Chemical Equilibria - Beck-Shop
... Q: Why are the terms involving solids and liquids not included in the equilibrium constant expression for heterogeneous equilibrium? A: For a given temperature, the saturated vapour pressures of solids (and that of liquids) are constant. In addition, even though their actual amounts may change, both ...
... Q: Why are the terms involving solids and liquids not included in the equilibrium constant expression for heterogeneous equilibrium? A: For a given temperature, the saturated vapour pressures of solids (and that of liquids) are constant. In addition, even though their actual amounts may change, both ...
Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry
... expression CnH2n+2. The structural formula, shown for the first five alkanes in the table, shows each carbon atom and the elements that are attached to it. This structural formula is important when we begin to discuss more complex hydrocarbons. The simple alkanes share many properties in common. All ...
... expression CnH2n+2. The structural formula, shown for the first five alkanes in the table, shows each carbon atom and the elements that are attached to it. This structural formula is important when we begin to discuss more complex hydrocarbons. The simple alkanes share many properties in common. All ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry STOICHIOMETRY: The chemical arithmetic
... • Chemical Reactions do not always go the way we expect them to • Using stoichiometry we can calculate the theoretical (Maximum) amount of product formed in a reaction. ...
... • Chemical Reactions do not always go the way we expect them to • Using stoichiometry we can calculate the theoretical (Maximum) amount of product formed in a reaction. ...
Chapter 8
... There are three types of yields we can define for a chemical reaction. Theoretical yield - The maximum amount of product that can be formed from the starting materials used in the reaction. Actual yield - The observed yield for a chemical reaction. Percent yield - The percent of the theoretical yiel ...
... There are three types of yields we can define for a chemical reaction. Theoretical yield - The maximum amount of product that can be formed from the starting materials used in the reaction. Actual yield - The observed yield for a chemical reaction. Percent yield - The percent of the theoretical yiel ...
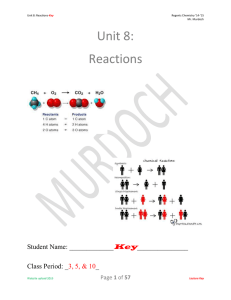
Unit 8: Reactions
... The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical reaction or physical change. Missing Mass examples: 1. Given that 35.0 g ...
... The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical reaction or physical change. Missing Mass examples: 1. Given that 35.0 g ...
Amino Acids and Proteins
... two enantiomers obtained must be separated if they are to be used in biological applications. This is not an easy task. Two enantiomers have the same physical properties, so they cannot be separated by common physical methods, such as distillation or chromatography. Moreover, they react in the same ...
... two enantiomers obtained must be separated if they are to be used in biological applications. This is not an easy task. Two enantiomers have the same physical properties, so they cannot be separated by common physical methods, such as distillation or chromatography. Moreover, they react in the same ...
Chapter 14 Review
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
1. What energy changes occur when chemical bonds are formed
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
molecules
... All of the reactions were carried out at room temperature under air in a 25 mL flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar. A solution of NaIO4 (2 mmol) in H2O (10 mL) was added to a mixture of alkene or alkane (1 mmol), Mn(Br8TPPS)-Ad 400 (11 mol) and imidazole (0.2 mmol) in CH3CN (10 mL). The pro ...
... All of the reactions were carried out at room temperature under air in a 25 mL flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar. A solution of NaIO4 (2 mmol) in H2O (10 mL) was added to a mixture of alkene or alkane (1 mmol), Mn(Br8TPPS)-Ad 400 (11 mol) and imidazole (0.2 mmol) in CH3CN (10 mL). The pro ...
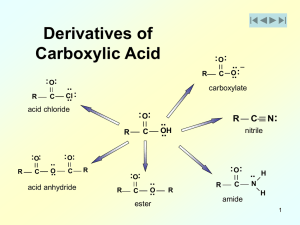
8.1 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers 8.2 Naming Alcohols
... Methyl Alcohol (CH3OH, methanol) Methyl alcohol is the simplest (smallest) alcohol and is commonly known as wood alcohol because it was once prepared by heating wood in the absence of air. Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH, ethanol) Ethyl alcohol is one of the oldest known pure organic compounds. Ethyl alcoho ...
... Methyl Alcohol (CH3OH, methanol) Methyl alcohol is the simplest (smallest) alcohol and is commonly known as wood alcohol because it was once prepared by heating wood in the absence of air. Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH, ethanol) Ethyl alcohol is one of the oldest known pure organic compounds. Ethyl alcoho ...
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics
... The third condition that must be met for a reaction to occur is that the orientation of the collision must allow for the breaking and forming of bonds necessary to form products. For example, chloride ions react with the cationic species C(CH3)31 to form 2-chloro-2-methyl propane. If the chloride io ...
... The third condition that must be met for a reaction to occur is that the orientation of the collision must allow for the breaking and forming of bonds necessary to form products. For example, chloride ions react with the cationic species C(CH3)31 to form 2-chloro-2-methyl propane. If the chloride io ...
Chapter 7. Alcohols, Thiols, Phenols, Ethers
... functional groups contain two pairs of non-bonding electrons and are the cornerstone of many organic processes. The structures for alcohols, phenols, thiols, ethers and thioethers are shown below. Alkyl-OH alcohol ...
... functional groups contain two pairs of non-bonding electrons and are the cornerstone of many organic processes. The structures for alcohols, phenols, thiols, ethers and thioethers are shown below. Alkyl-OH alcohol ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.