Asymmetric Organocatalysis
... One of these approaches consists in activating the acceptors – mostly α,β-unsaturated aldehydes (R4 = H) and ketones (R4 = alkyl) – by reversible conversion to a chiral iminium ion. As shown in Scheme 4.2a, reversible condensation of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with a chiral secondary ami ...
... One of these approaches consists in activating the acceptors – mostly α,β-unsaturated aldehydes (R4 = H) and ketones (R4 = alkyl) – by reversible conversion to a chiral iminium ion. As shown in Scheme 4.2a, reversible condensation of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with a chiral secondary ami ...
today`s PowerPoint
... • Both aldehydes and ketones will test positively. No other compounds (e.g. Carboxylic acids or esters) will • The precipitate is called 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone ...
... • Both aldehydes and ketones will test positively. No other compounds (e.g. Carboxylic acids or esters) will • The precipitate is called 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone ...
Organic Tutorial 1st Year MT03
... Peter Sykes,“A Guidebook to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, and Eames & Peach “Stereochemistry at a Glance”. Notes and Questions a) Summary on not more than 6 sides. This should outline the possible mechanisms and the evidence on which they are based, in particular the evidence for inversion during ...
... Peter Sykes,“A Guidebook to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, and Eames & Peach “Stereochemistry at a Glance”. Notes and Questions a) Summary on not more than 6 sides. This should outline the possible mechanisms and the evidence on which they are based, in particular the evidence for inversion during ...
10.5 Carbonyl Compounds (a) describe: (i) the
... with one; remember to include the number e.g. butan-2-one. ...
... with one; remember to include the number e.g. butan-2-one. ...
Relative Reactivity of Aldehydes and Ketones: Generally
... electron density and forms a hydrate easily, welcoming in a second oxygen atom with electron density. But this is an exception, as is the hydration of trichloroacetaldehyde: O Cl3C ...
... electron density and forms a hydrate easily, welcoming in a second oxygen atom with electron density. But this is an exception, as is the hydration of trichloroacetaldehyde: O Cl3C ...
Slides for Chapter 1-4 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... Nucleophiles will replace the halide in C-X bonds of many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
... Nucleophiles will replace the halide in C-X bonds of many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
DESIGN OF CHIRAL IMINO- AND AMINOPYRIDINE LIGANDS
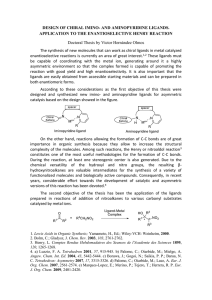
... The synthesis of new molecules that can work as chiral ligands in metal catalyzed enantioselective reactions is currently an area of great interest.1,2 These ligands must be capable of coordinating with the metal ion, generating around it a highly asymmetric environment so that the complex formed is ...
... The synthesis of new molecules that can work as chiral ligands in metal catalyzed enantioselective reactions is currently an area of great interest.1,2 These ligands must be capable of coordinating with the metal ion, generating around it a highly asymmetric environment so that the complex formed is ...
REVISED syllabus for CHEM F494 - Asymmetric Organic Synthesis
... synthesized using examples relating to metal chelation, steric effects, chiral reagents and chiral catalysts. To demonstrate to how the chirality of naturally occurring single-enantiomer compounds can be transmitted to non-chiral starting materials through reactivity. To show how the relative amount ...
... synthesized using examples relating to metal chelation, steric effects, chiral reagents and chiral catalysts. To demonstrate to how the chirality of naturally occurring single-enantiomer compounds can be transmitted to non-chiral starting materials through reactivity. To show how the relative amount ...
Viju B - IS MU
... 5 Pirrung, M. C.; Shuey, S. W. Journal of Organic Chemistry 1994, 59, 38903897. 6 Pirrung, M. C.; Bradley, J. C. Journal of Organic Chemistry 1995, 60, 11161117. ...
... 5 Pirrung, M. C.; Shuey, S. W. Journal of Organic Chemistry 1994, 59, 38903897. 6 Pirrung, M. C.; Bradley, J. C. Journal of Organic Chemistry 1995, 60, 11161117. ...
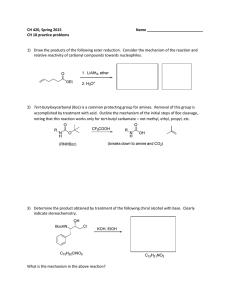
CH 420, Spring 2015 Name ___________________________ CH 18 practice problems
... 7) Rank the following compounds according to their relative acidity: cyclohexanol, phenol, pmethoxyphenol, p-nitrophenol. ...
... 7) Rank the following compounds according to their relative acidity: cyclohexanol, phenol, pmethoxyphenol, p-nitrophenol. ...
reactions of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones
... A curly arrow is a symbol used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of an electron pair in the braking or forming of a covalent bond ...
... A curly arrow is a symbol used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of an electron pair in the braking or forming of a covalent bond ...
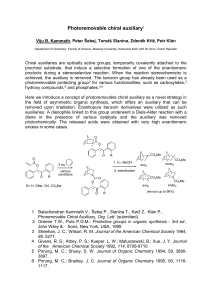
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.