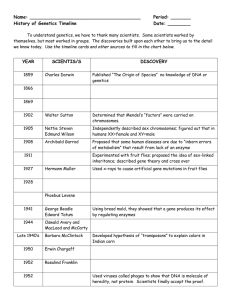
NOTES: 12.2 – 12.3 – DNA Structure
... -# of chromosomes varies widely from species to species DNA molecules are long…how does DNA fit in the nucleus? ● It forms ...
... -# of chromosomes varies widely from species to species DNA molecules are long…how does DNA fit in the nucleus? ● It forms ...
Molecular Genetics Outcome Checklist
... _____ I can describe the contributions that were made by James Watson and Francis Crick to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the contributions that Rosalind Franklin made to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the structure of DNA, including the three components of nucleotides, the ...
... _____ I can describe the contributions that were made by James Watson and Francis Crick to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the contributions that Rosalind Franklin made to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the structure of DNA, including the three components of nucleotides, the ...
DNA Sequencing
... Today, DNA sequencing is automated Automated system originally based on Dideoxy Chain Termination Method Invented by Frederick Sanger - received Nobel Prize in 1980 ...
... Today, DNA sequencing is automated Automated system originally based on Dideoxy Chain Termination Method Invented by Frederick Sanger - received Nobel Prize in 1980 ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 13. What organism did Beadle and Tatum use for their experiments? 14. What did Beadle and Tatum do to this organisms to produce genetic changes? 15. What changes did this process cause to the organisms being studied? 16. Genes direct the production of what type of biochemical? (skip transposon secti ...
... 13. What organism did Beadle and Tatum use for their experiments? 14. What did Beadle and Tatum do to this organisms to produce genetic changes? 15. What changes did this process cause to the organisms being studied? 16. Genes direct the production of what type of biochemical? (skip transposon secti ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
... dna replication is necessary for the transmission of genetic information and thus such a process must achieve accurate copying of the genome. Since the last century the replicon model has been proposed in order to explain the general mechanism of genome duplication in bacteria. Later work in yeast l ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
ib biology………………
... material into the host cell, host cell reproduces new virus particles and host cell bursts releasing new virus particles. Nucleotide - monomer of DNA and RNA. Composed of a five carbon sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base. Helix - twisted, spiral shaped molecule. Histones — proteins that DNA wraps ...
... material into the host cell, host cell reproduces new virus particles and host cell bursts releasing new virus particles. Nucleotide - monomer of DNA and RNA. Composed of a five carbon sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base. Helix - twisted, spiral shaped molecule. Histones — proteins that DNA wraps ...
Biology Summary Sheet
... Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell. Genes are located on chromosomes and are made of DNA. DNA is a molecule that consists of two strands connected together by bases. DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ...
... Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell. Genes are located on chromosomes and are made of DNA. DNA is a molecule that consists of two strands connected together by bases. DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... 5. How many bonds are there between A/T? __________ G/C? _________ 6. What are the chemicals that make up the backbone? ______________ & ___________________. 7. What is the enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA so it can replicate? _____________________ 8. What is the enzyme responsible for makin ...
... 5. How many bonds are there between A/T? __________ G/C? _________ 6. What are the chemicals that make up the backbone? ______________ & ___________________. 7. What is the enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA so it can replicate? _____________________ 8. What is the enzyme responsible for makin ...
Fall 2005 Due: 9/9 GENETICS Homework 1 1. (1 point) The
... following table. Give the order of compound A, B, C, and D in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
... following table. Give the order of compound A, B, C, and D in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
DNA Connection
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
PE #8 DNA Structure, Biotechnology, and its use in Conservation
... I can summarize the structure of DNA and an individual nucleotide. I can summarize the pairing rules for nitrogen bases within the structure of DNA. I can recognize that sections of DNA that code for proteins are genes. I can identify that the sections of DNA used for DNA profiling are not made up o ...
... I can summarize the structure of DNA and an individual nucleotide. I can summarize the pairing rules for nitrogen bases within the structure of DNA. I can recognize that sections of DNA that code for proteins are genes. I can identify that the sections of DNA used for DNA profiling are not made up o ...
IntrotoBiotechRestrictionEnzymes2011
... • They originate from bacteria and are used in their native environment to destroy (by chopping up) any DNA that is not property of the bacteria. • Restriction enzymes will cut DNA at a specific sequence (called a recognition site). • One example, EcoRI, cuts DNA at the following sequence. ...
... • They originate from bacteria and are used in their native environment to destroy (by chopping up) any DNA that is not property of the bacteria. • Restriction enzymes will cut DNA at a specific sequence (called a recognition site). • One example, EcoRI, cuts DNA at the following sequence. ...
13-3 Cell Transformation
... What is Transformation? Transformation = cell takes in DNA from outside the cell The external DNA becomes a component of the cell’s DNA ...
... What is Transformation? Transformation = cell takes in DNA from outside the cell The external DNA becomes a component of the cell’s DNA ...
Jeopardy - Grayslake Central High School
... a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
... a few different types of somatic cells. ESCs are totipotent. They can divide to produce any cell in the body (or a whole new embryo). ...
Name - EdWeb
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
Bill Nye: Genes - stephaniemcoggins
... 1. Where do your genes come from? 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. Wha ...
... 1. Where do your genes come from? 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. Wha ...
DNA versus RNA Notes File
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
2nd Semester Review The second semester test covers Meiosis
... Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
... Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering, Chapter Summary Date
... 1. the risk of inbreeding can cause this. 2. scientists manipulate the DNA molecule in hopes to increase this. 3. a tool used to ensure that the characteristics that make each breed unique will preserved by crossing individuals with similar characteristics. 4. these bacteria have been engineered to ...
... 1. the risk of inbreeding can cause this. 2. scientists manipulate the DNA molecule in hopes to increase this. 3. a tool used to ensure that the characteristics that make each breed unique will preserved by crossing individuals with similar characteristics. 4. these bacteria have been engineered to ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.