Nucleic acid review sheet
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
DNA -- The Double Helix
... particular protein which in turn codes for a trait. For example, it may be the gene for baldness or the gene for blue eyes. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick established the structure of DNA. The shape of DNA is a double helix, which is like a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made o ...
... particular protein which in turn codes for a trait. For example, it may be the gene for baldness or the gene for blue eyes. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick established the structure of DNA. The shape of DNA is a double helix, which is like a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made o ...
DNA Replication Graphic Organizer
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
jeopardy honors DNA 12-1 thru 12-4 only
... strand; and therefore, the new DNA consists of only one newly synthesized strand per double helix. ...
... strand; and therefore, the new DNA consists of only one newly synthesized strand per double helix. ...
No Slide Title
... What is the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes for the number of orgins for DNA replication? ...
... What is the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes for the number of orgins for DNA replication? ...
The Story of DNA vs. RNA
... did we find out that DNA was the molecule responsible for inheritance? ...
... did we find out that DNA was the molecule responsible for inheritance? ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and ...
... Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and ...
Go to - Net Start Class
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
MolecularBiology1APLab6
... • Enzymes that cut DNA at very specific base sequences (often palindromes) • Make blunt or sticky ends • Evolved to combat invasive DNA from viruses • Does not cut bacterium’s DNA because it’s missing correct DNA sequence • Different bacterial strains have different RE ...
... • Enzymes that cut DNA at very specific base sequences (often palindromes) • Make blunt or sticky ends • Evolved to combat invasive DNA from viruses • Does not cut bacterium’s DNA because it’s missing correct DNA sequence • Different bacterial strains have different RE ...
Study Guide for LS
... - Rosalind Franklin was able to create images of DNA molecules and discover that DNA was spiral shaped. ...
... - Rosalind Franklin was able to create images of DNA molecules and discover that DNA was spiral shaped. ...
notes
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
a10c Biotechnology
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
DNA Worksheet
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
Name:
... 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? Draw a picture if it would help. (This is discussed in the paragraph prior to the ...
... 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? Draw a picture if it would help. (This is discussed in the paragraph prior to the ...
Manipulating DNA - Lemon Bay High School
... How are changes made to DNA? • Scientists use their knowledge of the structure of DNA and its chemical properties to study and change DNA molecules. • Making changes in the DNA code of a living organism ...
... How are changes made to DNA? • Scientists use their knowledge of the structure of DNA and its chemical properties to study and change DNA molecules. • Making changes in the DNA code of a living organism ...
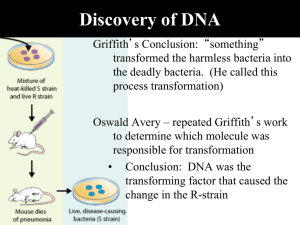
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
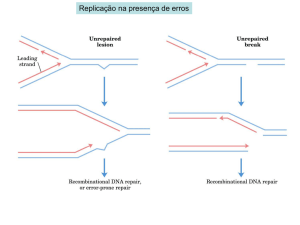
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Section 6-3
... to the DNA of another organism • Can be done in bacteria to produce medication (insulin) • Some tomatoes have been engineered to survive cold, pests, etc – Gene therapy • splice “healthy” DNA into the DNA of a sick individual ...
... to the DNA of another organism • Can be done in bacteria to produce medication (insulin) • Some tomatoes have been engineered to survive cold, pests, etc – Gene therapy • splice “healthy” DNA into the DNA of a sick individual ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... * Develop and use models at different scales to explain the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to ...
... * Develop and use models at different scales to explain the relationship between DNA, genes, and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.