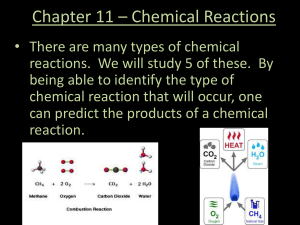
22.4: Acidity of Phenols.
... to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcohols the OH group of phenols cab participate in hydrogen bo ...
... to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcohols the OH group of phenols cab participate in hydrogen bo ...
Compounds Containing A Single Bond To A
... of alkyl halides is determined by this polar C—X bond. The characteristic reactions of alkyl halides are ...
... of alkyl halides is determined by this polar C—X bond. The characteristic reactions of alkyl halides are ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... substituents come from the Grignard reagent Grignard reagents do not add to carboxylic acids – they undergo an acid-base reaction, generating the hydrocarbon of the Grignard reagent ...
... substituents come from the Grignard reagent Grignard reagents do not add to carboxylic acids – they undergo an acid-base reaction, generating the hydrocarbon of the Grignard reagent ...
Disproportionation of Monolithium Acetylide into
... This Note establishes for the first time that disproportionation of lithium acetylide into dilithium carbide and acetylene is a reversible process in THF at 0 °C and that such an equilibrium may be readily displaced by addition of an electrophile (Scheme 2). Addition of a 1.6 M solution of n-butylli ...
... This Note establishes for the first time that disproportionation of lithium acetylide into dilithium carbide and acetylene is a reversible process in THF at 0 °C and that such an equilibrium may be readily displaced by addition of an electrophile (Scheme 2). Addition of a 1.6 M solution of n-butylli ...
Catalytic Functionalization of Methyl Group on Silicon: Iridium
... organosilicon compounds have been synthesized from methylchlorosilanes and utilized in organic and inorganic synthesis.2In these applications, the conversion of methylchlorosilanes is based on reactions at their Si−Cl bonds, which are efficiently converted into Si−O, Si−N, and Si−C bonds. In contrast, ...
... organosilicon compounds have been synthesized from methylchlorosilanes and utilized in organic and inorganic synthesis.2In these applications, the conversion of methylchlorosilanes is based on reactions at their Si−Cl bonds, which are efficiently converted into Si−O, Si−N, and Si−C bonds. In contrast, ...
Carbonyl Compounds notes
... it can be used to make pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. So the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produces soap, which usually has the formula C17H35COO-Na+. Glycerol is also formed as a useful by-product. Soap molecules have a polar end, which is the carboxylate end, which attracts water and other ...
... it can be used to make pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. So the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produces soap, which usually has the formula C17H35COO-Na+. Glycerol is also formed as a useful by-product. Soap molecules have a polar end, which is the carboxylate end, which attracts water and other ...
Unit 6: Reactions and Stoichiometry
... At the most fundamental level, the chemist needs a unit that describes a very large quantity. One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physicist). The mole is defined ...
... At the most fundamental level, the chemist needs a unit that describes a very large quantity. One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physicist). The mole is defined ...
fulltext $(function(){PrimeFaces.cw("Tooltip","widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",{id:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:j_idt801",widgetVar:"widget_formSmash_items_resultList_20_j_idt799_0_j_idt801",showEffect:"fade",hideEffect:"fade",target:"formSmash:items:resultList:20:j_idt799:0:fullText"});});
... calculations have provided a better understanding of the reaction pathways in some catalytic systems.17 Some catalysts have shown very high reactivities.10a, 12b, 18 However, this reaction typically requires high temperature (>100 oC) and there are only a few reported examples of the reaction at low ...
... calculations have provided a better understanding of the reaction pathways in some catalytic systems.17 Some catalysts have shown very high reactivities.10a, 12b, 18 However, this reaction typically requires high temperature (>100 oC) and there are only a few reported examples of the reaction at low ...
C-OH
... functional group of an amine is an amino group - a nitrogen atom bonded to one, two or three carbon atoms Really just ammonia, NH3, with one, two or three hydrogens replaced by a bond to a carbon atom ...
... functional group of an amine is an amino group - a nitrogen atom bonded to one, two or three carbon atoms Really just ammonia, NH3, with one, two or three hydrogens replaced by a bond to a carbon atom ...
24. The following reaction is at equilibrium
... (D) If the concentration of B is halved and that of A is doubled at the same time, the initial rate will double. (E) If the initial rate of appearance of A at a particular time is 0.1 M/s, the initial rate of disappearance of B is 0.2 M/s. ...
... (D) If the concentration of B is halved and that of A is doubled at the same time, the initial rate will double. (E) If the initial rate of appearance of A at a particular time is 0.1 M/s, the initial rate of disappearance of B is 0.2 M/s. ...
Review of Organic Chem II
... § mechanisms should involve cationic intermediates and reactants, not strongly anionic ones • (except for do-nothing spectators like halide or hydrogen sulfate anions) § The first step in the mechanism will involve the acid that appears in the recipe. The last step will often involve a deprotonati ...
... § mechanisms should involve cationic intermediates and reactants, not strongly anionic ones • (except for do-nothing spectators like halide or hydrogen sulfate anions) § The first step in the mechanism will involve the acid that appears in the recipe. The last step will often involve a deprotonati ...
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Alkenes
... An ''a'' is added due to inclusion of di put two consonants consecutive ...
... An ''a'' is added due to inclusion of di put two consonants consecutive ...
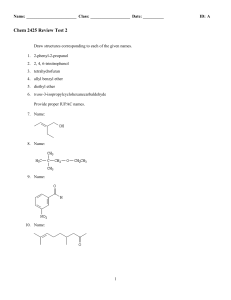
Chem 2425-Test 2 Review
... Consider the data below to answer the following question(s). Cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids from ketones and aldehydes. The nitrile functional group can be hydrolyzed by aqueous acid to yield a carboxylic acid. Nitriles can also be hydrolyzed t ...
... Consider the data below to answer the following question(s). Cyanohydrins are important intermediates in the synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids from ketones and aldehydes. The nitrile functional group can be hydrolyzed by aqueous acid to yield a carboxylic acid. Nitriles can also be hydrolyzed t ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.