An Introduction to Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry What are
... The carboxylic acid functional group has a hydrogen atom bonded to this oxygen atom. It is generally acidic, for reasons we discussed in Chapter One. The other bond need not be specified; it may be an alkyl group, a hydrogen atom, or another –OH. ...
... The carboxylic acid functional group has a hydrogen atom bonded to this oxygen atom. It is generally acidic, for reasons we discussed in Chapter One. The other bond need not be specified; it may be an alkyl group, a hydrogen atom, or another –OH. ...
Document
... Organic reactions can convert simple organic molecules into large, complex ones. TAXOL is an anti-cancer drug that chemists can synthesize. ...
... Organic reactions can convert simple organic molecules into large, complex ones. TAXOL is an anti-cancer drug that chemists can synthesize. ...
The Gibbs Function of a Chemical Reaction*
... in most stoichiometric calculations this value is used. Similarly H+ does not denote a proton, although often termed this way when considering acid dissociation, but a hypothetical average particle (so-called hydron) in an isotopic mixture of protons, 1H+, and deuterons, 2H+. As a result, we have a ...
... in most stoichiometric calculations this value is used. Similarly H+ does not denote a proton, although often termed this way when considering acid dissociation, but a hypothetical average particle (so-called hydron) in an isotopic mixture of protons, 1H+, and deuterons, 2H+. As a result, we have a ...
Development of Multi-Component Reactions using Catalytically Generated Allyl Metal Reagents
... played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and unwanted side-reactions. Furthermore, the timematching of the distinct reactions are ...
... played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and unwanted side-reactions. Furthermore, the timematching of the distinct reactions are ...
A matter of Equilibrium
... 2 pump in extra H2 …. …. then the reaction will be driven to the __________ 3 remove some of the ammonia…. …. then the reaction will be driven to the __________ 4 Increase the volume of the container…. …. then the reaction will be driven to the __________ ...
... 2 pump in extra H2 …. …. then the reaction will be driven to the __________ 3 remove some of the ammonia…. …. then the reaction will be driven to the __________ 4 Increase the volume of the container…. …. then the reaction will be driven to the __________ ...
9647 H2 Chemistry
... describe, in simple terms, the lattice structure of a crystalline solid which is: (i) ionic, as in sodium chloride, magnesium oxide (ii) simple molecular, as in iodine (iii) giant molecular, as in graphite; diamond (iv) hydrogen-bonded, as in ice (v) metallic, as in copper [the concept of the ‘unit ...
... describe, in simple terms, the lattice structure of a crystalline solid which is: (i) ionic, as in sodium chloride, magnesium oxide (ii) simple molecular, as in iodine (iii) giant molecular, as in graphite; diamond (iv) hydrogen-bonded, as in ice (v) metallic, as in copper [the concept of the ‘unit ...
Lecture8
... N-oxides are strongly nucleophilic reagents that can be used to abstract CO ligands. The ligand substitution occurs exclusively cis to the phosphine. N-oxides (R = Me or Et) is commonly used instead of heat or UV-irradiation to remove CO ligands in order to speed up dissociative substitution reactio ...
... N-oxides are strongly nucleophilic reagents that can be used to abstract CO ligands. The ligand substitution occurs exclusively cis to the phosphine. N-oxides (R = Me or Et) is commonly used instead of heat or UV-irradiation to remove CO ligands in order to speed up dissociative substitution reactio ...
reactions of alcohols with alkenes over an aluminum
... organic reactions catalyzed by clay minerals (see, e.g., Fripiat and Cruz-Cumplido, 1974; Theng, 1974; Thomas et al., 1977; Bittles et al., 1964a, 1964b, 1964c). Recently, renewed interest has been shown in the use of natural and synthetic smectitic clays as highly selective acid catalysts (e.g., Ad ...
... organic reactions catalyzed by clay minerals (see, e.g., Fripiat and Cruz-Cumplido, 1974; Theng, 1974; Thomas et al., 1977; Bittles et al., 1964a, 1964b, 1964c). Recently, renewed interest has been shown in the use of natural and synthetic smectitic clays as highly selective acid catalysts (e.g., Ad ...
NAME Chem 204 Spring, 1990 Final Exam FINAL EXAM: Chaps. 1
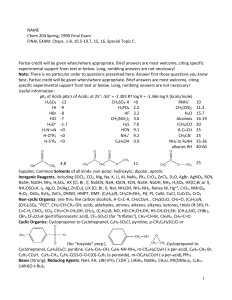
... Inorganic Reagents, including SOCl2, CO2, Mg, Na, K, Li, Al, NaN3, PX3, CrO3, ZnCl2, D2O, AgBr, AgNO3, RCN, NaSH, NaOH, NH3, H2SO4, HX (Cl, Br, I), NaSCN, NaH, KSCN, KCN, NaSH, NaOH, NH3, H2SO4, HX(Cl,Br,or I), NH2OSO3H, I2, Ag2O, Zn(Ag), Zn(Cu), LiX (Cl, Br, I), NaI, NH2OH, NH2-NH2, Raney Ni, Hg+2, ...
... Inorganic Reagents, including SOCl2, CO2, Mg, Na, K, Li, Al, NaN3, PX3, CrO3, ZnCl2, D2O, AgBr, AgNO3, RCN, NaSH, NaOH, NH3, H2SO4, HX (Cl, Br, I), NaSCN, NaH, KSCN, KCN, NaSH, NaOH, NH3, H2SO4, HX(Cl,Br,or I), NH2OSO3H, I2, Ag2O, Zn(Ag), Zn(Cu), LiX (Cl, Br, I), NaI, NH2OH, NH2-NH2, Raney Ni, Hg+2, ...
9851a doc..9851a chapter .. Page97
... Unlike the TPAP/NMO system the TPAP/O2/CuCl/2-aminopyridine system is almost entirely selective towards benzylic alcohols. As with the NMO system, the alcohols in entries 2 and 3 are smoothly oxidized to the aldehyde in 24 h with no other products being observed (Table 4). The oxidation of benzyl al ...
... Unlike the TPAP/NMO system the TPAP/O2/CuCl/2-aminopyridine system is almost entirely selective towards benzylic alcohols. As with the NMO system, the alcohols in entries 2 and 3 are smoothly oxidized to the aldehyde in 24 h with no other products being observed (Table 4). The oxidation of benzyl al ...
1 Bite Angle Effects of Diphosphines in Carbonylation Reactions
... Scheme 1.2. The catalytically active species is a trigonal bipyramidal hydrido rhodium complex, which usually contains two phosphorus donor ligands. In early mechanistic studies [18], it was already demonstrated that this catalyst exists with two isomeric structures, depending on the coordination of ...
... Scheme 1.2. The catalytically active species is a trigonal bipyramidal hydrido rhodium complex, which usually contains two phosphorus donor ligands. In early mechanistic studies [18], it was already demonstrated that this catalyst exists with two isomeric structures, depending on the coordination of ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... 37. Give plausible explanation for each of the following: (i) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,2,6Trimethylcyclohexanone does not. (ii) There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones. (iii) During the preparation of est ...
... 37. Give plausible explanation for each of the following: (i) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,2,6Trimethylcyclohexanone does not. (ii) There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones. (iii) During the preparation of est ...
Air-Stable Trialkylphosphonium Salts
... focusing on the phosphonium salts of P(n-Bu)3 and P(t-Bu)3. We show that [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4 and [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 are stable to oxygen and to moisture and that they can be stored in air for long periods of time (>4 months) without any detectable deterioration. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these phospho ...
... focusing on the phosphonium salts of P(n-Bu)3 and P(t-Bu)3. We show that [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4 and [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 are stable to oxygen and to moisture and that they can be stored in air for long periods of time (>4 months) without any detectable deterioration. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these phospho ...
Chapter 9. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
... Hydrogen bonding with water also explains the complete water-solubility of the first four liquid monocarboxylic acids (including butyric acid) and the good solubility of the first four solid dicarboxylic acids (including glutaric acid). Acid strength. Most monocarboxylic acids of an aliphatic or ar ...
... Hydrogen bonding with water also explains the complete water-solubility of the first four liquid monocarboxylic acids (including butyric acid) and the good solubility of the first four solid dicarboxylic acids (including glutaric acid). Acid strength. Most monocarboxylic acids of an aliphatic or ar ...
1 This is the pre-review version of the paper published in Journal of
... unlike the relaxed molecules, the strained conformations of the analyzed vinylogues are not minima in their potential energy landscapes, and therefore inclusion of vibrational effects would add a distracting factor to our study. For the relaxed systems, inclusion of the vibrational effects introduce ...
... unlike the relaxed molecules, the strained conformations of the analyzed vinylogues are not minima in their potential energy landscapes, and therefore inclusion of vibrational effects would add a distracting factor to our study. For the relaxed systems, inclusion of the vibrational effects introduce ...
CHEMISTRY INVESTIGATION FACTORS EFFECTING THE
... Graph 4 shows that the boiling points of the 1-alcohols are significantly higher than the corresponding 2-alcohols and 3-alcohols. Where we have the CRC Handbook experimental data available for all three series (up until the dodecanol C12H26O isomers) the 2- and 3- alcohols have similar boiling temp ...
... Graph 4 shows that the boiling points of the 1-alcohols are significantly higher than the corresponding 2-alcohols and 3-alcohols. Where we have the CRC Handbook experimental data available for all three series (up until the dodecanol C12H26O isomers) the 2- and 3- alcohols have similar boiling temp ...
Chemical Equations
... 5. Balance the electrons lost and gained by multiplying one or both half-reactions through by an integer (so the electrons cancel when the half-reactions are added together). 6. Add the half-reactions together and combine like terms, if necessary. By default, this gives the balanced reaction in acid ...
... 5. Balance the electrons lost and gained by multiplying one or both half-reactions through by an integer (so the electrons cancel when the half-reactions are added together). 6. Add the half-reactions together and combine like terms, if necessary. By default, this gives the balanced reaction in acid ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.