CHAPTER 9
... (1) Replacement reactions and addition reactions are two terms which describe the same type of reaction. (2) Orientation relative to one another, at the moment of collision, is always a factor in determining whether a collision is effective. (3) An increase in temperature will always cause an endoth ...
... (1) Replacement reactions and addition reactions are two terms which describe the same type of reaction. (2) Orientation relative to one another, at the moment of collision, is always a factor in determining whether a collision is effective. (3) An increase in temperature will always cause an endoth ...
Worksheet Key
... 36. For each system described below, indicate in which direction the equilibrium will shift when each stress is added or removed. Also explain how the system will react to alleviate the stress. a) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g): more H2 is added to this reaction at equilibrium. Reaction will shift to ...
... 36. For each system described below, indicate in which direction the equilibrium will shift when each stress is added or removed. Also explain how the system will react to alleviate the stress. a) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g): more H2 is added to this reaction at equilibrium. Reaction will shift to ...
Alcohols, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... CO(g) + 2 H2(g)→ CH3OH(l ) Methanol is highly toxic and can cause blindness and death if taken internally. During Prohibition in the United States, many people died or became seriously ill from drinking methanol, either because they were not aware of the difference between methanol and ethanol o ...
... CO(g) + 2 H2(g)→ CH3OH(l ) Methanol is highly toxic and can cause blindness and death if taken internally. During Prohibition in the United States, many people died or became seriously ill from drinking methanol, either because they were not aware of the difference between methanol and ethanol o ...
Chapter 11 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... methylene group. The boiling points of the alkanes increase with molecular weight. All alkanes have this general formula. ...
... methylene group. The boiling points of the alkanes increase with molecular weight. All alkanes have this general formula. ...
Introductory Chemistry, 2nd Edition Nivaldo Tro
... • Even though a reaction has a negative G it may occur too slowly to be observed (i.e. combustion). • Thermodynamics gives us the direction of a spontaneous process, it does not give us the rate of the process. • A nonspontaneous process can be driven if coupled with a spontaneous process – this is ...
... • Even though a reaction has a negative G it may occur too slowly to be observed (i.e. combustion). • Thermodynamics gives us the direction of a spontaneous process, it does not give us the rate of the process. • A nonspontaneous process can be driven if coupled with a spontaneous process – this is ...
Lecture (8)
... Alcohols, like water, are both weakly basic and weakly acidic. Alcohols contain the very polar –OH group. This group contains hydrogen attached to the very electronegative element OXYGEN, and therefore permits hydrogen bonding R─O…..H-O-R H The boiling point of alcohols is higher than hydrocarbons o ...
... Alcohols, like water, are both weakly basic and weakly acidic. Alcohols contain the very polar –OH group. This group contains hydrogen attached to the very electronegative element OXYGEN, and therefore permits hydrogen bonding R─O…..H-O-R H The boiling point of alcohols is higher than hydrocarbons o ...
Ir-catalysed formation of C− F bonds. From allylic alcohols to α
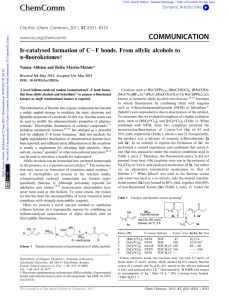
... same reaction conditions, NFSI or N-fluoropyridinium tetrafluoroborate (NFPY) failed to give any fluorinated products (Table 1, entries 4 and 5). Only monofluorinated products were obtained (i.e. no difluorinated ketones), under any of the reaction conditions. Since SelectF in THF/water mixtures successf ...
... same reaction conditions, NFSI or N-fluoropyridinium tetrafluoroborate (NFPY) failed to give any fluorinated products (Table 1, entries 4 and 5). Only monofluorinated products were obtained (i.e. no difluorinated ketones), under any of the reaction conditions. Since SelectF in THF/water mixtures successf ...
Three-dimensional Arrangement Of Atoms
... Addition of HBr to a chiral alkene: reactions of a chiral reactant with an achiral reagent gives diastereomeric products which may or may not be formed in equal amounts. The intermediate carbocation is asymmetric, therefore attack of Br- from the top or bottom faces may not be equally probable. The ...
... Addition of HBr to a chiral alkene: reactions of a chiral reactant with an achiral reagent gives diastereomeric products which may or may not be formed in equal amounts. The intermediate carbocation is asymmetric, therefore attack of Br- from the top or bottom faces may not be equally probable. The ...
Part II
... Free radicals – have unpaired electron(s). Atmospheric lifetimes seconds, minutes. e.g., •O-H radical, missing one bond (H), wants to steal one from somewhere. Similar story for •CH3 radical, missing one bond. Or the HO2 radical, H-O-O• These free radicals are usually generated by sunlight (photoche ...
... Free radicals – have unpaired electron(s). Atmospheric lifetimes seconds, minutes. e.g., •O-H radical, missing one bond (H), wants to steal one from somewhere. Similar story for •CH3 radical, missing one bond. Or the HO2 radical, H-O-O• These free radicals are usually generated by sunlight (photoche ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... W n RT2 1 . After some calculations with different integer n, we find that n = 13. ...
... W n RT2 1 . After some calculations with different integer n, we find that n = 13. ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... W n RT2 1 . After some calculations with different integer n, we find that n = 13. ...
... W n RT2 1 . After some calculations with different integer n, we find that n = 13. ...
examination paper - University of Calgary
... appropriate space, A, B, C, D or E on the answer sheet. Use a pencil only and not ink. In some cases it is required that you indicate multiple items for a complete and/or correct answer by blackening out more than one space. In some other cases more than five options are available and some of these ...
... appropriate space, A, B, C, D or E on the answer sheet. Use a pencil only and not ink. In some cases it is required that you indicate multiple items for a complete and/or correct answer by blackening out more than one space. In some other cases more than five options are available and some of these ...
32.6
... To study the effect of the structure of haloalkanes on the rate of hydrolysis of them and to compare the rates of hydrolysis of haloalkanes and halobenzene ...
... To study the effect of the structure of haloalkanes on the rate of hydrolysis of them and to compare the rates of hydrolysis of haloalkanes and halobenzene ...
chm238f02.pracexam2.ans
... (b) What is the reactive electrophile in the above reaction? NO2+, nitronium ion. (c) If we used only pure (fuming) sulfuric acid, what would be the product(s)? mostly sulfonation of Cl benzene, both o and p, because SO3H+ becomes the superelectrophile and there is not as much protons for the dehydr ...
... (b) What is the reactive electrophile in the above reaction? NO2+, nitronium ion. (c) If we used only pure (fuming) sulfuric acid, what would be the product(s)? mostly sulfonation of Cl benzene, both o and p, because SO3H+ becomes the superelectrophile and there is not as much protons for the dehydr ...
2011-2012 ACAD REVIEW SHEET Chapter 16
... What does it mean if the Keq is much greater than 1? (ANS: The equilibrium favors products.) What does it mean if the Keq is much smaller than 1 (like 0.001)? (ANS: The equilibrium favors reactants) What does it mean if the Keq is around 1? (ANS: There is a lot of both reactants and products.) Write ...
... What does it mean if the Keq is much greater than 1? (ANS: The equilibrium favors products.) What does it mean if the Keq is much smaller than 1 (like 0.001)? (ANS: The equilibrium favors reactants) What does it mean if the Keq is around 1? (ANS: There is a lot of both reactants and products.) Write ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.