Copper-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions Using Carbon
... incorporate the use of C-H bonds as substrates for C-C bond formation processes. In this chapter, a concise review of oxidative cross-coupling reactions relevant to this thesis will be presented. Furthermore, the examples will be focused heavily on the use of organic peroxides as the oxidant, with s ...
... incorporate the use of C-H bonds as substrates for C-C bond formation processes. In this chapter, a concise review of oxidative cross-coupling reactions relevant to this thesis will be presented. Furthermore, the examples will be focused heavily on the use of organic peroxides as the oxidant, with s ...
PDF File
... observed distances between electron densities. The possible reasons for this difference have been discussed in the literature (10, 13, 16) and are not the subject of this report. Here we determine to what extent the observed ground state ribozyme environment around the catalytic metal ion, MA, is su ...
... observed distances between electron densities. The possible reasons for this difference have been discussed in the literature (10, 13, 16) and are not the subject of this report. Here we determine to what extent the observed ground state ribozyme environment around the catalytic metal ion, MA, is su ...
Practice Problems in Biomedical Organic Chemistry
... that students might encounter during their professional careers. Our plan is to release sets of organic chemistry problems in a three volume series. The problems are intended to serve as self-directed learning tools, which students can use at a pace that meets their individual educational needs. We ...
... that students might encounter during their professional careers. Our plan is to release sets of organic chemistry problems in a three volume series. The problems are intended to serve as self-directed learning tools, which students can use at a pace that meets their individual educational needs. We ...
Chemical Reactivity and Biological Activity of Diketene
... The alkylating potential of diketene (4-methylene-2-oxetanone), the basic unit of many derivatives of pesticides, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs, was investigated kinetically. The nucleophile 4-(pnitrobenzyl)pyridine (NBP), a trap for alkylating agents with nucleophilic characteristics si ...
... The alkylating potential of diketene (4-methylene-2-oxetanone), the basic unit of many derivatives of pesticides, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs, was investigated kinetically. The nucleophile 4-(pnitrobenzyl)pyridine (NBP), a trap for alkylating agents with nucleophilic characteristics si ...
Alcohols - La Salle University
... carbon with the —OH group. • Drop the -e from the alkane name; add -ol. • Number the chain, giving the —OH group the ...
... carbon with the —OH group. • Drop the -e from the alkane name; add -ol. • Number the chain, giving the —OH group the ...
Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules. These forces are much weaker than all other types of bonding. They are formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles caused by movement of electrons in atoms and molecules. The strength of Lon ...
... attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules. These forces are much weaker than all other types of bonding. They are formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles caused by movement of electrons in atoms and molecules. The strength of Lon ...
SMK RAJA PEREMPUAN, IPOH
... atoms which are joined directly to the benzene ring to become a carboxyl group, and the remaining alkyl chains will turn into water and CO2 21. determine the products of halogenation of methylbenzene (toluene) with Lewis acid catalysts such as AlCl3and FeCl3 and in the presence of light only 22. pre ...
... atoms which are joined directly to the benzene ring to become a carboxyl group, and the remaining alkyl chains will turn into water and CO2 21. determine the products of halogenation of methylbenzene (toluene) with Lewis acid catalysts such as AlCl3and FeCl3 and in the presence of light only 22. pre ...
Oxidation involving CO System ( O
... Metabolizes 1° and 2° alcohols and aldehydes containing at least one “H” attached to a-C; 1° alcohols typically go to the aldehyde then acid; 2° alcohols are converted to ketone, which cannot be further converted to the acid. The aldehyde is converted back to an alcohol by alcohol (keto) reductases ...
... Metabolizes 1° and 2° alcohols and aldehydes containing at least one “H” attached to a-C; 1° alcohols typically go to the aldehyde then acid; 2° alcohols are converted to ketone, which cannot be further converted to the acid. The aldehyde is converted back to an alcohol by alcohol (keto) reductases ...
unit-4-notes-1_enthalpy-and-entropy
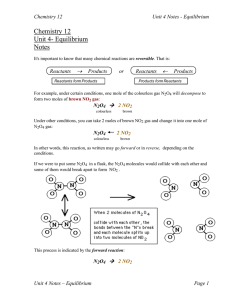
... 2. Letting material into or out of the system will affect rates so a system at equilibrium is a closed system. 3. Again, consider the equilibrium reaction: N2O4 2 NO2 In the example that we did to construct the graphs, we had started with pure N2O4 and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at t ...
... 2. Letting material into or out of the system will affect rates so a system at equilibrium is a closed system. 3. Again, consider the equilibrium reaction: N2O4 2 NO2 In the example that we did to construct the graphs, we had started with pure N2O4 and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at t ...
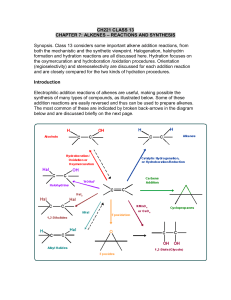
CH221 CLASS 13
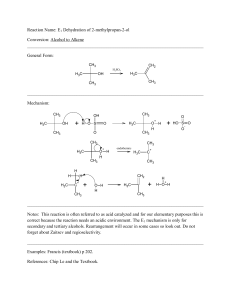
... Addition of water to alkenes to give alcohols is one of the most important reactions of alkenes. In industry, this is accomplished by the use of strong acid catalysts and high temperatures, but this is not really of much value in the laboratory. However, tertiary alcohols can be produced from highly ...
... Addition of water to alkenes to give alcohols is one of the most important reactions of alkenes. In industry, this is accomplished by the use of strong acid catalysts and high temperatures, but this is not really of much value in the laboratory. However, tertiary alcohols can be produced from highly ...
Organic Chemistry
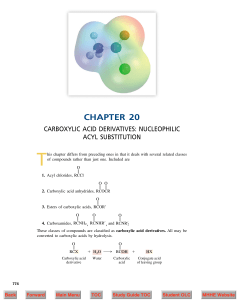
... Use of Carboxylate Anion Nucleophile to form Esters . 87 Hydrolysis of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Reaction of Acyl Halide with Ammonia or Amine . . . 89 Esterification of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 Esterification of Acid Anhydrides . . . . . . ...
... Use of Carboxylate Anion Nucleophile to form Esters . 87 Hydrolysis of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Reaction of Acyl Halide with Ammonia or Amine . . . 89 Esterification of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 Esterification of Acid Anhydrides . . . . . . ...
Chemistry 360 - Athabasca University
... beginning the labs. In order to successfully complete the laboratory component, please be aware of the following 4 step process of instruction. It is the intention of this Chem360 Report Workbook to provide you with the means of completing all four steps. Step 1: First we tell you what you are going ...
... beginning the labs. In order to successfully complete the laboratory component, please be aware of the following 4 step process of instruction. It is the intention of this Chem360 Report Workbook to provide you with the means of completing all four steps. Step 1: First we tell you what you are going ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... of the TMS-enol ether of 2 (TMSOTf, Et3N), cleanly provided the C10 tertiary alcohol (18, 99 %). This was then utilized to set the adjacent C11 alcohol stereocenter through hydroxydirected reduction with Me4NBH(OAc)3 (87 %, > 19:1 d.r.).[22] TES protection proved necessary to facilitate the subseque ...
... of the TMS-enol ether of 2 (TMSOTf, Et3N), cleanly provided the C10 tertiary alcohol (18, 99 %). This was then utilized to set the adjacent C11 alcohol stereocenter through hydroxydirected reduction with Me4NBH(OAc)3 (87 %, > 19:1 d.r.).[22] TES protection proved necessary to facilitate the subseque ...
Test bank questions
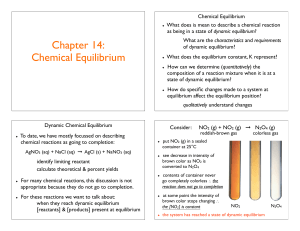
... Which of the following is a true statement about chemical equilibria in general? A. At equilibrium the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants, that is, [products] = [reactants]. B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is onl ...
... Which of the following is a true statement about chemical equilibria in general? A. At equilibrium the total concentration of products equals the total concentration of reactants, that is, [products] = [reactants]. B. Equilibrium is the result of the cessation of all chemical change. C. There is onl ...
Nomenclature Chapter
... R = any general carbon group (it sometimes includes hydrogen too) Ar = any general aromatic group, (when more specificity than ‘just’ R is desired) The foundation of organic nomenclature requires an ability to name alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. Learning the rules for these groups will be your bigges ...
... R = any general carbon group (it sometimes includes hydrogen too) Ar = any general aromatic group, (when more specificity than ‘just’ R is desired) The foundation of organic nomenclature requires an ability to name alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. Learning the rules for these groups will be your bigges ...
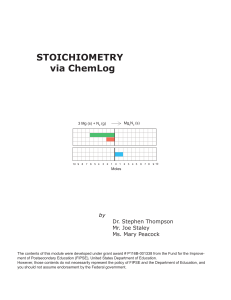
STOICHIOMETRY via ChemLog - Small
... Count the number of red elements before the reaction. Count the number of red elements after the reaction. Count the number of blue elements before the reaction. Count the number of blue elements after the reaction. Compare the number of red elements before and after the reaction. Compare the number ...
... Count the number of red elements before the reaction. Count the number of red elements after the reaction. Count the number of blue elements before the reaction. Count the number of blue elements after the reaction. Compare the number of red elements before and after the reaction. Compare the number ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.