The DNA connection - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... Unlike DNA (two strands), RNA has only one strand. RNA contains different sugar molecules. RNA also has four nitrogen bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil) ...
... Unlike DNA (two strands), RNA has only one strand. RNA contains different sugar molecules. RNA also has four nitrogen bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil) ...
Ch 17 From Gene to Protei
... 1. Transcription cannot begin in eukaryotic cells until a. the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. b. several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. c. the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. e. DNA nucleases ...
... 1. Transcription cannot begin in eukaryotic cells until a. the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. b. several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. c. the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. e. DNA nucleases ...
DNA Test Review
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
Packet 9: Transcription and Translation Name: Hour: _____ Notes
... • DNA: The _______________ for _____ _______ _____________ • RNA: The _______________ system that takes the instructions _____ ______ and makes ______________ for the cell. • Gene: are ________ ______ instructions that control the production of ...
... • DNA: The _______________ for _____ _______ _____________ • RNA: The _______________ system that takes the instructions _____ ______ and makes ______________ for the cell. • Gene: are ________ ______ instructions that control the production of ...
How Proteins are Made
... a. mRNA – messenger RNA – a portable complement of DNA that travels from the nucleus to the ribosome b. rRNA – ribosomal RNA – part of the structure of a ribosome c. tRNA – transfer RNA – carries or transfers a specific amino acid and contains the anticodon ...
... a. mRNA – messenger RNA – a portable complement of DNA that travels from the nucleus to the ribosome b. rRNA – ribosomal RNA – part of the structure of a ribosome c. tRNA – transfer RNA – carries or transfers a specific amino acid and contains the anticodon ...
Study Guide Foldable .Answer Key
... a mutation that increases an organism’s chances for survival ...
... a mutation that increases an organism’s chances for survival ...
P-RNA (Phyto-Ribonucleic Acid) What is RNA? Why do we need it
... Nutritional Therapy”, Dr Milton Fried and HEM Pharmaceuticals shows clearly, those who supplement with RNA on a regular basis showed improvement in their memory function, increased energy levels, better tolerance of extreme temperature changes, enhance immunity, better vision and tighter, radiant sk ...
... Nutritional Therapy”, Dr Milton Fried and HEM Pharmaceuticals shows clearly, those who supplement with RNA on a regular basis showed improvement in their memory function, increased energy levels, better tolerance of extreme temperature changes, enhance immunity, better vision and tighter, radiant sk ...
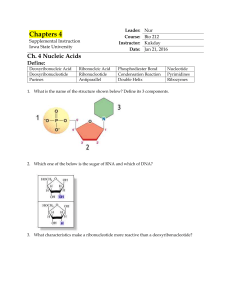
Ch. 4 Nucleic Acids Define
... We know that two strands of DNA form a double helix when they bond via hydrogen bonds. Regions in DNA rich in G and C nucleotides are harder to break apart. What might be the ...
... We know that two strands of DNA form a double helix when they bond via hydrogen bonds. Regions in DNA rich in G and C nucleotides are harder to break apart. What might be the ...
dsRNA synthesis RNAi (Howard Clarke)
... Selection and preparation of DNA template: Chose an exon-rich region of genomic DNA 300bp in length (>500 is better, and 3’ UTR sequence is fine). Alternatively, cDNA clones or first-strand cDNA generated by RT-PCR can be used as template (see protocol “Oligo d(T) primed cDNA synthesis”). cDNA templ ...
... Selection and preparation of DNA template: Chose an exon-rich region of genomic DNA 300bp in length (>500 is better, and 3’ UTR sequence is fine). Alternatively, cDNA clones or first-strand cDNA generated by RT-PCR can be used as template (see protocol “Oligo d(T) primed cDNA synthesis”). cDNA templ ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression ppt
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
Major Functions
... The mRNA and the DNA are base-pairing. One strand is involved in transcription. ...
... The mRNA and the DNA are base-pairing. One strand is involved in transcription. ...
Ch 25 Origin of Life on Earth Guided Rdg
... Origin of Life on Earth Guide Reading Biology, 8th Edition, 25.1 (507-510). If any of the questions is not explicitly defined in the reading, you are responsible for using your text or another reliable source to answer the questions. 1. Define the term macroevolution. ...
... Origin of Life on Earth Guide Reading Biology, 8th Edition, 25.1 (507-510). If any of the questions is not explicitly defined in the reading, you are responsible for using your text or another reliable source to answer the questions. 1. Define the term macroevolution. ...
Bacterial Nucleic Acids
... • Their information is used to make protein with the help of RNA through Transcription...Translation. • The DNA double helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the bases attached to the two strands. • One major difference between DNA and RNA is the sugar, with the 2deoxyribose in DNA being repl ...
... • Their information is used to make protein with the help of RNA through Transcription...Translation. • The DNA double helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the bases attached to the two strands. • One major difference between DNA and RNA is the sugar, with the 2deoxyribose in DNA being repl ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
... SO, how does this occur? • Transcription and translation are linguistic terms, so….. • nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and polypeptides (chain of amino acids linked by peptide bond) Have their own language! What is their language? • A, T, G, C in DNA and A, U, G, C in RNA ...
... SO, how does this occur? • Transcription and translation are linguistic terms, so….. • nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and polypeptides (chain of amino acids linked by peptide bond) Have their own language! What is their language? • A, T, G, C in DNA and A, U, G, C in RNA ...
replication (nucleus) transcription (nucleus) translation (cytoplasm
... contains the sugar ribose Has the bases A, C, G and T ...
... contains the sugar ribose Has the bases A, C, G and T ...
suggested essay-type questions for next exam
... pairs, thereby unwinding the supercoils. However, the linking number of the DNA is not changed! Explain the physical basis for the ability of ethidium bromide to “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the definition of the linking difference. In this definition, Lo refers to the linkin ...
... pairs, thereby unwinding the supercoils. However, the linking number of the DNA is not changed! Explain the physical basis for the ability of ethidium bromide to “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the definition of the linking difference. In this definition, Lo refers to the linkin ...
NGS library facility request form
... __________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________________________________ ...
powerpoint
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
... SEQUENCES OF MONOMERS- NUCLEOTIDES AND AMINO ACIDS, RESPECTIVELY. • TRANSCRIPTION IS THE NUCLEOTIDE-TONUCLEOTIDE TRANSFER OF INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA, WHILE TRANSLATION IS THE INFORMATIONAL TRANSFER FROM NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE IN RNA TO AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A POLYPEPTIDE. ...
Chapter 24
... and cytosine, while RNA substitutes uracil for thymine. You aren’t responsible for the structures of the individual bases, but you should remember which bases are associated with which nucleic acid. The base always attaches at the aldol carbon. You should know the difference between ribose and deox ...
... and cytosine, while RNA substitutes uracil for thymine. You aren’t responsible for the structures of the individual bases, but you should remember which bases are associated with which nucleic acid. The base always attaches at the aldol carbon. You should know the difference between ribose and deox ...
Nucleic acid tertiary structure

The tertiary structure of a nucleic acid is its precise three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates. RNA and DNA molecules are capable of diverse functions ranging from molecular recognition to catalysis. Such functions require a precise three-dimensional tertiary structure. While such structures are diverse and seemingly complex, they are composed of recurring, easily recognizable tertiary structure motifs that serve as molecular building blocks. Some of the most common motifs for RNA and DNA tertiary structure are described below, but this information is based on a limited number of solved structures. Many more tertiary structural motifs will be revealed as new RNA and DNA molecules are structurally characterized.