Matter- Types and Changes
... • Element - the simplest type of substance with unique physical and chemical properties. It cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by physical or chemical means. • Compound - a substance composed of two or more elements which are chemically combined. ...
... • Element - the simplest type of substance with unique physical and chemical properties. It cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by physical or chemical means. • Compound - a substance composed of two or more elements which are chemically combined. ...
elements of chemistry unit
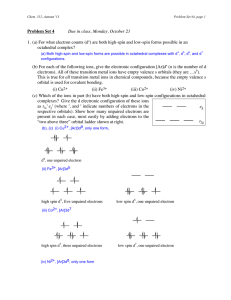
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
1 - vnhsteachers
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
Chem Ch 4 test review
... What is a period? Identify elements on the periodic table by their periods or groups. What do elements in groups have in common? Why? 9. Describe the natural states of the elements, i.e., which are solids, liquids, or gases at around 25oC. What is a diatomic molecule? Which elements are diatomic mol ...
... What is a period? Identify elements on the periodic table by their periods or groups. What do elements in groups have in common? Why? 9. Describe the natural states of the elements, i.e., which are solids, liquids, or gases at around 25oC. What is a diatomic molecule? Which elements are diatomic mol ...
Organic Naming Notes
... two carbon groups. Naming: 1. Name the carbon chains coming off the oxygen as alkyl groups. 2. End the name in ether. 3. Put a the prefix di on the name of the carbon chain if they repeat themselves ...
... two carbon groups. Naming: 1. Name the carbon chains coming off the oxygen as alkyl groups. 2. End the name in ether. 3. Put a the prefix di on the name of the carbon chain if they repeat themselves ...
Chapter 20 Carbohydrates
... • The new carbon stereocenter created in forming the cyclic structure is called the anomeric carbon. • Stereoisomers that differ in configuration only at the anomeric carbon are called anomers. • The anomeric carbon of an aldose is C-1; that of the most common ketose is C-2. ...
... • The new carbon stereocenter created in forming the cyclic structure is called the anomeric carbon. • Stereoisomers that differ in configuration only at the anomeric carbon are called anomers. • The anomeric carbon of an aldose is C-1; that of the most common ketose is C-2. ...
Lecture outline handouts
... In molecules with multiple carbon atoms, every carbon atom bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape. ...
... In molecules with multiple carbon atoms, every carbon atom bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape. ...
Ch. 4
... In molecules with multiple carbon atoms, every carbon atom bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape. ...
... In molecules with multiple carbon atoms, every carbon atom bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape. ...
Chem 30B Spring 2004 QUIZ #1 KEY Weds April 14th / 30
... BONUS QUESTION: What is the product of the Pinacol rearrangement shown below? Write your answer (just the structure) clearly in the box provided on the cover sheet to this quiz. There will be NO partial credit – either your structure is right or wrong. The next blank page can be used for working thr ...
... BONUS QUESTION: What is the product of the Pinacol rearrangement shown below? Write your answer (just the structure) clearly in the box provided on the cover sheet to this quiz. There will be NO partial credit – either your structure is right or wrong. The next blank page can be used for working thr ...
Class Notes
... In molecules with multiple carbon atoms, every carbon atom bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape. ...
... In molecules with multiple carbon atoms, every carbon atom bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape. ...
Outline Ch 8 - Mead`s Fabulous Weebly
... Molecules: neutral group of atoms joined by covalent bonds or sharing of electrons Some molecules are diatomic Oxygen has 2 atoms that bond together Properties of molecular compounds Lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds Many are liquid or gas at room temp Ionic compoun ...
... Molecules: neutral group of atoms joined by covalent bonds or sharing of electrons Some molecules are diatomic Oxygen has 2 atoms that bond together Properties of molecular compounds Lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds Many are liquid or gas at room temp Ionic compoun ...
04 DetailLectOut 2012
... A carboxyl group acts as an acid because the combined electronegativities of the two adjacent oxygen atoms increase the chance of dissociation of hydrogen as an ion (H+). ...
... A carboxyl group acts as an acid because the combined electronegativities of the two adjacent oxygen atoms increase the chance of dissociation of hydrogen as an ion (H+). ...
chapter 4 carbon and the molecular diversity of life
... replace one or more of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon skeleton of a hydrocarbon. These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o As an example, the basic s ...
... replace one or more of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon skeleton of a hydrocarbon. These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o As an example, the basic s ...
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... This paper reports unusual two-coordinate nickel complexes. The nickel can only bind two ligands because the ligands are so huge (also called bulky or sterically large or sterically encumbered). Figures 1 and 3 show the large size of the ligands. They are the results of Xray diffraction experiments ...
... This paper reports unusual two-coordinate nickel complexes. The nickel can only bind two ligands because the ligands are so huge (also called bulky or sterically large or sterically encumbered). Figures 1 and 3 show the large size of the ligands. They are the results of Xray diffraction experiments ...
Slide 1
... They are stronger acids (pKa = 10) than alcohols, but do not exhibit hydrogen-binding ...
... They are stronger acids (pKa = 10) than alcohols, but do not exhibit hydrogen-binding ...
Hydrocarbons
... Alkanes are insoluble in water This is because water molecules are polar, whereas alkanes are non-polar (all the C - C and C - H bonds are nearly purely covalent) The O - H bond in a water molecule is highly polar due to the high electronegativity of oxygen ...
... Alkanes are insoluble in water This is because water molecules are polar, whereas alkanes are non-polar (all the C - C and C - H bonds are nearly purely covalent) The O - H bond in a water molecule is highly polar due to the high electronegativity of oxygen ...
CHM 094 - Durham Tech
... satisfactory score on placement test Corequisites: DMA 040, or MAT 060 and MAT 070, or satisfactory score on placement test ...
... satisfactory score on placement test Corequisites: DMA 040, or MAT 060 and MAT 070, or satisfactory score on placement test ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review: 2015-2016
... 25. What does the term STP mean? 26. What is the volume of 1 mole of any gas at STP? 27. When given the name of the compound or the formula of the ions, how do you write formulas for ionic compounds? 28. What is Avogadro’s number? 29. What is a mole? 30. What are representative particles of elements ...
... 25. What does the term STP mean? 26. What is the volume of 1 mole of any gas at STP? 27. When given the name of the compound or the formula of the ions, how do you write formulas for ionic compounds? 28. What is Avogadro’s number? 29. What is a mole? 30. What are representative particles of elements ...
enthalpy - winterk
... b) All organic compounds have a backbone of carbon atoms. c) Pentane and 2-methylbutane are isomers. d) C6H10 is an example of a saturated hydrocarbon. e) C8H16 is an alkyne. f) As the number of carbons atoms in a hydrocarbon chain increases, the boiling point increases. g) The accurate IUPAC name f ...
... b) All organic compounds have a backbone of carbon atoms. c) Pentane and 2-methylbutane are isomers. d) C6H10 is an example of a saturated hydrocarbon. e) C8H16 is an alkyne. f) As the number of carbons atoms in a hydrocarbon chain increases, the boiling point increases. g) The accurate IUPAC name f ...
Ch. 8 Carbon Chemistry
... Substituted Hydrocarbons A. Contain only Hydrogen and Carbon B. Form stable compounds with halogen family C. If Hydrogen is substituted, entirely different compound is made D. A substituted hydrocarbon is when atoms of other elements replace one or more atom/s. ...
... Substituted Hydrocarbons A. Contain only Hydrogen and Carbon B. Form stable compounds with halogen family C. If Hydrogen is substituted, entirely different compound is made D. A substituted hydrocarbon is when atoms of other elements replace one or more atom/s. ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.