Senses - HumanAandP
... Science formally acknowledges that human have at least 11 senses and some list 19 or more. • Input receptor which provides information to the brain. • 12 pairs of cranial nerves branching out from the brain assist in this. • Dependent on 6 senses, all which directly have direct connections to the b ...
... Science formally acknowledges that human have at least 11 senses and some list 19 or more. • Input receptor which provides information to the brain. • 12 pairs of cranial nerves branching out from the brain assist in this. • Dependent on 6 senses, all which directly have direct connections to the b ...
Neurotransmission
... Chemical messengers that carry messages across the synapse. They either excite or inhibit neurons Examples of neurotransmitters include Dopamine Serotonin Norepinephrine ...
... Chemical messengers that carry messages across the synapse. They either excite or inhibit neurons Examples of neurotransmitters include Dopamine Serotonin Norepinephrine ...
Poster
... In the mammalian central nervous system, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the primary inhibitory signaling molecule. One receptor for this molecule, GABAB, has been linked to feelings of calmness, as well as mental disorders such as alcoholism and depression. Pharmaceutical compounds that bind the ...
... In the mammalian central nervous system, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the primary inhibitory signaling molecule. One receptor for this molecule, GABAB, has been linked to feelings of calmness, as well as mental disorders such as alcoholism and depression. Pharmaceutical compounds that bind the ...
Week 2 Section Handout
... nucleus. The axons of these second-order sensory neurons then decussate (cross over) to the contralateral (opposite) side of the medulla and form a column projecting up to the thalamus where they in turn synapse onto third-order sensory neurons in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. ...
... nucleus. The axons of these second-order sensory neurons then decussate (cross over) to the contralateral (opposite) side of the medulla and form a column projecting up to the thalamus where they in turn synapse onto third-order sensory neurons in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. ...
1. Receptor cells
... 1- Sensory neurons: carry information form sense organs to the brain & spinal cord. 2-Motor neurons: carry signals from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands . 3-Inter-neurons: connect neuron to other neurons . ...
... 1- Sensory neurons: carry information form sense organs to the brain & spinal cord. 2-Motor neurons: carry signals from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands . 3-Inter-neurons: connect neuron to other neurons . ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
... point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
Nervous System Neuron: nerve cell, functional unit of nervous
... Glutamate: Major neurotransmitter in the brain ● learning, memory, plasticity ● Open/allows entry (synaptic connects) Na+,Ca+2 channels into receiving or post-synaptic neuron. This is an excitatory signal because it makes inside of cell positive and thus excitatory. ● K+ channels may also close whic ...
... Glutamate: Major neurotransmitter in the brain ● learning, memory, plasticity ● Open/allows entry (synaptic connects) Na+,Ca+2 channels into receiving or post-synaptic neuron. This is an excitatory signal because it makes inside of cell positive and thus excitatory. ● K+ channels may also close whic ...
BLoA Neurotransmission
... So now the neurotransitting chemicals are in the synapse. They float across the tiny space in a random way, and in the process, bump into receptors on the other side. The receptors here are important. This is because there tend to be many different types of receptor for one type of neurotransmitter. ...
... So now the neurotransitting chemicals are in the synapse. They float across the tiny space in a random way, and in the process, bump into receptors on the other side. The receptors here are important. This is because there tend to be many different types of receptor for one type of neurotransmitter. ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CH 16: SPECIAL SENSES
... 2.Biconcave, flexible eye structure used to focus light on the retina 3.Taste elicited by bases 4.Olfactory receptor cells are unique because they are the only neurons known to undergo ______ through out adult life. 5.Projections on the tongue which contain taste buds 6.Antibacterial enzyme in tears ...
... 2.Biconcave, flexible eye structure used to focus light on the retina 3.Taste elicited by bases 4.Olfactory receptor cells are unique because they are the only neurons known to undergo ______ through out adult life. 5.Projections on the tongue which contain taste buds 6.Antibacterial enzyme in tears ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The skin and many internal organs and tissues have pain receptors that are sensitive to chemicals released by damaged cells. 18.3 Senses of Taste and Smell Taste and smell are called chemical senses because their receptors are sensitive to molecules in the food we eat and the air we breathe. Sense o ...
... The skin and many internal organs and tissues have pain receptors that are sensitive to chemicals released by damaged cells. 18.3 Senses of Taste and Smell Taste and smell are called chemical senses because their receptors are sensitive to molecules in the food we eat and the air we breathe. Sense o ...
No Slide Title
... peptide that is highly homologous to peptide YY (PYY). NPY exerts its various biological effects through at least six classes of receptors, designated Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4, Y5, and Y6. It has been demonstrated that NPY inhibits catecholamine synthesis via the Y3 receptor subtype, in contrast to the Y2 sub ...
... peptide that is highly homologous to peptide YY (PYY). NPY exerts its various biological effects through at least six classes of receptors, designated Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4, Y5, and Y6. It has been demonstrated that NPY inhibits catecholamine synthesis via the Y3 receptor subtype, in contrast to the Y2 sub ...
Mouse anti-GPCR-K2 Mouse anti-β-Adrenergic Receptor Kinase 1
... similarity to other kinases only in the centrally located catalytic domain of about 240 amino acid residues. Rapid phosphorylation of many G protein coupled receptors accompanies stimulus-driven desensitization. There are two types of kinases known to mediate these modifications: second messenger ki ...
... similarity to other kinases only in the centrally located catalytic domain of about 240 amino acid residues. Rapid phosphorylation of many G protein coupled receptors accompanies stimulus-driven desensitization. There are two types of kinases known to mediate these modifications: second messenger ki ...
Depressants and stimulants
... • Cannabis strains with relatively high CBD:THC ratios are less likely to induce anxiety • known for its sedative effects: • more calming, soothing, and numbing experience • can be used to relax or relieve pain. • Also seems to reduce the frequency of seizures: probably due to antagonist effects at ...
... • Cannabis strains with relatively high CBD:THC ratios are less likely to induce anxiety • known for its sedative effects: • more calming, soothing, and numbing experience • can be used to relax or relieve pain. • Also seems to reduce the frequency of seizures: probably due to antagonist effects at ...
Publication JournalArticle (Originalarbeit in einer wissenschaftlichen
... Orphan nuclear receptors belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily of liganded transcription factors, whose ligands either do not exist or remain to be identified. We report here the cloning and characterization of the chicken orphan nuclear receptor, cTR2 (chicken testicular receptor 2). The cTR2 ...
... Orphan nuclear receptors belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily of liganded transcription factors, whose ligands either do not exist or remain to be identified. We report here the cloning and characterization of the chicken orphan nuclear receptor, cTR2 (chicken testicular receptor 2). The cTR2 ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
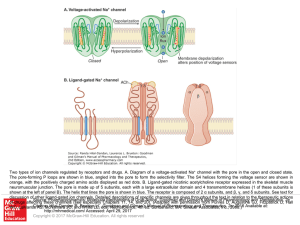
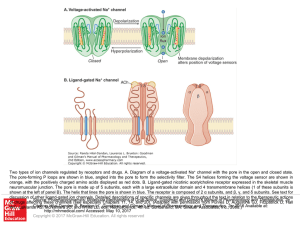
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Slide ()
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
The Nervous System
... • Cold receptors -sensitive to 50˚F(10˚C)~68˚F(20˚C) -unresponsive below 10˚C (stimulate pain receptors) (freezing sensation) ...
... • Cold receptors -sensitive to 50˚F(10˚C)~68˚F(20˚C) -unresponsive below 10˚C (stimulate pain receptors) (freezing sensation) ...
Nervous and Immune Systems
... Sensory or afferent neuron: nerve cell that receives signals from __________________ inside and outside of the body then sends information to CNS Interneuron: nerve cells that interconnect other neurons ...
... Sensory or afferent neuron: nerve cell that receives signals from __________________ inside and outside of the body then sends information to CNS Interneuron: nerve cells that interconnect other neurons ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
BIOL 2402 Lecture Outline Chapter 5
... successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” neurons c. how do we wake up? the RAS receives interna ...
... successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” neurons c. how do we wake up? the RAS receives interna ...
Outline 12
... inadequate to meet is metabolic needs They respond to excessive stimulation from _______ or chemicals Mechanoreceptors respond to physical forces on cells caused by touch, pressure, stretch, tension, or vibration They include the organs of _________________ and balance They include many rece ...
... inadequate to meet is metabolic needs They respond to excessive stimulation from _______ or chemicals Mechanoreceptors respond to physical forces on cells caused by touch, pressure, stretch, tension, or vibration They include the organs of _________________ and balance They include many rece ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... output which is axon. Axons may be very long (over a foot) Synaptic junction: an axon impinges on a dendrite which causes input/output signal transitions ...
... output which is axon. Axons may be very long (over a foot) Synaptic junction: an axon impinges on a dendrite which causes input/output signal transitions ...