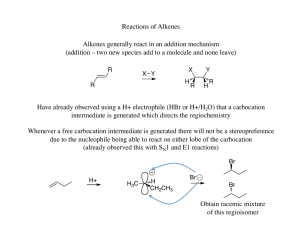
2009 Final Exam - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... This fat contains 3 cis- and 2 trans- bonds This fat is an omega-3 fat This fat contains three ether groups One carbon chain is saturated ...
... This fat contains 3 cis- and 2 trans- bonds This fat is an omega-3 fat This fat contains three ether groups One carbon chain is saturated ...
Synthesis of Alcohols Using Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents
... CH3(CH2)3C CCH2OH other than a Grignard? Grignard? ...
... CH3(CH2)3C CCH2OH other than a Grignard? Grignard? ...
Chapter 11
... The electrophilic mercury reacts with an alkene to form a mercurinium ion which is similar to bromonium ions in that a three membered ring is formed with a partial bond to the carbon that can best handle the partial positive charge ...
... The electrophilic mercury reacts with an alkene to form a mercurinium ion which is similar to bromonium ions in that a three membered ring is formed with a partial bond to the carbon that can best handle the partial positive charge ...
2013 Final Exam File - Fiji National University
... Assuming that the compound only contains C, H, and possibly (but not necessarily) O, write down all reasonable molecular formulae for this compound. [12 marks] (e) Each of the molecules shown below has one stereocentre, whose configuration is as shown. For each molecule, arrange the 4 substituents a ...
... Assuming that the compound only contains C, H, and possibly (but not necessarily) O, write down all reasonable molecular formulae for this compound. [12 marks] (e) Each of the molecules shown below has one stereocentre, whose configuration is as shown. For each molecule, arrange the 4 substituents a ...
Properties
... primary amides have two N-H bonds they have stronger hydrogen bonding than carboxylic acids Secondary amides also experience hydrogen bonding are soluble in water The solubility decreases as the non-polar alkyl chain increases in size amides have much higher melting and boiling points than carbo ...
... primary amides have two N-H bonds they have stronger hydrogen bonding than carboxylic acids Secondary amides also experience hydrogen bonding are soluble in water The solubility decreases as the non-polar alkyl chain increases in size amides have much higher melting and boiling points than carbo ...
Introduction - Bulgarian Chemical Communications
... alternate conformation with equatorial 5-methyl will give rise to the strong repulsion between axial 6methyl and axial OH at 4-C, see Scheme 2, R4↔OH). 3-N is positively charged because of rate determining ureido group attack [21] and solvated respectively causing strong steric repulsion with an axi ...
... alternate conformation with equatorial 5-methyl will give rise to the strong repulsion between axial 6methyl and axial OH at 4-C, see Scheme 2, R4↔OH). 3-N is positively charged because of rate determining ureido group attack [21] and solvated respectively causing strong steric repulsion with an axi ...
problem 18.33b Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Protons on the α-carbon (next to the C=O) of esters and amides have a typical chemical shift range of δ 2.0 - 2.5 ppm. Protons on the carbon attached to the ester oxygen atom have a typical chemical shift range of δ 3.5 - 4.5 ppm. The chemical shift of an amide N-H proton is typically between δ 5-8 ...
... Protons on the α-carbon (next to the C=O) of esters and amides have a typical chemical shift range of δ 2.0 - 2.5 ppm. Protons on the carbon attached to the ester oxygen atom have a typical chemical shift range of δ 3.5 - 4.5 ppm. The chemical shift of an amide N-H proton is typically between δ 5-8 ...
Organomet-2
... Housecroft & Sharpe Inorganic Chemistry Main group Chapter 18, p 410 Transition metals Chapter 23, p 584 Claydon, Greeves, Warren & Wothers Organic Chemistry Main group Chapter 9 & Chapter 47 Transition metals Chapter 48 Metal-organo compounds can be conveniently divided into those ...
... Housecroft & Sharpe Inorganic Chemistry Main group Chapter 18, p 410 Transition metals Chapter 23, p 584 Claydon, Greeves, Warren & Wothers Organic Chemistry Main group Chapter 9 & Chapter 47 Transition metals Chapter 48 Metal-organo compounds can be conveniently divided into those ...
Ch12-Alcohols-Grignard
... What remains is the combination of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that can be used to prepare the alcohol. ...
... What remains is the combination of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that can be used to prepare the alcohol. ...
Chapter 12 Packet
... provide molten steel to weld steel rails together when laying track. Suppose that in one batch of reactants 4.20mol Al was mixed with 1.75mol Fe2O3. a. Which reactant, if either, was the limiting reactant? b. Calculate the mass of iron (in grams) that can be formed from this mixture of reactants. 22 ...
... provide molten steel to weld steel rails together when laying track. Suppose that in one batch of reactants 4.20mol Al was mixed with 1.75mol Fe2O3. a. Which reactant, if either, was the limiting reactant? b. Calculate the mass of iron (in grams) that can be formed from this mixture of reactants. 22 ...
7. Organic halides
... strain, also called Baeyer strain. Because the sp3 orbitals in cyclopropane cannot overlap so effectively as they do in alkanes, the C–C bonds are weaker and the molecule has greater potential energy and higher reactivity. Furthermore, the hydrogens in the planar ring are all eclipsed, that is torsi ...
... strain, also called Baeyer strain. Because the sp3 orbitals in cyclopropane cannot overlap so effectively as they do in alkanes, the C–C bonds are weaker and the molecule has greater potential energy and higher reactivity. Furthermore, the hydrogens in the planar ring are all eclipsed, that is torsi ...
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
... Two carbon atoms joined by a single bond are capable of free rotation about themselves. When two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond, they cannot rotate freely and the relative positions of the various groups attached to these carbon atoms get fixed. This gives rise to geometric isomers. Such c ...
... Two carbon atoms joined by a single bond are capable of free rotation about themselves. When two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond, they cannot rotate freely and the relative positions of the various groups attached to these carbon atoms get fixed. This gives rise to geometric isomers. Such c ...
Alcohols and Phenols - faculty at Chemeketa
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel additive, produced in large quantities Ethanol, CH3CH2OH, called ethyl alcohol, is a solvent, fuel, bevera ...
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel additive, produced in large quantities Ethanol, CH3CH2OH, called ethyl alcohol, is a solvent, fuel, bevera ...
Problem 14. MAGNESIUM DETERMINATION
... In chemical reactions molecular structure changes over time so that the electronic state of a molecule is a function of time. In some cases structure of a molecule can be presented by a superposition of the initial and final states with time-dependent coefficients. Let’s assume that a molecule oscil ...
... In chemical reactions molecular structure changes over time so that the electronic state of a molecule is a function of time. In some cases structure of a molecule can be presented by a superposition of the initial and final states with time-dependent coefficients. Let’s assume that a molecule oscil ...
Workshop #1 Part 1. Organic Chemistry Nomenclature
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
November 2016 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-level
... (a) Ibuprofen and paracetamol both contain the aryl (benzene) functional group. Name the other functional groups present in each molecule. ibuprofen .................................................................................................................................... paracetamol ...... ...
... (a) Ibuprofen and paracetamol both contain the aryl (benzene) functional group. Name the other functional groups present in each molecule. ibuprofen .................................................................................................................................... paracetamol ...... ...
2 C2H6 (g)
... Li3N (s) + 3 D2O (l) ND3 (g) + 3 LiOD (aq) Calculate how many grams of heavy water are required to produce 150.0 mg of ND3 (g). (The molar mass of deuterium, D, is 2.014 g/mole) Question 15 of 28 What is the maxiumum mass of S8 that can be produced by combining 78.0 g of each reactant? 8 SO2 + 16 ...
... Li3N (s) + 3 D2O (l) ND3 (g) + 3 LiOD (aq) Calculate how many grams of heavy water are required to produce 150.0 mg of ND3 (g). (The molar mass of deuterium, D, is 2.014 g/mole) Question 15 of 28 What is the maxiumum mass of S8 that can be produced by combining 78.0 g of each reactant? 8 SO2 + 16 ...
Redox Reactions C12-1-10
... Several types of chemical reactions were carried out in this laboratory session, some redox and some non-redox. Remember that although redox reactions are common, not all chemical reactions are redox reactions. All redox reactions involve complete or partial transfer of electrons from one atom to an ...
... Several types of chemical reactions were carried out in this laboratory session, some redox and some non-redox. Remember that although redox reactions are common, not all chemical reactions are redox reactions. All redox reactions involve complete or partial transfer of electrons from one atom to an ...
chm238f02.exam2
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
Test-tube Reactions - University of Manitoba
... Several types of chemical reactions were carried out in this laboratory session, some redox and some non-redox. Remember that although redox reactions are common, not all chemical reactions are redox reactions. All redox reactions involve complete or partial transfer of electrons from one atom to an ...
... Several types of chemical reactions were carried out in this laboratory session, some redox and some non-redox. Remember that although redox reactions are common, not all chemical reactions are redox reactions. All redox reactions involve complete or partial transfer of electrons from one atom to an ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.