Study Guide and Solutions Manual
... chlorine. When bonded to carbon, hydrogen and lithium bear a partial positive charge, and carbon bears a partial negative charge. Conversely, when chlorine is bonded to carbon, it bears a partial negative charge, and carbon becomes partially positive. In this group of compounds, lithium is the least ...
... chlorine. When bonded to carbon, hydrogen and lithium bear a partial positive charge, and carbon bears a partial negative charge. Conversely, when chlorine is bonded to carbon, it bears a partial negative charge, and carbon becomes partially positive. In this group of compounds, lithium is the least ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4th ed Solution Manual
... chlorine. When bonded to carbon, hydrogen and lithium bear a partial positive charge, and carbon bears a partial negative charge. Conversely, when chlorine is bonded to carbon, it bears a partial negative charge, and carbon becomes partially positive. In this group of compounds, lithium is the least ...
... chlorine. When bonded to carbon, hydrogen and lithium bear a partial positive charge, and carbon bears a partial negative charge. Conversely, when chlorine is bonded to carbon, it bears a partial negative charge, and carbon becomes partially positive. In this group of compounds, lithium is the least ...
Organic Chemistry - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... An atom consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons arranged in orbitals. The electrons in the outer shell, or the valence electrons, are involved in bonding. Ionic bonds are formed by electron transfer from an electropositive atom to an electronegative atom. Atoms with similar electronegativities ...
... An atom consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons arranged in orbitals. The electrons in the outer shell, or the valence electrons, are involved in bonding. Ionic bonds are formed by electron transfer from an electropositive atom to an electronegative atom. Atoms with similar electronegativities ...
organic chemistry - carey - problems solutions
... chlorine. When bonded to carbon, hydrogen and lithium bear a partial positive charge, and carbon bears a partial negative charge. Conversely, when chlorine is bonded to carbon, it bears a partial negative charge, and carbon becomes partially positive. In this group of compounds, lithium is the least ...
... chlorine. When bonded to carbon, hydrogen and lithium bear a partial positive charge, and carbon bears a partial negative charge. Conversely, when chlorine is bonded to carbon, it bears a partial negative charge, and carbon becomes partially positive. In this group of compounds, lithium is the least ...
Haloalkanes-haloarenes
... 11. Free radical halogenation of alkanes is not preferred for the preparation of haloalkanes. A. This method gives a complex mixture of isomeric mono and polyhaloalkanes which is difficult to separate. Consequently the yield of any one compound is low. 12. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cy ...
... 11. Free radical halogenation of alkanes is not preferred for the preparation of haloalkanes. A. This method gives a complex mixture of isomeric mono and polyhaloalkanes which is difficult to separate. Consequently the yield of any one compound is low. 12. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cy ...
CHAPTER 12 | The Chemistry of Solids
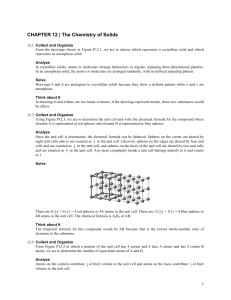
... Be careful to not assume that the edge length of every unit cell is l = 2r as in a simple cubic. 12.47. Collect and Organize We are to determine the type of unit cell for a form of copper using the density of the crystal (8.95 g/cm3) and the radius of the Cu atom (127.8 pm). Analyze For each type of ...
... Be careful to not assume that the edge length of every unit cell is l = 2r as in a simple cubic. 12.47. Collect and Organize We are to determine the type of unit cell for a form of copper using the density of the crystal (8.95 g/cm3) and the radius of the Cu atom (127.8 pm). Analyze For each type of ...
presentation source
... Elimination reactions are the opposite of addition; they occur when a more saturated reactant becomes a less saturated product: X Y ...
... Elimination reactions are the opposite of addition; they occur when a more saturated reactant becomes a less saturated product: X Y ...
Recent developments in the synthesis of functional poly(olefin)s
... The signi®cance of metallocene catalysts lies in their high polymerization activity as well as in the breadth of the type and level of comonomer that can be incorporated. Proper tuning of the ligands around the metal enables the synthesis of isotactic, hemiisotactic, elastomeric, high molecular weig ...
... The signi®cance of metallocene catalysts lies in their high polymerization activity as well as in the breadth of the type and level of comonomer that can be incorporated. Proper tuning of the ligands around the metal enables the synthesis of isotactic, hemiisotactic, elastomeric, high molecular weig ...
Microporous polymer beads for chemical
... reach the active site of AChE and inhibit the enzyme, it was hoped that effective polymeric decontaminants could be prepared by mimicking the structural and functional characteristics of AChE. In the present study, a suspension polymerization method suitable for polymerization of water-soluble monom ...
... reach the active site of AChE and inhibit the enzyme, it was hoped that effective polymeric decontaminants could be prepared by mimicking the structural and functional characteristics of AChE. In the present study, a suspension polymerization method suitable for polymerization of water-soluble monom ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Locate the carbonyl group and name the parent carboxylic acid. Replace the “oic acid” with the ending –amide. A - Primary Amide – if there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen. This name needs no prefix. B – Secondary Amide – if there is one alkyl group attached to the nitrogen. Name and lo ...
... Locate the carbonyl group and name the parent carboxylic acid. Replace the “oic acid” with the ending –amide. A - Primary Amide – if there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen. This name needs no prefix. B – Secondary Amide – if there is one alkyl group attached to the nitrogen. Name and lo ...
What is Organic Chemistry?
... if one electron is in the sigma and one in the sigma*, the molecule is of higher energy than the two separate atoms because the s* is slightly >∆E higher than the s orbitals while the s is ∆E lower Bonding orbital...high electron density between nuclei Antibonding orbital..node between nuclei (zero ...
... if one electron is in the sigma and one in the sigma*, the molecule is of higher energy than the two separate atoms because the s* is slightly >∆E higher than the s orbitals while the s is ∆E lower Bonding orbital...high electron density between nuclei Antibonding orbital..node between nuclei (zero ...
direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide from oxygen and hydrogen
... Figure 2 Chemical principle of the AO process........................................................................... 10 Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the AO process .......................................................................... 11 Figure 4 Flow sheet of a typical AO process for the p ...
... Figure 2 Chemical principle of the AO process........................................................................... 10 Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the AO process .......................................................................... 11 Figure 4 Flow sheet of a typical AO process for the p ...
PowerPoint ******
... Equatorial substituents are unlikely to migrate. (4) Steric factors may also significantly affect the open-chain cations. Non-migrating substituents are forced into “eclipsed position in the TS for rearrangement. ...
... Equatorial substituents are unlikely to migrate. (4) Steric factors may also significantly affect the open-chain cations. Non-migrating substituents are forced into “eclipsed position in the TS for rearrangement. ...
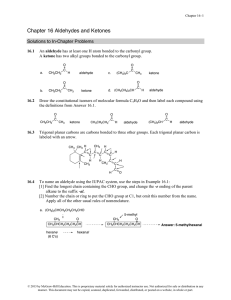
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones
... An aldehyde cannot have the molecular formula C5H12O. C5H12 has too many H’s. Since an aldehyde has a double bond, the number of C’s and H’s resembles an alkene, not an alkane. An aldehyde with 5 C’s would have the molecular formula C5H10O. ...
... An aldehyde cannot have the molecular formula C5H12O. C5H12 has too many H’s. Since an aldehyde has a double bond, the number of C’s and H’s resembles an alkene, not an alkane. An aldehyde with 5 C’s would have the molecular formula C5H10O. ...
Full-Text PDF
... bearing the efforts in characterizing the decomposition reactions [15]. However, olefin metathesis has successfully achieved the goal of organic synthesis that consists of reactions that drive to the formation of carbon-carbon bonds [16–18], and provides a route to unsaturated molecules. Basically, ...
... bearing the efforts in characterizing the decomposition reactions [15]. However, olefin metathesis has successfully achieved the goal of organic synthesis that consists of reactions that drive to the formation of carbon-carbon bonds [16–18], and provides a route to unsaturated molecules. Basically, ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.