With this data comes a computational and statistical challenge because the biology must be inferred from millions of short sequences. Along with technical biases, there is ...
NUCLEIC ACID
... • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains of DNA and proteins. ...
... • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains of DNA and proteins. ...
Worksheet 6 - Iowa State University
... 5. What roll does conformational changes play in transcription? Why are they important? ...
... 5. What roll does conformational changes play in transcription? Why are they important? ...
Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria.
... 8. What is a consensus sequence? 9. What is the function of the σ unit of RNA polymerase? 10. RNA polymerase does not have a proofreading activity to correct errors resulting in a higher error frequency in the transcript than for DNA polymerase. Why is the higher frequency of RNA polymerase acceptab ...
... 8. What is a consensus sequence? 9. What is the function of the σ unit of RNA polymerase? 10. RNA polymerase does not have a proofreading activity to correct errors resulting in a higher error frequency in the transcript than for DNA polymerase. Why is the higher frequency of RNA polymerase acceptab ...
Bio 1 Unit Objectives Protein Synthesis Readings
... Exploring Life: Chapter 11 (Concepts 11.4, 11.5, 11.6) Exploring Life: Chapter 11 Online Activities ...
... Exploring Life: Chapter 11 (Concepts 11.4, 11.5, 11.6) Exploring Life: Chapter 11 Online Activities ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
... 1. DNA is also known as the _________________________________. 2. A protein is made up of ____________________________. 3. A protein’s function is determined by its ___________ and ______________________________________. 4. Draw and label the 3 major parts of a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. ...
Study_Guide
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
Name
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The process of making proteins is called protein ...
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The process of making proteins is called protein ...
Nucleic acid tertiary structure

The tertiary structure of a nucleic acid is its precise three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates. RNA and DNA molecules are capable of diverse functions ranging from molecular recognition to catalysis. Such functions require a precise three-dimensional tertiary structure. While such structures are diverse and seemingly complex, they are composed of recurring, easily recognizable tertiary structure motifs that serve as molecular building blocks. Some of the most common motifs for RNA and DNA tertiary structure are described below, but this information is based on a limited number of solved structures. Many more tertiary structural motifs will be revealed as new RNA and DNA molecules are structurally characterized.