Discovery and synthetic applications of novel silicon
... enhanced electrophilicity of the ligand L, the author has been interested in the latter concept for the enhanced nucleophilicity of the group R, especially in organosilicon compounds. A brief comparison of silicon with carbon in four categories is first made to determine key characteristic features o ...
... enhanced electrophilicity of the ligand L, the author has been interested in the latter concept for the enhanced nucleophilicity of the group R, especially in organosilicon compounds. A brief comparison of silicon with carbon in four categories is first made to determine key characteristic features o ...
reaction rate - davis.k12.ut.us
... Expressing Reaction Rates (cont.) • Reaction rates are determined experimentally (and always expressed as a positive value). • Average rate of reaction: the change in concentration of a reactant or product that occurs during a specific time interval. ...
... Expressing Reaction Rates (cont.) • Reaction rates are determined experimentally (and always expressed as a positive value). • Average rate of reaction: the change in concentration of a reactant or product that occurs during a specific time interval. ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... Amides (RCONH2) in general are not proton acceptors except in very strong acid The C=O group is strongly electron-withdrawing, making the N a very weak base Addition of a proton occurs on O but this destroys the double bond character of C=O as a requirement of stabilization by N= ...
... Amides (RCONH2) in general are not proton acceptors except in very strong acid The C=O group is strongly electron-withdrawing, making the N a very weak base Addition of a proton occurs on O but this destroys the double bond character of C=O as a requirement of stabilization by N= ...
No Slide Title
... thrombin has three binding sites, labeled as S1, S2 and S3, that determine the strength and specificity of binding • The lipophilicity of S3 has been well determined • Lipophilicity represents the affinity of a molecule or moiety for a lipophilic environment (i.e. hydrophobicity) ...
... thrombin has three binding sites, labeled as S1, S2 and S3, that determine the strength and specificity of binding • The lipophilicity of S3 has been well determined • Lipophilicity represents the affinity of a molecule or moiety for a lipophilic environment (i.e. hydrophobicity) ...
STUDY GUIDE
... cotton, and wood are all composed of polymers made by living organisms. Polymers are large molecules—natural or synthetic—made up of many monomers linked together. Homopolymers are polymers made of only a single type of monomer. Copolymers are polymers made of two or more types of monomers. Addition ...
... cotton, and wood are all composed of polymers made by living organisms. Polymers are large molecules—natural or synthetic—made up of many monomers linked together. Homopolymers are polymers made of only a single type of monomer. Copolymers are polymers made of two or more types of monomers. Addition ...
Neuman Chapter - Department of Chemistry
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but ...
... The C-A and C-B bonds break in the elimination reaction, and a second bond forms between the two C's to form a C=C bond. "A-B" in Figure 9.01 may not be an actual reaction product, but ...
top organomet chem-2006-19-207 pauson
... a lack of scope is generally observed in these reports. In addition there are few examples of intermolecular reactions performed in catalytic conditions [21]. The first important advances in the development of a catalytic PKR were by the groups of Livinghouse [67, 68] and Krafft [69, 70] who reported ...
... a lack of scope is generally observed in these reports. In addition there are few examples of intermolecular reactions performed in catalytic conditions [21]. The first important advances in the development of a catalytic PKR were by the groups of Livinghouse [67, 68] and Krafft [69, 70] who reported ...
16.18 Summary
... and enflurane. These compounds are isomeric; isoflurane is 1-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether; enflurane is 2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether. Write the structural formulas of isoflurane and enflurane. ...
... and enflurane. These compounds are isomeric; isoflurane is 1-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether; enflurane is 2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether. Write the structural formulas of isoflurane and enflurane. ...
Module 2 Alcohols, halogenoalkanes and analysis
... investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials. In the recent past, organic chemists have developed a broad range of original and exciting materials, such as pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, solvents and plastics. Halogenoalkanes are important starting materials for many synthet ...
... investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials. In the recent past, organic chemists have developed a broad range of original and exciting materials, such as pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, solvents and plastics. Halogenoalkanes are important starting materials for many synthet ...
C 1 hapter
... organoboron compounds and one of the most studied reactions in organic synthesis. Introduced by H. C. Brown [1] in 1959, it is based on the syn addition of borane reagent H-BR’2 to alkenes or alkynes. In fact, it is considered to be the initial step in the introduction of a very wide variety of func ...
... organoboron compounds and one of the most studied reactions in organic synthesis. Introduced by H. C. Brown [1] in 1959, it is based on the syn addition of borane reagent H-BR’2 to alkenes or alkynes. In fact, it is considered to be the initial step in the introduction of a very wide variety of func ...
Chapter 18
... Esters are named according to the parent carboxylic acid and the –ic acid is replaced with an –ate suffix, the alkyl ester substituent is named as a separate alkyl group with the name in front of the alkanoate name ...
... Esters are named according to the parent carboxylic acid and the –ic acid is replaced with an –ate suffix, the alkyl ester substituent is named as a separate alkyl group with the name in front of the alkanoate name ...
Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... Single-Displacement Reactions, continued Displacement of Halogens • Fluorine is the most-active halogen. • It can replace any of the other halogens in their compounds. • In Group 17 each element can replace any element below it, but not any element above it. Cl2(g) + 2KBr(aq) F2(g) + 2NaCl(aq) Br2(l ...
... Single-Displacement Reactions, continued Displacement of Halogens • Fluorine is the most-active halogen. • It can replace any of the other halogens in their compounds. • In Group 17 each element can replace any element below it, but not any element above it. Cl2(g) + 2KBr(aq) F2(g) + 2NaCl(aq) Br2(l ...
Stereoselective Construction of a β
... did not proceed in Et2O14 (entry 5). The rearrangement of (Z)-8 proceeded with relatively high diastereoselectivity (84-92%de) compared with that of (E)-8 (entries 8-10). Assignment of the relative stereochemistry of both anti- and syn-9 was based on 2D-NOE experiments15 and comparison of the 1H NMR ...
... did not proceed in Et2O14 (entry 5). The rearrangement of (Z)-8 proceeded with relatively high diastereoselectivity (84-92%de) compared with that of (E)-8 (entries 8-10). Assignment of the relative stereochemistry of both anti- and syn-9 was based on 2D-NOE experiments15 and comparison of the 1H NMR ...
Sample Exam #2 Answer Key
... thiols. Finally, alcohols are much more water soluble than thiols due to their greater polarity and hydrogen bonding. 2) Compare the molecular structure and physical properties of aldehydes and ketones. Include descriptions of geometry, orbital hybridization, hydrogen bonding, relative melting point ...
... thiols. Finally, alcohols are much more water soluble than thiols due to their greater polarity and hydrogen bonding. 2) Compare the molecular structure and physical properties of aldehydes and ketones. Include descriptions of geometry, orbital hybridization, hydrogen bonding, relative melting point ...
A Convenient Synthesis of Amino Acid Methyl Esters
... Compared with other methods, the yields obtained with the TMSCl/MeOH system were in most cases comparable to or even higher than those obtained with the thionyl chloride/MeOH and HCl(SO4H2)/MeOH systems and the method is certainly more convenient from an operational point of view. For example, for b ...
... Compared with other methods, the yields obtained with the TMSCl/MeOH system were in most cases comparable to or even higher than those obtained with the thionyl chloride/MeOH and HCl(SO4H2)/MeOH systems and the method is certainly more convenient from an operational point of view. For example, for b ...
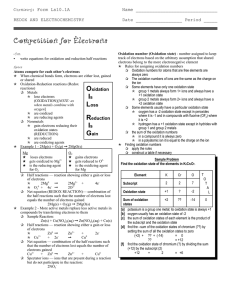
Competition for Electrons
... track of electrons based on the arbitrary assumption that shared electrons belong to the more electronegative element n Rules for assigning oxidation numbers q Oxidation numbers for atoms that are free elements are always zero q The oxidation numbers of ions are the same as the charge on the ion q S ...
... track of electrons based on the arbitrary assumption that shared electrons belong to the more electronegative element n Rules for assigning oxidation numbers q Oxidation numbers for atoms that are free elements are always zero q The oxidation numbers of ions are the same as the charge on the ion q S ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.