which together form the gene "stories" NOTE
... DNA can make a copy of it itself BECAUSE of the way the bases pair up ...
... DNA can make a copy of it itself BECAUSE of the way the bases pair up ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... 2. What type of macromolecule is DNA? 3. DNA is composed of what monomer? 4. What are the three units to the above monomer? 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units m ...
... 2. What type of macromolecule is DNA? 3. DNA is composed of what monomer? 4. What are the three units to the above monomer? 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units m ...
Test Study Guide
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
What`s the Big Deal About DNA?
... 1. Describe what DNA looks like, or draw a picture in the space provided. What is a double helix? What do the letters A, T, C, and G stand for? ...
... 1. Describe what DNA looks like, or draw a picture in the space provided. What is a double helix? What do the letters A, T, C, and G stand for? ...
Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 5. Define NUCLEOTIDE…be sure to know the 3 parts of the DNA nucleotide! 6. How would the amount of purines & pyrimidines found in the DNA molecule compare? *Remember that purines are: Adenine & Guaine; Pyrimidines are: Thymine & Cytosine; 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. ...
... 5. Define NUCLEOTIDE…be sure to know the 3 parts of the DNA nucleotide! 6. How would the amount of purines & pyrimidines found in the DNA molecule compare? *Remember that purines are: Adenine & Guaine; Pyrimidines are: Thymine & Cytosine; 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. ...
7.1 - DNA Structure
... proteins and held together by another histone protein. The DNA double helix has major and minor groves on the outer diameter, exposing chemical groups that can form hydrogen bonds. These groups are bonded to positively-charged proteins called histones, forming two loops around them. DNA is wound aro ...
... proteins and held together by another histone protein. The DNA double helix has major and minor groves on the outer diameter, exposing chemical groups that can form hydrogen bonds. These groups are bonded to positively-charged proteins called histones, forming two loops around them. DNA is wound aro ...
DNA info
... chromosomes which are made up of DNA, histones, and other support proteins. Therefore genes are found on DNA. All of the hereditary material could be called ‘instructions for making a living thing’! A gene is a specific segment of DNA that has a specific location on a chromosome. Humans have 23 pair ...
... chromosomes which are made up of DNA, histones, and other support proteins. Therefore genes are found on DNA. All of the hereditary material could be called ‘instructions for making a living thing’! A gene is a specific segment of DNA that has a specific location on a chromosome. Humans have 23 pair ...
ap: chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 2. From initial logic, which component would be the most likely candidate for the genetic material and why? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 3. What did Griffith, Avery, and others ac ...
... 2. From initial logic, which component would be the most likely candidate for the genetic material and why? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 3. What did Griffith, Avery, and others ac ...
Genetics
... There are 2 kinds of nitrogenous bases: purines & pyrimidines In nucleic acids, the purines are ADENINE & GUANINE, the pyrimidines are CYTOSINE, THYMINE, & URACIL ...
... There are 2 kinds of nitrogenous bases: purines & pyrimidines In nucleic acids, the purines are ADENINE & GUANINE, the pyrimidines are CYTOSINE, THYMINE, & URACIL ...
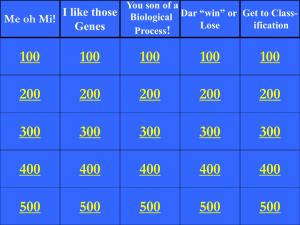
Me oh Mi!
... You son of a I like those Biological Dar “win” or Get to ClassMe oh Mi! Lose ification Genes Process! ...
... You son of a I like those Biological Dar “win” or Get to ClassMe oh Mi! Lose ification Genes Process! ...
SW describe how techniques such as DNA
... differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
... differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
DNA Structure Worksheet
... 5. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. 6. The two bases that are purines are _____________________ and _________________ ...
... 5. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. 6. The two bases that are purines are _____________________ and _________________ ...
Fast Facts about Human Genetics • DNA stands for Deoxy
... On February 28, 1953, Francis Crick and James Watson figured out the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). That structure, a 'double helix', can "unzip" (separate into two long strands) to make copies of itself. This discovery confirmed suspicions that DNA carried an organism's hereditary inform ...
... On February 28, 1953, Francis Crick and James Watson figured out the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). That structure, a 'double helix', can "unzip" (separate into two long strands) to make copies of itself. This discovery confirmed suspicions that DNA carried an organism's hereditary inform ...
DNA and the genetic code
... How do bases pair together? Base pairs hold the two strands of the DNA helix together. The rules for base pairing are… ‘A’ always pairs with ‘T’ ...
... How do bases pair together? Base pairs hold the two strands of the DNA helix together. The rules for base pairing are… ‘A’ always pairs with ‘T’ ...
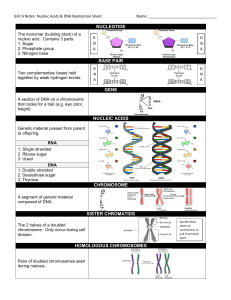
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... nucleic acid. Contains 3 parts: 1. Sugar 2. Phosphate group 3. Nitrogen base ...
... nucleic acid. Contains 3 parts: 1. Sugar 2. Phosphate group 3. Nitrogen base ...
Journey Into dna
... There is a lot of DNA within the nucleus-about _________feet if you could unravel it and stretch it out. Chromatin scaffold: Chromatin refers to ___________________ that help organize the long DNA molecule. Nucleosome: Double helix: Which two scientists used Rosalind Franklin’s photo 51 to piece tog ...
... There is a lot of DNA within the nucleus-about _________feet if you could unravel it and stretch it out. Chromatin scaffold: Chromatin refers to ___________________ that help organize the long DNA molecule. Nucleosome: Double helix: Which two scientists used Rosalind Franklin’s photo 51 to piece tog ...
Researchers ACT on DNA Storage
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... ____, and G always pairs with ______ a. C, U b. U, T c. C, T d. T, C 4. During DNA replication, what pulls apart DNA? a. Protease b. Helicase c. Primase d. Ligase 5. The amino acid’s ____________ determines what protein is created: a. size b. order c. color d. ribosome e. ribosomal RNA ...
... ____, and G always pairs with ______ a. C, U b. U, T c. C, T d. T, C 4. During DNA replication, what pulls apart DNA? a. Protease b. Helicase c. Primase d. Ligase 5. The amino acid’s ____________ determines what protein is created: a. size b. order c. color d. ribosome e. ribosomal RNA ...
ws: DNA Alphabet Activity
... “A Coded Alphabet.” Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________ ...
... “A Coded Alphabet.” Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________ ...
Virtual DNA Lab
... 12. a. How long would DNA be if stretched out? a. _______________________________ ...
... 12. a. How long would DNA be if stretched out? a. _______________________________ ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.