Study Guide on Ch 5 and 6
... a. What are alpha- () and beta- () anomers? (p. 229 bottom) H. Primary alcohols Oxidize to corresponding aldehydes (see the equation below) I. Aldehydes are further oxidized to carboxylic acids. J. Secondary alcohols to corresponding ketones. No more oxidation! ...
... a. What are alpha- () and beta- () anomers? (p. 229 bottom) H. Primary alcohols Oxidize to corresponding aldehydes (see the equation below) I. Aldehydes are further oxidized to carboxylic acids. J. Secondary alcohols to corresponding ketones. No more oxidation! ...
Carbohydrates Typical formula: C (H O) , eg glucose: C H O
... solution is called a reducing sugar. It is the aldehyde or a-hydroxyketone group that is oxidized. Therefore, glycosides are not reducing sugars (unless R, itself, is a hemicactal that can open to an aldose or ketose.) ...
... solution is called a reducing sugar. It is the aldehyde or a-hydroxyketone group that is oxidized. Therefore, glycosides are not reducing sugars (unless R, itself, is a hemicactal that can open to an aldose or ketose.) ...
Chem 130 Fall 2004 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 8.1
... Conversion into alkyl halides (with HCl, HBr, SOCl2) Dehydration to form alkene (with H2SO4, concentrated, ∆) Oxidation: Primary alcohol to aldehydes (with PCC) Primary alcohol to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Secondary alcohol to ketones (with PCC or CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Tertiary alcoho ...
... Conversion into alkyl halides (with HCl, HBr, SOCl2) Dehydration to form alkene (with H2SO4, concentrated, ∆) Oxidation: Primary alcohol to aldehydes (with PCC) Primary alcohol to carboxylic acids (with CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Secondary alcohol to ketones (with PCC or CrO3 or K2Cr2O7) Tertiary alcoho ...
Chem 3.5 Answers #7
... Aldehydes are produced by the oxidation of primary alcohols using acidified potassium dichromate solution. The aldehyde must be distilled off as it is made or it will oxidise further, up to the carboxylic acid. Ketones are made by the same oxidation reaction with secondary alcohols, but they do not ...
... Aldehydes are produced by the oxidation of primary alcohols using acidified potassium dichromate solution. The aldehyde must be distilled off as it is made or it will oxidise further, up to the carboxylic acid. Ketones are made by the same oxidation reaction with secondary alcohols, but they do not ...
Chapter 4 - The Study of Chemical Reactions
... 3. Problem 17a and b The halonium ion model in Exercise 2 is presumably an intermediate in these reactions. Note that the two carbon atoms of the double bond are not identical. Since the more highly substituted carbon bears more positive charge than the less substituted carbon, attack by the nucleop ...
... 3. Problem 17a and b The halonium ion model in Exercise 2 is presumably an intermediate in these reactions. Note that the two carbon atoms of the double bond are not identical. Since the more highly substituted carbon bears more positive charge than the less substituted carbon, attack by the nucleop ...
This is the first exam with targeted syntheses that you
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to form triphenylphosphine oxide and an alkene product to complete the process. If the nucleophile is a weaker base than t ...
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to form triphenylphosphine oxide and an alkene product to complete the process. If the nucleophile is a weaker base than t ...
Document
... • Imine formation is also a nucleophilic addition. • There is a different end result here, though as elimination of water occurs. • The initial reaction is attack of the amine on the carbonyl to give the alkoxide intermediate as normal. • Following protonation of the alkoxide and loss of the proton ...
... • Imine formation is also a nucleophilic addition. • There is a different end result here, though as elimination of water occurs. • The initial reaction is attack of the amine on the carbonyl to give the alkoxide intermediate as normal. • Following protonation of the alkoxide and loss of the proton ...
aldehydes and ketones
... lone pair with carbonyl carbon Carbonyl compound other than aldehyde and ketone have a lone pair on an atom which attached to carbonyl compound group that can be shared by resonance edonation. This makes the carbonyl carbon less electron deficient and less reactive. ...
... lone pair with carbonyl carbon Carbonyl compound other than aldehyde and ketone have a lone pair on an atom which attached to carbonyl compound group that can be shared by resonance edonation. This makes the carbonyl carbon less electron deficient and less reactive. ...
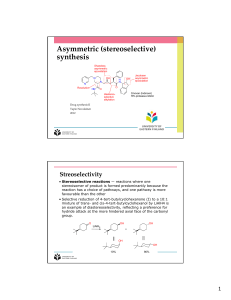
Stereoselective reactions of the carbonyl group
... • Underrated chiral auxiliary - easily introduced, performs many reactions & can be readily removed • One auxiliary can give either enantiomer of product • Selectivity dependent on whether reagent can chelate two groups Advanced organic ...
... • Underrated chiral auxiliary - easily introduced, performs many reactions & can be readily removed • One auxiliary can give either enantiomer of product • Selectivity dependent on whether reagent can chelate two groups Advanced organic ...
Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
... There are three regions of reactivity in aldehydes and ketones. ...
... There are three regions of reactivity in aldehydes and ketones. ...
1 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (Conjugate Addition) If we look
... In this reaction, an enolate is the nuclophile; one aldehyde molecule becomes the enolate while the other molecule serves as the electrophile. With aldehydes, the equilibrium usually favors the aldol products. But with ketones, the equilibrium usually favors starting materials. Of course, there are ...
... In this reaction, an enolate is the nuclophile; one aldehyde molecule becomes the enolate while the other molecule serves as the electrophile. With aldehydes, the equilibrium usually favors the aldol products. But with ketones, the equilibrium usually favors starting materials. Of course, there are ...
Chem 30CL - Lecture 1c - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... substrates and well controlled conditions • The Lipitor synthesis requires halohydrin dehalogenase, nitrilase, aldolase • The reduction of benzil using cryptococcus macerans leads to the formation of (R,R)-hydrobenzoin (dl:meso=95:5, 99 % e.e.) ...
... substrates and well controlled conditions • The Lipitor synthesis requires halohydrin dehalogenase, nitrilase, aldolase • The reduction of benzil using cryptococcus macerans leads to the formation of (R,R)-hydrobenzoin (dl:meso=95:5, 99 % e.e.) ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... • Can aldehydes and ketones set up hydrogen bonds with each other? • Can they set them up with water? ...
... • Can aldehydes and ketones set up hydrogen bonds with each other? • Can they set them up with water? ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.