RNA & Protein Synthesis
... The double helix structure explains how DNA can be copied, but it does not explain how genes work. Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. Genetic messages can be decoded by copying part of the nucleotide sequence from DNA into RNA. RNA contains code ...
... The double helix structure explains how DNA can be copied, but it does not explain how genes work. Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. Genetic messages can be decoded by copying part of the nucleotide sequence from DNA into RNA. RNA contains code ...
Chapter 13
... These affect a particular gene only. A. Substitution – replace one base with another. - affects only one amino acid in the protein. - May not even cause a problem ...
... These affect a particular gene only. A. Substitution – replace one base with another. - affects only one amino acid in the protein. - May not even cause a problem ...
HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www
... HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www.embl-heidelberg.de/info/sage) Each type of RNA has a unique chemical composition that is a direct transcription of information stored in a particular gene. The basic units that make up DNA and RNAs are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small ...
... HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www.embl-heidelberg.de/info/sage) Each type of RNA has a unique chemical composition that is a direct transcription of information stored in a particular gene. The basic units that make up DNA and RNAs are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
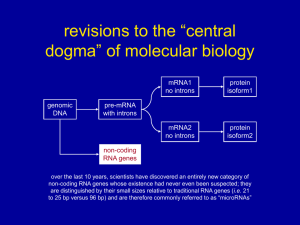
... RNA genes over the last 10 years, scientists have discovered an entirely new category of non-coding RNA genes whose existence had never even been suspected; they are distinguished by their small sizes relative to traditional RNA genes (i.e. 21 to 25 bp versus 96 bp) and are therefore commonly referr ...
... RNA genes over the last 10 years, scientists have discovered an entirely new category of non-coding RNA genes whose existence had never even been suspected; they are distinguished by their small sizes relative to traditional RNA genes (i.e. 21 to 25 bp versus 96 bp) and are therefore commonly referr ...
rnalabreport_1
... Ownership and contributors - Go to the Home or About page of the website and find out who sponsors and writes for the site. Look for contributors who have reliable credentials, such as "Harvey Jones, Professor, University of Wisconsin—Madison." Writing style and mechanics - Check the grammar, spelli ...
... Ownership and contributors - Go to the Home or About page of the website and find out who sponsors and writes for the site. Look for contributors who have reliable credentials, such as "Harvey Jones, Professor, University of Wisconsin—Madison." Writing style and mechanics - Check the grammar, spelli ...
Genetics Introduction:
... relationship= chromosome no. constant within species but different between species Proteins as genetic material o Proteins far more diverse than DNA so assumed it was proteins that must have been genetic material o Series of exp’s provided evidence that DNA was hereditary material No known exception ...
... relationship= chromosome no. constant within species but different between species Proteins as genetic material o Proteins far more diverse than DNA so assumed it was proteins that must have been genetic material o Series of exp’s provided evidence that DNA was hereditary material No known exception ...
The DNA Connection
... genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different pro ...
... genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different pro ...
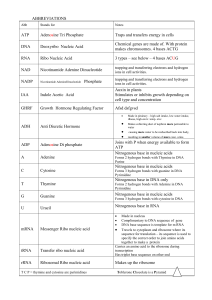
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
INHERITANCE
... Physically sequencing the amino acids that were carried to the building site by the tRNA and chemically connected by the rRNA The mRNA directs the sequence based on the order it obtains from the DNA molecule ...
... Physically sequencing the amino acids that were carried to the building site by the tRNA and chemically connected by the rRNA The mRNA directs the sequence based on the order it obtains from the DNA molecule ...
Slide 1
... Identify the main product on a western blot and other components (subunits) that can be co-purified ...
... Identify the main product on a western blot and other components (subunits) that can be co-purified ...
Last Name - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... Test Prep Sections: These questions were taken from New York and Texas State Tests. Can you compete with the brightest around the nation? ...
... Test Prep Sections: These questions were taken from New York and Texas State Tests. Can you compete with the brightest around the nation? ...
Chapter 22
... A short sequence (R) is repeated at each end of the viral RNA, so the 5’ and 3’ ends are R-U5 and U3R, respectively. Reverse transcriptase starts synthesis when a tRNA primer binds to a site 100 to 200 bases from the 5’ end. When the enzyme reaches the end, the 5’-terminal bases of RNA are degraded, ...
... A short sequence (R) is repeated at each end of the viral RNA, so the 5’ and 3’ ends are R-U5 and U3R, respectively. Reverse transcriptase starts synthesis when a tRNA primer binds to a site 100 to 200 bases from the 5’ end. When the enzyme reaches the end, the 5’-terminal bases of RNA are degraded, ...
Lecture3 (1/22/08) "Nucleic Acids, RNA, and Proteins"
... Sign up via web for Physics 597 (independent study) with me. My # is 25016. No extra effort on your part. Grade in 597 = grade in Physics 498Bio. ...
... Sign up via web for Physics 597 (independent study) with me. My # is 25016. No extra effort on your part. Grade in 597 = grade in Physics 498Bio. ...
Slides - nanoHUB
... Sign up via web for Physics 597 (independent study) with me. My # is 25016. No extra effort on your part. Grade in 597 = grade in Physics 498Bio. ...
... Sign up via web for Physics 597 (independent study) with me. My # is 25016. No extra effort on your part. Grade in 597 = grade in Physics 498Bio. ...
DNA - Ellis Benjamin
... DNA • Double helix • “Rungs” are base pairs joined by hydrogen bonds • Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) • Cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G) • Complementary strands • Strands oriented in opposite directions – 5’ to 3’ or 3’ to 5’ ...
... DNA • Double helix • “Rungs” are base pairs joined by hydrogen bonds • Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) • Cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G) • Complementary strands • Strands oriented in opposite directions – 5’ to 3’ or 3’ to 5’ ...
jeopardy honors DNA 12-1 thru 12-4 only
... If a cell was doubly fertilized (by two sperm), this would be the term to describe its chromosomes ...
... If a cell was doubly fertilized (by two sperm), this would be the term to describe its chromosomes ...
Directed Reading 13
... In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes the statement. ...
... In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes the statement. ...
Dicer-Like
... What is Dicer’s role in RNAi? • Activated by exogenous double-stranded (ds) RNA • miRNA (micro RNA) -small, non-coding regions of double-stranded (ds) RNA 21-22 nucleotides ...
... What is Dicer’s role in RNAi? • Activated by exogenous double-stranded (ds) RNA • miRNA (micro RNA) -small, non-coding regions of double-stranded (ds) RNA 21-22 nucleotides ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
... 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13–1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d. adenine 3. What is produced during transcription? a. RNA molecules c. RNA polymerase b. DNA molecules d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. comp ...
Structure,Function of RNA
... 3. Nitrogenous base hold together by covalent bonds 4. RNA molecule have two purine base (adenine, guanine) and two pyrimidine base (uracil, cytocine) 5. Ribose sugar bonded with one nitrogen base form Ribonucleoside, ...
... 3. Nitrogenous base hold together by covalent bonds 4. RNA molecule have two purine base (adenine, guanine) and two pyrimidine base (uracil, cytocine) 5. Ribose sugar bonded with one nitrogen base form Ribonucleoside, ...
RNA Tertiary Structure
... Type I: The O2' and N3 atoms of the A residue are inside the minor groove of the receptor helix. The inserted base for the Type I interaction must be an adenine. Type II: The O2' of the A residue is outside the near strand O2' of the helix and the N3 of the A residue is inside the minor groove. The ...
... Type I: The O2' and N3 atoms of the A residue are inside the minor groove of the receptor helix. The inserted base for the Type I interaction must be an adenine. Type II: The O2' of the A residue is outside the near strand O2' of the helix and the N3 of the A residue is inside the minor groove. The ...
Document
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all organisms. ...
... The storage of genetic information in DNA, the use of an RNA intermediate that is read in three letter words, and the mechanism of protein synthesis are essentially the same in all organisms. ...
Nucleic acid tertiary structure

The tertiary structure of a nucleic acid is its precise three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates. RNA and DNA molecules are capable of diverse functions ranging from molecular recognition to catalysis. Such functions require a precise three-dimensional tertiary structure. While such structures are diverse and seemingly complex, they are composed of recurring, easily recognizable tertiary structure motifs that serve as molecular building blocks. Some of the most common motifs for RNA and DNA tertiary structure are described below, but this information is based on a limited number of solved structures. Many more tertiary structural motifs will be revealed as new RNA and DNA molecules are structurally characterized.