Organic Synthesis of aromatic compounds
... • Explain that synthetic molecules often contain a mixture of optical isomers, whereas natural molecules often have only one optical isomer. • Explain that the synthesis of a pharmaceutical that is a single optical isomer increases costs, reduces side effects and improves pharmacological activity. • ...
... • Explain that synthetic molecules often contain a mixture of optical isomers, whereas natural molecules often have only one optical isomer. • Explain that the synthesis of a pharmaceutical that is a single optical isomer increases costs, reduces side effects and improves pharmacological activity. • ...
102 Lecture Ch15
... • Tollens’ reagent (silver nitrate plus ammonia) can be used to distinguish between ketones and aldehydes - with aldehydes the Ag2+ is reduced to elemental silver, which forms a mirror-like coat on the reaction container • Sugars (like glucose) often contain a hydroxy group adjacent to an aldehyde - ...
... • Tollens’ reagent (silver nitrate plus ammonia) can be used to distinguish between ketones and aldehydes - with aldehydes the Ag2+ is reduced to elemental silver, which forms a mirror-like coat on the reaction container • Sugars (like glucose) often contain a hydroxy group adjacent to an aldehyde - ...
Name
... b. C=O- carbonyl c. COOH- carboxyl d. NH2- amino e. OPO32-- phosphate f. CH3- methyl 5. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid? (1) Saturated fats do not have double bonded C and have the max number of H possible. Unsaturated have double bonds and not the max number ...
... b. C=O- carbonyl c. COOH- carboxyl d. NH2- amino e. OPO32-- phosphate f. CH3- methyl 5. What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid? (1) Saturated fats do not have double bonded C and have the max number of H possible. Unsaturated have double bonds and not the max number ...
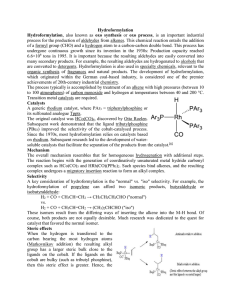
Hydroformylation Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or
... carbon into the C-M bond is likely to be greater than the rate of beta-hydride elimination. If the converse was true then some n-C8H17CHO would have been formed.[7] Hydroformylation of 2octene: the rhodium catalyst is coordinated to acac and carbon monoxide and encapsulated in a molecular self-assem ...
... carbon into the C-M bond is likely to be greater than the rate of beta-hydride elimination. If the converse was true then some n-C8H17CHO would have been formed.[7] Hydroformylation of 2octene: the rhodium catalyst is coordinated to acac and carbon monoxide and encapsulated in a molecular self-assem ...
Addition of Alcohols to Form Hemiacetals and Acetals
... Cyclic acetal formation protects carbonyl groups from attack by nucleophiles. 1,2-Ethanediol is a particularly effective reagent for forming acetals compared to ordinary alcohols because it forms a more stable cyclic intermediate. The stability of the cyclic acetal is due to a more favorable entropy ...
... Cyclic acetal formation protects carbonyl groups from attack by nucleophiles. 1,2-Ethanediol is a particularly effective reagent for forming acetals compared to ordinary alcohols because it forms a more stable cyclic intermediate. The stability of the cyclic acetal is due to a more favorable entropy ...
Document
... Deprotonation of the phosphonium salt with a strong base gives the ylide. A phosphorane is a neutral resonance structure of the ylide. ...
... Deprotonation of the phosphonium salt with a strong base gives the ylide. A phosphorane is a neutral resonance structure of the ylide. ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... ii. Reduction of Esters and Carboxylic Acids with LiAlH4 only LEARNING OUTCOMES: Understand the formation of alcohols through use of organometallics in carboncarbon bond forming reactions with electrophiles Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of it ...
... ii. Reduction of Esters and Carboxylic Acids with LiAlH4 only LEARNING OUTCOMES: Understand the formation of alcohols through use of organometallics in carboncarbon bond forming reactions with electrophiles Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of it ...
asymmetric alkyne addition to aldehydes
... Chiral propargylic alcohols are important compounds, as this structural motif is often found in pharmaceutical compounds as well as natural products and can also serve as versatile synthetic intermediates.1 Although there are many methods available for the preparation of these compounds (e.g. asymme ...
... Chiral propargylic alcohols are important compounds, as this structural motif is often found in pharmaceutical compounds as well as natural products and can also serve as versatile synthetic intermediates.1 Although there are many methods available for the preparation of these compounds (e.g. asymme ...
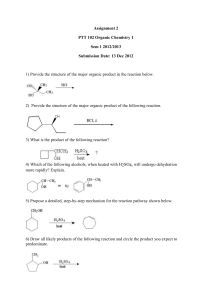
Assignment 2 Group A and B
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes: Relative Stability of
... Removal of a secondary hydrogen (C3 in the starting bromide) is sterically more difficult than abstracting a more exposed methyl hydrogen when a hindered base is used. The transition state leading to the more stable product is increased in energy by steric interference with the bulky base. An E2 rea ...
... Removal of a secondary hydrogen (C3 in the starting bromide) is sterically more difficult than abstracting a more exposed methyl hydrogen when a hindered base is used. The transition state leading to the more stable product is increased in energy by steric interference with the bulky base. An E2 rea ...
Microsoft Word - Final Exam Study Guide
... synthesis of ethers, alcohols, and epoxides, dehydration of alcohols, carbocation rearrangements, reactions of alcohols/ethers/epoxides, multistep synthesis, protecting groups, redox reactions, reagents for redox reactions, Grignard reaction ...
... synthesis of ethers, alcohols, and epoxides, dehydration of alcohols, carbocation rearrangements, reactions of alcohols/ethers/epoxides, multistep synthesis, protecting groups, redox reactions, reagents for redox reactions, Grignard reaction ...
Homework
... Problems must be solved, or written out, in their entirety with all work shown on engineering graph paper. You must label each set in the upper left hand corner with your name, the date and the chapter. Problems must be identified by number and all work must be shown with answers boxed. Be sure your ...
... Problems must be solved, or written out, in their entirety with all work shown on engineering graph paper. You must label each set in the upper left hand corner with your name, the date and the chapter. Problems must be identified by number and all work must be shown with answers boxed. Be sure your ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... ketone with a phosphonium ylide- a compound with a negatively-charged carbon bonded to a positively-charged phosphorus atom. The result is the replacement of the carbonyl oxygen with the carbon group on the ylide. We will learn how to prepare this Wittig reagent (the ylide), and how it reacts with t ...
... ketone with a phosphonium ylide- a compound with a negatively-charged carbon bonded to a positively-charged phosphorus atom. The result is the replacement of the carbonyl oxygen with the carbon group on the ylide. We will learn how to prepare this Wittig reagent (the ylide), and how it reacts with t ...
Exam 3 Review
... What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction of RO–) to prepare an unsymmetrical ether. Why are aldehydes more r ...
... What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction of RO–) to prepare an unsymmetrical ether. Why are aldehydes more r ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
... Which of the following produce a silver mirror with Tollens’ reagent? • C2H5CHO ...
... Which of the following produce a silver mirror with Tollens’ reagent? • C2H5CHO ...
ADVANCED SYNTHESIS Stereochemistry
... • Use of chirality present within the substrate to control the introduction of new chirality • This is a diastereoselective reaction • If the starting material is enantiopure then the product will be enantiomerically pure • Last year you would have briefly met: ...
... • Use of chirality present within the substrate to control the introduction of new chirality • This is a diastereoselective reaction • If the starting material is enantiopure then the product will be enantiomerically pure • Last year you would have briefly met: ...
blank lecture 11
... • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other attached groups as before. • Examples: ...
... • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other attached groups as before. • Examples: ...
Nucleophilic Substitution
... is the same order as for basicity. 2. If one is comparing the same central atom, higher electron density will increase the nucleophilicity, e.g. an anion will be a better Nu (lone pair donor) than a neutral atom such as HO> H2O. This is the same order as for basicity. 3. Within a group in the period ...
... is the same order as for basicity. 2. If one is comparing the same central atom, higher electron density will increase the nucleophilicity, e.g. an anion will be a better Nu (lone pair donor) than a neutral atom such as HO> H2O. This is the same order as for basicity. 3. Within a group in the period ...
Group G
... Drawing structure based on recognizing the names of functional groups and can be found in chapters 11 (aromatic rings), 15 (alcohols), and 22 (amines). Question 2: PPA is commonly prepared from propenylbenzene (IUPAC name: 1phenyl 1-propene). Discuss what reactions would be used to complete this pre ...
... Drawing structure based on recognizing the names of functional groups and can be found in chapters 11 (aromatic rings), 15 (alcohols), and 22 (amines). Question 2: PPA is commonly prepared from propenylbenzene (IUPAC name: 1phenyl 1-propene). Discuss what reactions would be used to complete this pre ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.