8. Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
... elimination of HX (double dehydrohalogenation) Vicinal dihalides are available from addition of bromine or chlorine to an ...
... elimination of HX (double dehydrohalogenation) Vicinal dihalides are available from addition of bromine or chlorine to an ...
Development of New Synthetic Routes to Organoboronates by Catalytic Allylic Substitution and
... This thesis describes the development of new catalytic methods for the synthesis and application of organometallic reagents, mainly focusing on allylboronic acid derivatives. Thus, palladium pincer-complex catalysis has been applied for extending the scope of palladiumcatalyzed borylation reactions ...
... This thesis describes the development of new catalytic methods for the synthesis and application of organometallic reagents, mainly focusing on allylboronic acid derivatives. Thus, palladium pincer-complex catalysis has been applied for extending the scope of palladiumcatalyzed borylation reactions ...
PDF - Nanyang Technological University
... these reactions, the oxidation of tertiary amines to generate iminium intermediates, as pioneered by Murahashi et al.,[7] Li et al.[8] and others,[9–11] has received considerable attention. Carbonyl compounds, such as 1,3-dicarbonyls,[8e,f,h, 10b,g] a,bunsaturated ketones,[8f] and simple ketones[2c, ...
... these reactions, the oxidation of tertiary amines to generate iminium intermediates, as pioneered by Murahashi et al.,[7] Li et al.[8] and others,[9–11] has received considerable attention. Carbonyl compounds, such as 1,3-dicarbonyls,[8e,f,h, 10b,g] a,bunsaturated ketones,[8f] and simple ketones[2c, ...
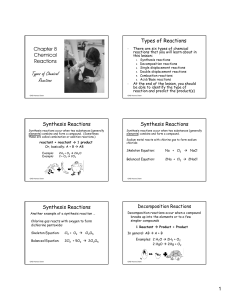
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... 1) Balance the number of atoms of each element. 2) Balance the number of electrons transferred. 3) Balance the total charge on reactants and products (Note: If #1 and #2 are done correctly, #3 will follow. Thus, it serves as a means of checking your work). ...
... 1) Balance the number of atoms of each element. 2) Balance the number of electrons transferred. 3) Balance the total charge on reactants and products (Note: If #1 and #2 are done correctly, #3 will follow. Thus, it serves as a means of checking your work). ...
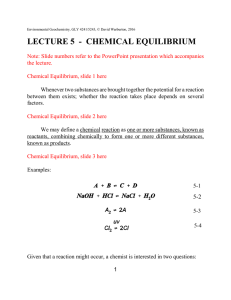
LECTURE 5 - CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
... The reason that metastable systems exist is the presence of a significant kinetic barrier. Kinetic barriers may be explained by examining the reaction on an atomic scale. To form water, breaking two H-H bonds and one O-O bond is necessary. The four resulting O-H bonds are stronger than the three bro ...
... The reason that metastable systems exist is the presence of a significant kinetic barrier. Kinetic barriers may be explained by examining the reaction on an atomic scale. To form water, breaking two H-H bonds and one O-O bond is necessary. The four resulting O-H bonds are stronger than the three bro ...
ppt
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
Equilibrium
... with one another, provided that the colliding particles have enough kinetic energy. Particles lacking the necessary kinetic energy to react, bounce apart unchanged when they collide. To illustrate the collision theory, If soft balls of clay are thrown together with great force, they will stick tight ...
... with one another, provided that the colliding particles have enough kinetic energy. Particles lacking the necessary kinetic energy to react, bounce apart unchanged when they collide. To illustrate the collision theory, If soft balls of clay are thrown together with great force, they will stick tight ...
Solutions (DOC format, upgraded July 20)
... W n RT2 1 . After some calculations with different integer n, we find that n = 13. ...
... W n RT2 1 . After some calculations with different integer n, we find that n = 13. ...
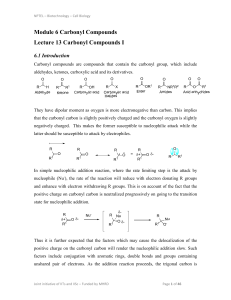
carboxylic acid
... • Carbon of original carbonyl group remains sp3-hybridized, singly bonded to four substituents ...
... • Carbon of original carbonyl group remains sp3-hybridized, singly bonded to four substituents ...
unit 6 alcohols
... Esters: Now the LG is RO-, not usually considered “good,” but the reaction takes place by nucleophilic acyl substitution, not by SN2. In this mechanism, RO- leaving is exothermic and therefore favorable. ...
... Esters: Now the LG is RO-, not usually considered “good,” but the reaction takes place by nucleophilic acyl substitution, not by SN2. In this mechanism, RO- leaving is exothermic and therefore favorable. ...
Organic Compounds containing Oxygen
... The formation of ether takes places by S N 2 mechanism mainly, with one molecule acting as the nucleophile and with another protonated molecules of the alcohol acting as the substrate. Finally this method is not useful for the preparation of ether with 30 alcohol because they form alkene too easily. ...
... The formation of ether takes places by S N 2 mechanism mainly, with one molecule acting as the nucleophile and with another protonated molecules of the alcohol acting as the substrate. Finally this method is not useful for the preparation of ether with 30 alcohol because they form alkene too easily. ...
Pauling Scale of Electronegativities for the Various Elements
... C12 → C131Step 4b: In KMnO4 manganese is at oxidation number +7 and will be reduced. If the solution is acidic, the Mn will go to a metallic oxidation number (+3 or +2). If the soluttion is basic, it goes to a nonmetallic oxidation number (+4, +6 or +7). H+ KMnO4 → Mn3+ (+3 is the first stable oxida ...
... C12 → C131Step 4b: In KMnO4 manganese is at oxidation number +7 and will be reduced. If the solution is acidic, the Mn will go to a metallic oxidation number (+3 or +2). If the soluttion is basic, it goes to a nonmetallic oxidation number (+4, +6 or +7). H+ KMnO4 → Mn3+ (+3 is the first stable oxida ...
View PDF
... d. no product can be formed. ____ 18. What is the maximum possible amount of product obtained in a chemical reaction? a. theoretical yield c. mole ratio b. percent yield d. actual yield ____ 19. A chemist interested in the efficiency of a chemical reaction would calculate the a. mole ratio. c. perce ...
... d. no product can be formed. ____ 18. What is the maximum possible amount of product obtained in a chemical reaction? a. theoretical yield c. mole ratio b. percent yield d. actual yield ____ 19. A chemist interested in the efficiency of a chemical reaction would calculate the a. mole ratio. c. perce ...
Exam 3 - Napa Valley College
... mean that you would get a lot of by-products but you would end up getting more product also (SN1 major, E1 minor). 4) There are a number of ways of substituting a halogen for an alcohol group, but some ways are better than others. What advantage is there in using PCl3 rather than HCl in the chloride ...
... mean that you would get a lot of by-products but you would end up getting more product also (SN1 major, E1 minor). 4) There are a number of ways of substituting a halogen for an alcohol group, but some ways are better than others. What advantage is there in using PCl3 rather than HCl in the chloride ...
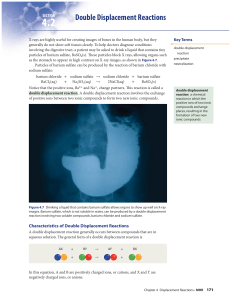
2 Chemical equilibrium occurs when a reaction and its reverse
... ∆n = (moles of gaseous product) − (moles of gaseous reactant) ...
... ∆n = (moles of gaseous product) − (moles of gaseous reactant) ...
Chemistry
... Stereoisomerism – geometrical and optical, examples, facial and meridional as geometrical isomers- example. Importance of coordination compounds: In biological systems, qualitative analysis, extraction of metals, examples. ...
... Stereoisomerism – geometrical and optical, examples, facial and meridional as geometrical isomers- example. Importance of coordination compounds: In biological systems, qualitative analysis, extraction of metals, examples. ...
Full answers
... The ratio of neutrons to protons (N/Z) is approximately 1 for low atomic numbers (Z 20), but it slowly rises to about 1.5 as Z increases. All elements with Z > 83 are unstable. Atoms with even numbers of N and Z tend to be more stable than those with odd numbers. There are some particularly stable ...
... The ratio of neutrons to protons (N/Z) is approximately 1 for low atomic numbers (Z 20), but it slowly rises to about 1.5 as Z increases. All elements with Z > 83 are unstable. Atoms with even numbers of N and Z tend to be more stable than those with odd numbers. There are some particularly stable ...
Crown ethers
... Crown ethers have the unique property of forming complexes with positive ions (Na+, K+ ) the positive ions fit within the macrocyclic rings selectively depending on the sizes. For example [18]crown-6 binds K+ more tightly than it does the smaller Na+ (too loose a fit) or the larger Cs+ (too large t ...
... Crown ethers have the unique property of forming complexes with positive ions (Na+, K+ ) the positive ions fit within the macrocyclic rings selectively depending on the sizes. For example [18]crown-6 binds K+ more tightly than it does the smaller Na+ (too loose a fit) or the larger Cs+ (too large t ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.