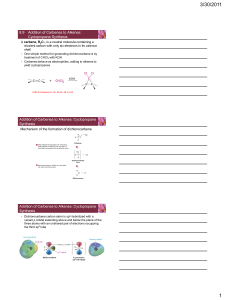
Carboxylic acids from primary alcohols and aldehydes by a
... As shown in Table 1 various primary alcohols were oxidized with PCC/H5IO6 to give the corresponding acids in quantitative yields. Benzylic (entries 1, 4–7 and 10), aliphatic (entries 2 and 12) as well as homobenzylic (entries 3, 8, 9, and 11) alcohols oxidized smoothly in a short amount of time. Ele ...
... As shown in Table 1 various primary alcohols were oxidized with PCC/H5IO6 to give the corresponding acids in quantitative yields. Benzylic (entries 1, 4–7 and 10), aliphatic (entries 2 and 12) as well as homobenzylic (entries 3, 8, 9, and 11) alcohols oxidized smoothly in a short amount of time. Ele ...
INTRODUCTION - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... carbonyl compounds using La(NO3)3.6H2O as a catalyst under solventfree conditions A mild and efficient 1, 4-addition of thiols to α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds in the presence of La(NO3)3.6H2O under solvent-free conditions at room temperature in excellent yields is described. The 1,4-addition ...
... carbonyl compounds using La(NO3)3.6H2O as a catalyst under solventfree conditions A mild and efficient 1, 4-addition of thiols to α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds in the presence of La(NO3)3.6H2O under solvent-free conditions at room temperature in excellent yields is described. The 1,4-addition ...
chapter 13 - Humble ISD
... PbCl2, AgCl, and HgCl2 are considered insoluble in water. That mean they do not dissolve in water, right? Actually, a very, very, very tiny amount will dissolve in water. We use the Ksp (Constant for Solid Products) to determine the amount that will dissolve. ...
... PbCl2, AgCl, and HgCl2 are considered insoluble in water. That mean they do not dissolve in water, right? Actually, a very, very, very tiny amount will dissolve in water. We use the Ksp (Constant for Solid Products) to determine the amount that will dissolve. ...
Reaction of orthoesters with alcohols in the presence of acidic
... binding in case of silicon dioxide which allows the nucleophilic attack by the alcohol on the positively charged carbon center of the intermediate (i) followed by the loss of alkyl group either to the substrate (forms unsymmetrical ether) or ethanol (forms diethyl ether) may result in the formation ...
... binding in case of silicon dioxide which allows the nucleophilic attack by the alcohol on the positively charged carbon center of the intermediate (i) followed by the loss of alkyl group either to the substrate (forms unsymmetrical ether) or ethanol (forms diethyl ether) may result in the formation ...
10.4 Alcohols - SCIS Teachers
... Properties of Alcohols •Alcohols have the general formula: CnH2n+1OH •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons ...
... Properties of Alcohols •Alcohols have the general formula: CnH2n+1OH •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons ...
Montmorillonite: An efficient, heterogeneous and
... report; however, some catalysis is expected. Under these conditions, the yield of the desired ketones was found to be dependent on acid chain length and the nature of the interlayer cation. (e) Friedlander synthesis: Friedlander condensation of 2-aminonicotinaldehyde on carbonyl compounds containing ...
... report; however, some catalysis is expected. Under these conditions, the yield of the desired ketones was found to be dependent on acid chain length and the nature of the interlayer cation. (e) Friedlander synthesis: Friedlander condensation of 2-aminonicotinaldehyde on carbonyl compounds containing ...
Alcohols
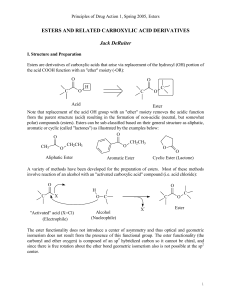
... Reaction is common in the laboratory and in living organisms • In the laboratory the reaction can be carried out in a single step if a strong acid is used as catalyst • The reactivity of the carboxylic acid is enhanced by first converting it into a carboxylic acid chloride, which then reacts with th ...
... Reaction is common in the laboratory and in living organisms • In the laboratory the reaction can be carried out in a single step if a strong acid is used as catalyst • The reactivity of the carboxylic acid is enhanced by first converting it into a carboxylic acid chloride, which then reacts with th ...
Kinetics and Equilibrium
... What can we conclude from each chart? How are the two charts defining what it means for a reaction to be in equilibrium? ...
... What can we conclude from each chart? How are the two charts defining what it means for a reaction to be in equilibrium? ...
No Slide Title
... 4.4 Families of Organic Compounds—Functional Groups, Continued Aromatics • Unsaturated cyclic compounds like benzene, which are unusually stable, are said to exhibit aromaticity. • Stability of the double bonds of benzene is due to the fact that the double bonds are not static. That is, the electro ...
... 4.4 Families of Organic Compounds—Functional Groups, Continued Aromatics • Unsaturated cyclic compounds like benzene, which are unusually stable, are said to exhibit aromaticity. • Stability of the double bonds of benzene is due to the fact that the double bonds are not static. That is, the electro ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1st Ed. ...
... Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 1st Ed. ...
Scope and Limitations - Organic Reactions Wiki
... Osmium tetroxide has since established itself as the reagent of choice for the syndihydroxylation of olefins, primarily because of its inertness toward other functional groups and lack of over-oxidation products.4 Researchers from the UpJohn company reported a convenient and reliable procedure for ...
... Osmium tetroxide has since established itself as the reagent of choice for the syndihydroxylation of olefins, primarily because of its inertness toward other functional groups and lack of over-oxidation products.4 Researchers from the UpJohn company reported a convenient and reliable procedure for ...
Alcohols and Carbonyls test
... a hint!!!! Ethanol, will in the presence of strong acids, or when the vapour is passed over aluminium oxide, undergoes dehydration to form ethene. ...
... a hint!!!! Ethanol, will in the presence of strong acids, or when the vapour is passed over aluminium oxide, undergoes dehydration to form ethene. ...
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... groups regularly spaced in alternating carbon atom long chain ...
... groups regularly spaced in alternating carbon atom long chain ...
Get Solutions - Iqraa group of institutes
... disease. Such as methemoglobinemia. SO42- : above 500 ppm of SO42- ion in drinking water causes laxative effect otherwise at moderate levels it is harmless F– : Above 2ppm concentration of F– in drinking water cause brown mottling of teeth. ∴ The concentration given in question of SO42- & NO3- in wa ...
... disease. Such as methemoglobinemia. SO42- : above 500 ppm of SO42- ion in drinking water causes laxative effect otherwise at moderate levels it is harmless F– : Above 2ppm concentration of F– in drinking water cause brown mottling of teeth. ∴ The concentration given in question of SO42- & NO3- in wa ...
Chemistry Name Mr. Reger Review Guide – Ch. 9
... 2 Al + 3 Br2 2 AlBr3 How many moles of AlBr3 are expected to form? a) 2.0 b) 3.0 c) 4.0 d) 6.0 e) 8.0 ...
... 2 Al + 3 Br2 2 AlBr3 How many moles of AlBr3 are expected to form? a) 2.0 b) 3.0 c) 4.0 d) 6.0 e) 8.0 ...
10.4 Alcohols 10.4 Alcohols
... •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •dissolve in water to some degree •are more polar ...
... •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •dissolve in water to some degree •are more polar ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.