Elimination Reactions
... Explaination of Zaitsev’s rule: When you remove a hydrogen atom from the more branched position, you are forming a more highly substituted alkene. ...
... Explaination of Zaitsev’s rule: When you remove a hydrogen atom from the more branched position, you are forming a more highly substituted alkene. ...
Organic Chemistry
... You can imagine complicated R' groups that may be much more difficult to name as alkyl or aryl groups than those we have shown in Figures 15.30 and 15.32. When faced with naming such complicated molecules, organic chemists often consult specialized books on organic nomenclature. However, many ester ...
... You can imagine complicated R' groups that may be much more difficult to name as alkyl or aryl groups than those we have shown in Figures 15.30 and 15.32. When faced with naming such complicated molecules, organic chemists often consult specialized books on organic nomenclature. However, many ester ...
aa-2005-38-71-negishi - University of Windsor
... types of cross-coupling reactions, and most of these reactions have indeed been developed. Until recently, the use of alkyl electrophiles lacking proximal π bonds had been considered to be categorically very difficult, and the task of Pd-catalyzed alkylation had been achieved by using alkylmetals. T ...
... types of cross-coupling reactions, and most of these reactions have indeed been developed. Until recently, the use of alkyl electrophiles lacking proximal π bonds had been considered to be categorically very difficult, and the task of Pd-catalyzed alkylation had been achieved by using alkylmetals. T ...
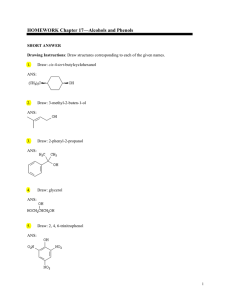
HOMEWORK Chapter 17—Alcohols and Phenols
... In E2 elimination, dehydration proceeds most readily when the two groups to be eliminated have a trans-diaxial relationship. In this compound, the only hydrogen with the proper geometric relationship to the −OH group is at C6 so the major product of this reaction is 3methylcyclohexene. ...
... In E2 elimination, dehydration proceeds most readily when the two groups to be eliminated have a trans-diaxial relationship. In this compound, the only hydrogen with the proper geometric relationship to the −OH group is at C6 so the major product of this reaction is 3methylcyclohexene. ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... Elimination occurs in the direction that gives the less-substituted double bond. This is called the Hofmann rule. H2C ...
... Elimination occurs in the direction that gives the less-substituted double bond. This is called the Hofmann rule. H2C ...
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur
... In Tollens’ test, • Tollens’ reagent, which contains Ag+, oxidizes aldehydes but not ketones. • Ag+ is reduced to metallic Ag, which appears as a “mirror” in the test tube. ...
... In Tollens’ test, • Tollens’ reagent, which contains Ag+, oxidizes aldehydes but not ketones. • Ag+ is reduced to metallic Ag, which appears as a “mirror” in the test tube. ...
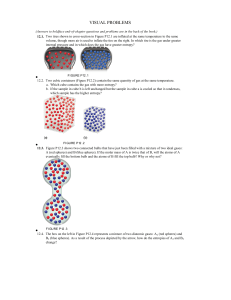
visual problems - Western Oregon University
... 12.38. Use the standard molar entropies in Appendix 4 to calculate the ∆S° value for each of the following reactions of sulfur compounds. a. H2S(g) + 3/2 O2(g) → H2O(g) + SO2(g) b. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) c. SO3(g) + H2O(ℓ) → H2SO4(aq) d. S(g) + O2(g) → SO2(g) 12.39. Ozone Layer The following re ...
... 12.38. Use the standard molar entropies in Appendix 4 to calculate the ∆S° value for each of the following reactions of sulfur compounds. a. H2S(g) + 3/2 O2(g) → H2O(g) + SO2(g) b. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) c. SO3(g) + H2O(ℓ) → H2SO4(aq) d. S(g) + O2(g) → SO2(g) 12.39. Ozone Layer The following re ...
Chapter 16: Reaction Rates
... molecules collide with enough energy to overcome the barrier, and the products formed lie at a lower energy level. Recall that reactions that lose energy are called exothermic reactions. For many reactions, the process from reactants to products is reversible. Figure 16.6 illustrates the reverse end ...
... molecules collide with enough energy to overcome the barrier, and the products formed lie at a lower energy level. Recall that reactions that lose energy are called exothermic reactions. For many reactions, the process from reactants to products is reversible. Figure 16.6 illustrates the reverse end ...
Rh(acac)(CO)(PR1R2R3) - University of the Free State
... octahedral geometries. The oxidative addition and reductive elimination reactions from Rh(I) to Rh(III) and vice versa, has transformed the catalytic industry and has produced many fascinating reactions over the years. ...
... octahedral geometries. The oxidative addition and reductive elimination reactions from Rh(I) to Rh(III) and vice versa, has transformed the catalytic industry and has produced many fascinating reactions over the years. ...
Equilibrium Booklet - mrstorie
... d) increasing the volume of the container. e) adding a catalyst. 2. For the reaction: CH4(g) + H2O(g) + 49.3 kJ CO(g) + 3 H2(g) Predict the effect on the position of the equilibrium that results from a) increasing temperature. b) decreasing temperature. c) decreasing the pressure. d) decreasing t ...
... d) increasing the volume of the container. e) adding a catalyst. 2. For the reaction: CH4(g) + H2O(g) + 49.3 kJ CO(g) + 3 H2(g) Predict the effect on the position of the equilibrium that results from a) increasing temperature. b) decreasing temperature. c) decreasing the pressure. d) decreasing t ...
RheniumCatalyzed Deoxydehydration of Diols and Polyols
... While the majority of oil, coal, and gas is used for energy production, the realization of an economy completely independent of fossil resources also requires biomass-based substitutes for polymers, medicine, pesticides, and so forth.[1] The evergrowing world population makes it questionable to use ...
... While the majority of oil, coal, and gas is used for energy production, the realization of an economy completely independent of fossil resources also requires biomass-based substitutes for polymers, medicine, pesticides, and so forth.[1] The evergrowing world population makes it questionable to use ...
Kinetics Workbook - School District 67
... Even though there are more than four billion collisions per second between N and O the amount of product after a year is too small to detect. Using the collision theory, give two reasons why this reaction might be slow. i) ii) ...
... Even though there are more than four billion collisions per second between N and O the amount of product after a year is too small to detect. Using the collision theory, give two reasons why this reaction might be slow. i) ii) ...
Document
... reverse reaction becomes large enough to create equilibrium. So, this equilibrium has a higher concentration of products than reactants. This type of equilibrium, also shown by using two arrows, is shown below. Notice that the forward reaction has a longer arrow to show that the products are favored ...
... reverse reaction becomes large enough to create equilibrium. So, this equilibrium has a higher concentration of products than reactants. This type of equilibrium, also shown by using two arrows, is shown below. Notice that the forward reaction has a longer arrow to show that the products are favored ...
alcohols03
... Alcohols and phenols have similar geometry to HOH. The R-O-H bond angle is approximately tetrahedral (109) and the ‘O’ atom is sp3 hybridized. Because of the presence of the hydroxyl group, alcohols (and phenols) have significantly higher boiling points than their constitutional (structural) is ...
... Alcohols and phenols have similar geometry to HOH. The R-O-H bond angle is approximately tetrahedral (109) and the ‘O’ atom is sp3 hybridized. Because of the presence of the hydroxyl group, alcohols (and phenols) have significantly higher boiling points than their constitutional (structural) is ...
review-rough
... 26. The structure given below is a polymer classified as a polyamide. This polymer is stable in temperatures above 350°C, and can be used as a protective coating on hot surfaces. What monomers were used to make this polyamide? ...
... 26. The structure given below is a polymer classified as a polyamide. This polymer is stable in temperatures above 350°C, and can be used as a protective coating on hot surfaces. What monomers were used to make this polyamide? ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.