Review topics-blog
... Chapter 7 deals with nuclear and periodic trends. One such periodic trend is ionization energy, which mostly increases from left to right across a row of the periodic table but decreases from top to bottom down a group. We will discuss why, as well we will discuss other trends like atomic size, i ...
... Chapter 7 deals with nuclear and periodic trends. One such periodic trend is ionization energy, which mostly increases from left to right across a row of the periodic table but decreases from top to bottom down a group. We will discuss why, as well we will discuss other trends like atomic size, i ...
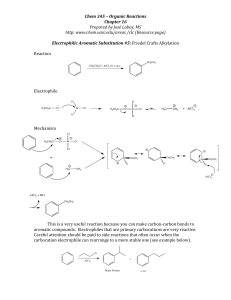
EAS Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
... This is a very useful reaction because you can make carbon-‐carbon bonds to aromatic compounds. Electrophiles that are primary carbocations are very reactive. Careful attention should be paid to side ...
... This is a very useful reaction because you can make carbon-‐carbon bonds to aromatic compounds. Electrophiles that are primary carbocations are very reactive. Careful attention should be paid to side ...
Slide 1 - Alfred State College intranet site
... Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
... Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet
... Reactants are written on the left, and products are written on the right. In a balanced equation the total numbers of atoms of each kind on both sides are the same. To achieve a balance, we write coefficients in front of each chemical species, although the number 1 is never written as a coefficient. ...
... Reactants are written on the left, and products are written on the right. In a balanced equation the total numbers of atoms of each kind on both sides are the same. To achieve a balance, we write coefficients in front of each chemical species, although the number 1 is never written as a coefficient. ...
Structure of Organic Compounds
... • Water is the most abundant and important inorganic material, making up 60% - 80% of all cells and 2/3 of body weight ...
... • Water is the most abundant and important inorganic material, making up 60% - 80% of all cells and 2/3 of body weight ...
Fundamentals Of Organic Chemistry
... In process of dehydration inter mediate carbocation formation takes place so that always remember reactivity of alcohols towards dehydration due to intermediate stability is 3°>2°>1°>CH3OH more the stability of intermediate higher is the reactivity of the initial ...
... In process of dehydration inter mediate carbocation formation takes place so that always remember reactivity of alcohols towards dehydration due to intermediate stability is 3°>2°>1°>CH3OH more the stability of intermediate higher is the reactivity of the initial ...
Science 1206 Unit 3 Part 1
... the nearest noble gas configuration. › These form cations › Since they lose electrons, these atoms now ...
... the nearest noble gas configuration. › These form cations › Since they lose electrons, these atoms now ...
04_Lecture_Presentation
... Overview: Carbon: The Backbone of Life • Living organisms consist mostly of carbon-based compounds • Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form large, complex, and diverse molecules • Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter are all composed of carbon comp ...
... Overview: Carbon: The Backbone of Life • Living organisms consist mostly of carbon-based compounds • Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form large, complex, and diverse molecules • Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter are all composed of carbon comp ...
Organic Chemistry Practice – Part 1
... 1. choose the longest chain of carbon atoms which contain the –OH group 2. number the chain so that the –OH group is the smallest number 3. Name all the side branches 4. The position of the –OH group is part of the parent chain name Example: ...
... 1. choose the longest chain of carbon atoms which contain the –OH group 2. number the chain so that the –OH group is the smallest number 3. Name all the side branches 4. The position of the –OH group is part of the parent chain name Example: ...
Ethers
... Common Name • Ethers can be named by naming the carbon groups as a separate word and ending it with the word ether. • They are named by the alkyl groups bonded to each other. ...
... Common Name • Ethers can be named by naming the carbon groups as a separate word and ending it with the word ether. • They are named by the alkyl groups bonded to each other. ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... conformations (10.4) discrete, distinct isomeric structures that may be converted one to the other by rotation about the bonds in the molecule. conformers (10.4) discrete, distinct isomeric structures that may be converted one to the other by rotation about the bonds in the molecule. constitutional ...
... conformations (10.4) discrete, distinct isomeric structures that may be converted one to the other by rotation about the bonds in the molecule. conformers (10.4) discrete, distinct isomeric structures that may be converted one to the other by rotation about the bonds in the molecule. constitutional ...
Chemistry 1110 – Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
... containing one degree of unsaturation does not necessarily have to be unsaturated (you will learn more about this topic from your instructor in the classroom). A saturated compound is one that contains only single bonds while an unsaturated compound is one that contains at least one multiple bond; i ...
... containing one degree of unsaturation does not necessarily have to be unsaturated (you will learn more about this topic from your instructor in the classroom). A saturated compound is one that contains only single bonds while an unsaturated compound is one that contains at least one multiple bond; i ...
III. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Reactions
... stable and therefore reactions involving these still need a boost of energy or the help of a catalyst. ...
... stable and therefore reactions involving these still need a boost of energy or the help of a catalyst. ...
Lecture 21 – Cations, Anions and Hydrolysis in
... (b) (3 marks) What is a diagonal relationship? To which elements does this term apply in the periodic table? (c) (4 marks) Explain the difference between hydrolysis and hydration of a metal ion. Illustrate your answer with an appropriate example. 1 (a) Answer In group 13-17, in 4th 5th and 6th perio ...
... (b) (3 marks) What is a diagonal relationship? To which elements does this term apply in the periodic table? (c) (4 marks) Explain the difference between hydrolysis and hydration of a metal ion. Illustrate your answer with an appropriate example. 1 (a) Answer In group 13-17, in 4th 5th and 6th perio ...
Introduction
... TMS is not useful for water soluble compounds,for this DSS used.(DSS-2,2-dimethyl-2 silapentane-5-sulphonate) ...
... TMS is not useful for water soluble compounds,for this DSS used.(DSS-2,2-dimethyl-2 silapentane-5-sulphonate) ...
Simplified Table of Proton NMR Chemical Shifts Chemical Shift
... Simplified Table of Proton NMR Chemical Shifts Chemical Shift, ...
... Simplified Table of Proton NMR Chemical Shifts Chemical Shift, ...
today`s PowerPoint
... • You can use 2,4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine or 2,4-DNP to test for the carbonyl group. • A solution of 2,4-DNP, methanol and H2SO4 is known as Brady’s reagent. • A positive test will give an orange/yellow precipitate. • Both aldehydes and ketones will test positively. No other compounds (e.g. Carboxy ...
... • You can use 2,4 – dinitrophenylhydrazine or 2,4-DNP to test for the carbonyl group. • A solution of 2,4-DNP, methanol and H2SO4 is known as Brady’s reagent. • A positive test will give an orange/yellow precipitate. • Both aldehydes and ketones will test positively. No other compounds (e.g. Carboxy ...
Chemistry - Choithram School
... iii)Reaction of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH , alkenes are the major products. iv)Chloroform is stored in closed dark coloured bottles completely filled so that air is kept out. v)Grignard’s reagent should be prepared under anhy ...
... iii)Reaction of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH , alkenes are the major products. iv)Chloroform is stored in closed dark coloured bottles completely filled so that air is kept out. v)Grignard’s reagent should be prepared under anhy ...
AP Chem -‐ Unit 1 Part 1 AP Chemistry 2016
... • Identify different properties of solids and liquids based on both differences in structure at both a particle and macro level. • Identify and name ionic compounds. • Identify and name molecular compound ...
... • Identify different properties of solids and liquids based on both differences in structure at both a particle and macro level. • Identify and name ionic compounds. • Identify and name molecular compound ...
Other useful things to know about atoms
... solid, liquid or gas. (see also download 2.3a) Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed in chemical or physical changes. (In chemical reactions the atoms are rearranged.) A good analogy is Lego blocks – you can make all sorts of models, but the blocks remain unchanged (see slide 18 of download 2.1 ...
... solid, liquid or gas. (see also download 2.3a) Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed in chemical or physical changes. (In chemical reactions the atoms are rearranged.) A good analogy is Lego blocks – you can make all sorts of models, but the blocks remain unchanged (see slide 18 of download 2.1 ...
Survival Organic Chemistry Part I: Molecular Models
... electron (Lewis) structures, covalent bond, ionic bond, single, double and triple bonds, and bond angles. As a way to get a handle on these concepts try the following problems; 1. Write the general rule for determining whether a chemical formula represents an ionic or a covalent compound. For exampl ...
... electron (Lewis) structures, covalent bond, ionic bond, single, double and triple bonds, and bond angles. As a way to get a handle on these concepts try the following problems; 1. Write the general rule for determining whether a chemical formula represents an ionic or a covalent compound. For exampl ...
Full answers
... • Transition metals are often found in coordination complexes such as [NiCl4]2–. What is a complex? A complex contains a metal cation surrounded by ligands which bond to the cation using one or more lone pairs. The complex can be positive, negative or neutral depending on the charges on the metal an ...
... • Transition metals are often found in coordination complexes such as [NiCl4]2–. What is a complex? A complex contains a metal cation surrounded by ligands which bond to the cation using one or more lone pairs. The complex can be positive, negative or neutral depending on the charges on the metal an ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) ISSN: 2278-5736.
... In this letter, we wish to report a mild efficient and ecofriendly method to protect 1,2 or 1,3 diols as their acetonides with acetone and a cation exchange resin. The reaction can be carried out in toluene or without toluene as a solvent. The selectivity and versatility of the of the thermal solven ...
... In this letter, we wish to report a mild efficient and ecofriendly method to protect 1,2 or 1,3 diols as their acetonides with acetone and a cation exchange resin. The reaction can be carried out in toluene or without toluene as a solvent. The selectivity and versatility of the of the thermal solven ...
Starter
... Give pupils copies of worksheet 8Fd/5 (on the website), and ask them to produce questions to fit the answers given. Pupils can work in small groups before holding a short class discussion to decide what the questions should be. This can be done orally or in writing. Note that the answers cover work ...
... Give pupils copies of worksheet 8Fd/5 (on the website), and ask them to produce questions to fit the answers given. Pupils can work in small groups before holding a short class discussion to decide what the questions should be. This can be done orally or in writing. Note that the answers cover work ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.