Ethers and Epoxides
... They are not considered a substituent but a ring such as cyclobutane. The O atom is understood as being in the first position. Oxetanes have ring strain, but not as much as epoxides. ...
... They are not considered a substituent but a ring such as cyclobutane. The O atom is understood as being in the first position. Oxetanes have ring strain, but not as much as epoxides. ...
- Sacramento - California State University
... Vanadium has been used as a catalyst for polymerization1, oxidation of alcohols2, sulfides3, and more importantly, allylic alcohols. Epoxides are useful building blocks for natural product synthesis and medicinal chemistry because new functional groups can easily be introduced by nucleophilic additi ...
... Vanadium has been used as a catalyst for polymerization1, oxidation of alcohols2, sulfides3, and more importantly, allylic alcohols. Epoxides are useful building blocks for natural product synthesis and medicinal chemistry because new functional groups can easily be introduced by nucleophilic additi ...
Class Notes Test 1
... Super Strong Bases and Nucleophiles • The counterion metal is a spectator • Stability-reactivity principle: very unstable à very reactive • This great reactivity is very useful (as nucleophile) • This great reactivity (as base) has implication for proper technical use (see following) 7. Solvent and ...
... Super Strong Bases and Nucleophiles • The counterion metal is a spectator • Stability-reactivity principle: very unstable à very reactive • This great reactivity is very useful (as nucleophile) • This great reactivity (as base) has implication for proper technical use (see following) 7. Solvent and ...
Synthesis of Cyclobutanes by Lewis Acid-Promoted Ketene
... The procedures described in Organic Syntheses are provided as published and are conducted at one's own risk. Organic Syntheses, Inc., its Editors, and its Board of Directors do not warrant or guarantee the safety of individuals using these procedures and hereby disclaim any liability for any injurie ...
... The procedures described in Organic Syntheses are provided as published and are conducted at one's own risk. Organic Syntheses, Inc., its Editors, and its Board of Directors do not warrant or guarantee the safety of individuals using these procedures and hereby disclaim any liability for any injurie ...
Electrophilic Selenium Catalysis with Electrophilic N
... Functionalization of alkenes is a perpetual goal in organic synthesis. One of the attractive routes to elaborate the carbon–carbon double bond of alkenes is through electrophilic selenium reagent-promoted selenofunctionalization. In this context, several electrophilic organoselenium reagents ArSeX ( ...
... Functionalization of alkenes is a perpetual goal in organic synthesis. One of the attractive routes to elaborate the carbon–carbon double bond of alkenes is through electrophilic selenium reagent-promoted selenofunctionalization. In this context, several electrophilic organoselenium reagents ArSeX ( ...
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES I. NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION TO …
... •Once the substrate (aldehyde or ketone) is bound to the enzyme, the active site of the enzyme is in a position to react with and modify the substrate. •At the end of the reaction, because imines come apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from ...
... •Once the substrate (aldehyde or ketone) is bound to the enzyme, the active site of the enzyme is in a position to react with and modify the substrate. •At the end of the reaction, because imines come apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from ...
chapter15-burno.1348..
... Significance of the Equilibrium Constant The significance of the equilibrium constant lies in the fact that for a chemical reaction taking place at a particular temperature T, the equilibrium constant (KC or Kp) has a particular numerical value. This means that no matter what the starting concentra ...
... Significance of the Equilibrium Constant The significance of the equilibrium constant lies in the fact that for a chemical reaction taking place at a particular temperature T, the equilibrium constant (KC or Kp) has a particular numerical value. This means that no matter what the starting concentra ...
ETHER
... Has a pair of alkyl or atomic groups attached to a linking oxygen atom. Functional group is ROR Have primary, secondary, and tertiary structures ...
... Has a pair of alkyl or atomic groups attached to a linking oxygen atom. Functional group is ROR Have primary, secondary, and tertiary structures ...
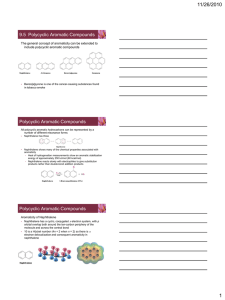
Aromatic Compounds
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds: Electrophilic Substitution One difference between electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and electrophilic alkene addition reactions is that aromatic rings are less reactive toward electrophiles than alkenes are ...
... Reactions of Aromatic Compounds: Electrophilic Substitution One difference between electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and electrophilic alkene addition reactions is that aromatic rings are less reactive toward electrophiles than alkenes are ...
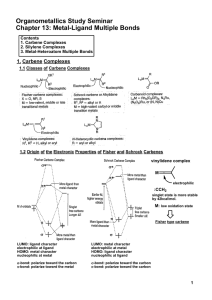
Metal-Ligand Multiple Bonds
... LUMO: ligand character electrophilic at ligand HOMO: metal character nucleophilic at metal -bond: polarize toward the carbon -bond: polarize toward the metal ...
... LUMO: ligand character electrophilic at ligand HOMO: metal character nucleophilic at metal -bond: polarize toward the carbon -bond: polarize toward the metal ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... However, the less highly substituted alkene predominates in the Hofmann elimination due to the large size of the trialkylamine leaving group The base must abstract a hydrogen from the most ...
... However, the less highly substituted alkene predominates in the Hofmann elimination due to the large size of the trialkylamine leaving group The base must abstract a hydrogen from the most ...
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes
... 7. Ozonolysis (strong oxidation): Oxidation of alkenes by ozone “O3” leads to destruction of both the σ and π bonds of the double-bond system. This cleavage of an alkene double bond, generally accomplished in good yield, is called ozonolysis. ...
... 7. Ozonolysis (strong oxidation): Oxidation of alkenes by ozone “O3” leads to destruction of both the σ and π bonds of the double-bond system. This cleavage of an alkene double bond, generally accomplished in good yield, is called ozonolysis. ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.