Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
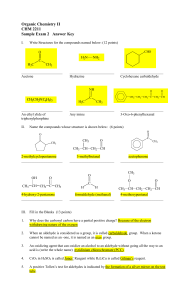
... •-diols or –triols mean two or three hydroxy groups in the molecule •Number the hydroxy group carbons with the lowest possible numbers •Prefix uses the full parent name, i.e butane ...
... •-diols or –triols mean two or three hydroxy groups in the molecule •Number the hydroxy group carbons with the lowest possible numbers •Prefix uses the full parent name, i.e butane ...
225 Unit 7, Lab 1 - Pope John Paul II High School
... In the example seen above, 3O2 had to be added to the right side of the equation to balance it and show that the excess oxygen is not consumed during the reaction. In this example, methane is called the limiting reactant. Although we have discussed balancing equations in terms of numbers of atoms an ...
... In the example seen above, 3O2 had to be added to the right side of the equation to balance it and show that the excess oxygen is not consumed during the reaction. In this example, methane is called the limiting reactant. Although we have discussed balancing equations in terms of numbers of atoms an ...
Slide 1
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
... Describing Ionic Compounds 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. Answer: H2 + Cl2 2HCl ...
Lab 9
... In this experiment, we will prepare an epoxide or oxirane by epoxidizing chlolesterol. Cholesterol is the most common compound in the class of compounds called sterols. As the name implies, sterols contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group. Because sterols are alcohols, they have the characteristic name ending ...
... In this experiment, we will prepare an epoxide or oxirane by epoxidizing chlolesterol. Cholesterol is the most common compound in the class of compounds called sterols. As the name implies, sterols contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group. Because sterols are alcohols, they have the characteristic name ending ...
1 Intro / Review : Chemical Kinetics
... The energy required to raise the energy levels of the species to a point of highest potential energy (called the activated complex)…where those intermediate products exist. ...
... The energy required to raise the energy levels of the species to a point of highest potential energy (called the activated complex)…where those intermediate products exist. ...
18_Lecture - Ventura College
... The carbonyl is assumed to be at the 1-position in cyclic ketones: ...
... The carbonyl is assumed to be at the 1-position in cyclic ketones: ...
Chem 226 — Problem Set #10
... Acetic acid boils at 118o C, but its ethyl ester boils at 77o C. Why is the boiling point of the acid so much higher, even though it has a lower molecular weight? The acid is an associated liquid. That is to say, molecules of the acid hydrogen bond to each other in the liquid. This hydrogen bonding ...
... Acetic acid boils at 118o C, but its ethyl ester boils at 77o C. Why is the boiling point of the acid so much higher, even though it has a lower molecular weight? The acid is an associated liquid. That is to say, molecules of the acid hydrogen bond to each other in the liquid. This hydrogen bonding ...
Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 18
... The carbonyl is assumed to be at the 1-position in cyclic ketones: ...
... The carbonyl is assumed to be at the 1-position in cyclic ketones: ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.