Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Chapter 4 PowerPoint Lectures for
... • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms • Vitalism, the idea that organic compounds arise only in organisms, was disproved when chemists synthesized the compounds • Mechanism is the view that all natural phenomena are governed by physical and chemical laws Copyrig ...
... • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms • Vitalism, the idea that organic compounds arise only in organisms, was disproved when chemists synthesized the compounds • Mechanism is the view that all natural phenomena are governed by physical and chemical laws Copyrig ...
Organic-IB-Short-Exam Questions-Answers
... curly arrow showing attack by – OH on end H; curly arrow showing C–Br bond fission; curly arrow showing formation of double bond; H2O and Br– shown as products; ...
... curly arrow showing attack by – OH on end H; curly arrow showing C–Br bond fission; curly arrow showing formation of double bond; H2O and Br– shown as products; ...
Introduction to Unknowns.
... mistake). You can write: "if I understand the question this way ..." No "late" exams... A midterm not taken earns the grade "F". ...
... mistake). You can write: "if I understand the question this way ..." No "late" exams... A midterm not taken earns the grade "F". ...
Atomic Structure - Hudson City School District
... • Water would not condense from vapor into solid or liquid forms if its molecules didn't attract each other. • Many properties of molecular compounds, including crystal structures (e. g. the shapes of snowflakes), melting points, boiling points, heats of fusion and vaporization, surface tension, and ...
... • Water would not condense from vapor into solid or liquid forms if its molecules didn't attract each other. • Many properties of molecular compounds, including crystal structures (e. g. the shapes of snowflakes), melting points, boiling points, heats of fusion and vaporization, surface tension, and ...
Chapter 12
... –With an increased number of C atoms, there is an exponentially increased number of isomers •Constitutional - same molecular formula, different structural formula; differ in connectivity of atoms –Ex. C4H10 butane ; isobutane Alkyl Groups & IUPAC names Use the following rules to properly name hydroc ...
... –With an increased number of C atoms, there is an exponentially increased number of isomers •Constitutional - same molecular formula, different structural formula; differ in connectivity of atoms –Ex. C4H10 butane ; isobutane Alkyl Groups & IUPAC names Use the following rules to properly name hydroc ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharing electrons through covalent bonding. ...
... especially stable. • This stability results from the fact that the noble-gas atoms’ outer s and p orbitals are completely filled by a total of eight electrons. • Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p orbitals by sharing electrons through covalent bonding. ...
Study guide - cloudfront.net
... 4.1 Identify the structural isomers, geometric isomers, and enantiomers from the following compounds. Which of the geometric isomers is the cis isomer? Ethanol and dimethyl ether, structural isomers, have the same number and kinds of atoms but a different boding sequence and very different propertie ...
... 4.1 Identify the structural isomers, geometric isomers, and enantiomers from the following compounds. Which of the geometric isomers is the cis isomer? Ethanol and dimethyl ether, structural isomers, have the same number and kinds of atoms but a different boding sequence and very different propertie ...
Review Sheet
... affinity change across a period and down a group? If given a set of elements, rank them according to these parameters and explain why this trend occurs. 4. Predict the relative atomic radii of atoms and ions in an isoelectric series and of an ion compared with its neutral atom. 5. Explain why succes ...
... affinity change across a period and down a group? If given a set of elements, rank them according to these parameters and explain why this trend occurs. 4. Predict the relative atomic radii of atoms and ions in an isoelectric series and of an ion compared with its neutral atom. 5. Explain why succes ...
1 12.1 Mass Spectrometry (MS) Mass Spectrometry (MS) Pentane
... Serves as a “fingerprint” for comparison with known materials in analysis (used in forensics) Positive charge goes to fragments that best can stabilize it The relative height of the M+ peak is greatest for straight chain compounds and decreases with the degree of branching The relative heigh ...
... Serves as a “fingerprint” for comparison with known materials in analysis (used in forensics) Positive charge goes to fragments that best can stabilize it The relative height of the M+ peak is greatest for straight chain compounds and decreases with the degree of branching The relative heigh ...
Ex: -F, -Cl, -Br
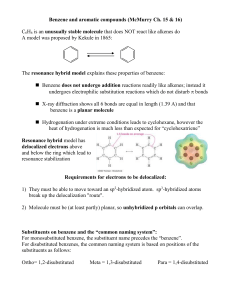
... X-ray diffraction shows all 6 bonds are equal in length (1.39 A) and that benzene is a planar molecule Hydrogenation under extreme conditions leads to cyclohexane, however the heat of hydrogenation is much less than expected for “cyclohexatriene” Resonance hybrid model has delocalized electrons ...
... X-ray diffraction shows all 6 bonds are equal in length (1.39 A) and that benzene is a planar molecule Hydrogenation under extreme conditions leads to cyclohexane, however the heat of hydrogenation is much less than expected for “cyclohexatriene” Resonance hybrid model has delocalized electrons ...
91391 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic
... Demonstrate understanding involves naming using IUPAC conventions (no more than eight carbons in the longest chain) and/or drawing structural formulae of organic compounds and giving an account of their physical properties and/or reactivity. This requires the use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols, an ...
... Demonstrate understanding involves naming using IUPAC conventions (no more than eight carbons in the longest chain) and/or drawing structural formulae of organic compounds and giving an account of their physical properties and/or reactivity. This requires the use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols, an ...
91391 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic
... Demonstrate understanding involves naming using IUPAC conventions (no more than eight carbons in the longest chain) and/or drawing structural formulae of organic compounds and giving an account of their physical properties and/or reactivity. This requires the use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols, an ...
... Demonstrate understanding involves naming using IUPAC conventions (no more than eight carbons in the longest chain) and/or drawing structural formulae of organic compounds and giving an account of their physical properties and/or reactivity. This requires the use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols, an ...
Topic Book periodicity
... to give a neutral solution, MgCl2 gives slightly acidic solution, while all other chlorides react vigorously with water to produce acidic solutions of HCl together with fumes of hydrogen chloride. ...
... to give a neutral solution, MgCl2 gives slightly acidic solution, while all other chlorides react vigorously with water to produce acidic solutions of HCl together with fumes of hydrogen chloride. ...
Metals
... A molecule is the smallest uncharged individual unit of a compound formed by two or more atoms. ...
... A molecule is the smallest uncharged individual unit of a compound formed by two or more atoms. ...
Document
... which the hydroxyl group has replaced the boron atom. In this reaction, the hydroxyl group ends up at the less substituted carbon: an antiMarkovnikov addition. ...
... which the hydroxyl group has replaced the boron atom. In this reaction, the hydroxyl group ends up at the less substituted carbon: an antiMarkovnikov addition. ...
Functional Groups
... Give the molecular formula for each type of hydrocarbon below if it contains seven carbon atoms, draw one possible isomer and name that isomer. ...
... Give the molecular formula for each type of hydrocarbon below if it contains seven carbon atoms, draw one possible isomer and name that isomer. ...
Study Guide for Chapter 2 in Fox
... 14. What is the relationship between the # of protons and electrons? The number of protons and electrons are relatively equal. 15. What is the electron configuration for the first 3 shells (orbits)? 1st - 2 electrons, 2nd – 8 electrons, 3rd – 8 electrons. 16. What are isotopes? Isotopes are a form o ...
... 14. What is the relationship between the # of protons and electrons? The number of protons and electrons are relatively equal. 15. What is the electron configuration for the first 3 shells (orbits)? 1st - 2 electrons, 2nd – 8 electrons, 3rd – 8 electrons. 16. What are isotopes? Isotopes are a form o ...
Science 10 Chem - Holy Trinity Academy
... To see if an ionic compound will be solid look at “Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water” in Appendix D o (-) ion on top o (+) ion on bottom - highly solubility = compound dissolve o low solubility = compound form solid * Practice problems on page 278 ...
... To see if an ionic compound will be solid look at “Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water” in Appendix D o (-) ion on top o (+) ion on bottom - highly solubility = compound dissolve o low solubility = compound form solid * Practice problems on page 278 ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... yourself, “How are they similar? How are they different?” As you read Lesson 23.1, use the compare and contrast table below to differentiate among functional groups. Compound type ...
... yourself, “How are they similar? How are they different?” As you read Lesson 23.1, use the compare and contrast table below to differentiate among functional groups. Compound type ...
Slide 1 In this lesson, we will give you a general
... Let us look at the definition of organic molecules. Organic Molecules are the compounds containing carbon atoms. We do not include Carbon dioxide and diamonds under this category. Early Thoughts were that only living things could synthesize organic compounds. But, in 1800, an organic compound was sy ...
... Let us look at the definition of organic molecules. Organic Molecules are the compounds containing carbon atoms. We do not include Carbon dioxide and diamonds under this category. Early Thoughts were that only living things could synthesize organic compounds. But, in 1800, an organic compound was sy ...
Lecture 1: RDCH 710 Introduction
... Extraction increases with increase concentration of TBP and nitric acid * 1-10 M HNO3 Separation from other actinides achieved by controlling Np oxidation state • CMPO ...
... Extraction increases with increase concentration of TBP and nitric acid * 1-10 M HNO3 Separation from other actinides achieved by controlling Np oxidation state • CMPO ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.