Real Neurons for Engineers
... neurons and neuromodulation. It can also involve recurrent signaling within a small network. • Long-term plasticity is believed to involve changes in receptor densities on the post-synaptic side and vesicle densities on the pre-synaptic side. ...
... neurons and neuromodulation. It can also involve recurrent signaling within a small network. • Long-term plasticity is believed to involve changes in receptor densities on the post-synaptic side and vesicle densities on the pre-synaptic side. ...
Sense Organs - human anatomy
... inadequate to meet is metabolic needs They respond to excessive stimulation from heat or chemicals Mechanoreceptors respond to physical forces on cells caused by touch, pressure, stretch, tension, or vibration They include the organs of hearing and balance They include many receptors of the ...
... inadequate to meet is metabolic needs They respond to excessive stimulation from heat or chemicals Mechanoreceptors respond to physical forces on cells caused by touch, pressure, stretch, tension, or vibration They include the organs of hearing and balance They include many receptors of the ...
Exam 3 suggested answers
... (3) Suggest a reason why the authors stimulated layer 4, rather than some other cortical layer, to induce LTP in this situation [4 points; 1 sentence] Inputs to visual cortex arrive in layer 4. (4) What kinds of data must have been published before the experiments reported in this paper, to show tha ...
... (3) Suggest a reason why the authors stimulated layer 4, rather than some other cortical layer, to induce LTP in this situation [4 points; 1 sentence] Inputs to visual cortex arrive in layer 4. (4) What kinds of data must have been published before the experiments reported in this paper, to show tha ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis during stress, it is the “flight-or-fight” system of the body. This is done by accelerating heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and raising the blood pressure. For this information to be communicated, it uses pre/post-ganglionic neurons. -Preganglionic ...
... Plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis during stress, it is the “flight-or-fight” system of the body. This is done by accelerating heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and raising the blood pressure. For this information to be communicated, it uses pre/post-ganglionic neurons. -Preganglionic ...
03/14 PPT
... Neurons with the same receptor converge on single glomeruli in olfactory bulb. The glomeruli serve as modules, and are selectively sensitive to particular odors Epithelium ...
... Neurons with the same receptor converge on single glomeruli in olfactory bulb. The glomeruli serve as modules, and are selectively sensitive to particular odors Epithelium ...
(580.422) Lecture 7, Synaptic Transmission
... The best understood metabotropic effects occur through activation of G-proteins. The general scheme of G-protein activation is shown below. When the receptor (R ) binds a transmitter (NT), the G-protein complex exchanges its GDP moiety for a GTP and cleaves into an α-subunit-GTP part and a β−γ subu ...
... The best understood metabotropic effects occur through activation of G-proteins. The general scheme of G-protein activation is shown below. When the receptor (R ) binds a transmitter (NT), the G-protein complex exchanges its GDP moiety for a GTP and cleaves into an α-subunit-GTP part and a β−γ subu ...
Biology 232
... sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect stimuli stimulus – change i ...
... sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect stimuli stimulus – change i ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... The sending neuron then reabsorbs excess NT molecules in a process called reuptake. NTs will only fit into particular receptor sites, like keys that only fit certain locks. NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it ...
... The sending neuron then reabsorbs excess NT molecules in a process called reuptake. NTs will only fit into particular receptor sites, like keys that only fit certain locks. NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it ...
The Sensory System
... • Nociceptors respond to intense mechanical deformation, excessive heat etc. which cause tissue damage and many chemicals that are released by damaged cells or cells of immune system. If the initial stimulus of pain leads to an increased sensitivity to subsequent painful stimuli it is called hyperal ...
... • Nociceptors respond to intense mechanical deformation, excessive heat etc. which cause tissue damage and many chemicals that are released by damaged cells or cells of immune system. If the initial stimulus of pain leads to an increased sensitivity to subsequent painful stimuli it is called hyperal ...
Control of Cell Adhesion
... In order to produce cellular responses, many other molecular steps are necessary. The sequences of these events is generally referred to as “signal transduction pathways” ...
... In order to produce cellular responses, many other molecular steps are necessary. The sequences of these events is generally referred to as “signal transduction pathways” ...
reprint in PDF format
... receptors are GR (X72211, a; X04435, m; M14053, r; X03225, h); MR (U15135 and U15133, a; M36074, r; Ml6801, h); AR (X56955, a; L25901, c; X53779 and X59592, m; M20133, r; M20132 and M21748, h); PR (M37518, c; M68915, m; L16922, r; M1.5716, h); ER (M31559 and D28954, f; L20736, a; X03805, c; M38651, ...
... receptors are GR (X72211, a; X04435, m; M14053, r; X03225, h); MR (U15135 and U15133, a; M36074, r; Ml6801, h); AR (X56955, a; L25901, c; X53779 and X59592, m; M20133, r; M20132 and M21748, h); PR (M37518, c; M68915, m; L16922, r; M1.5716, h); ER (M31559 and D28954, f; L20736, a; X03805, c; M38651, ...
Reflex and autonomic nervous system
... Controls the movement of skeletal muscles. Has both voluntary and involuntary components. Voluntary is under conscious control Involuntary maintains balance Includes reflexes: signals that go to the spinal column but not the brain. Pair share: Give a reason why it is important for the body ...
... Controls the movement of skeletal muscles. Has both voluntary and involuntary components. Voluntary is under conscious control Involuntary maintains balance Includes reflexes: signals that go to the spinal column but not the brain. Pair share: Give a reason why it is important for the body ...
Lab Test 2009 - The University of Auckland
... (a) Opioid receptors mediate increased neurotransmitter release via G-protein activation (b) Endogenous opioids show equal specificity to various opioid receptors (c) Opioid receptors are expressed solely in the central nervous system (d) Endogenous opioid peptide ligands are released both centrally ...
... (a) Opioid receptors mediate increased neurotransmitter release via G-protein activation (b) Endogenous opioids show equal specificity to various opioid receptors (c) Opioid receptors are expressed solely in the central nervous system (d) Endogenous opioid peptide ligands are released both centrally ...
Dopamine
... almost identical in structure to epinephrine, which is released into the bloodstream from the adrenal medulla under sympathetic activation. The sympathetic nervous system functions in response to short-term stress; hence norepinephrine and epinephrine increase the heart rate as well as blood pressur ...
... almost identical in structure to epinephrine, which is released into the bloodstream from the adrenal medulla under sympathetic activation. The sympathetic nervous system functions in response to short-term stress; hence norepinephrine and epinephrine increase the heart rate as well as blood pressur ...
Introduction to the Pharmacology of CNS Drugs: Introduction Drugs
... GABA receptors are divided into two main types: GABAA and GABAB. inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in many areas of the brain have a fast and slow component. The fast component is mediated by GABAA receptors and the slow component by GABAB receptors. The difference in kinetics stems from the differ ...
... GABA receptors are divided into two main types: GABAA and GABAB. inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in many areas of the brain have a fast and slow component. The fast component is mediated by GABAA receptors and the slow component by GABAB receptors. The difference in kinetics stems from the differ ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • ADRENERGIC neurons - neurons that release norepinephrine • Epinephrine/norepinephrine also released from adrenal medulla ...
... • ADRENERGIC neurons - neurons that release norepinephrine • Epinephrine/norepinephrine also released from adrenal medulla ...
Oxyntomodulin - Pacific Biomarkers
... weight gain and adiposity in rats. Delivery of oxyntomodulin into the GI tract of overweight BALB/C mice through a bacterial plasmid delivery system was associated with reduced food intake and weight gain, despite no changes in plasma levels. Studies of oxyntomodulin action in mice have demonstrated ...
... weight gain and adiposity in rats. Delivery of oxyntomodulin into the GI tract of overweight BALB/C mice through a bacterial plasmid delivery system was associated with reduced food intake and weight gain, despite no changes in plasma levels. Studies of oxyntomodulin action in mice have demonstrated ...
Intracellular signalling
... FIGURE 15.5. Calcium and cyclic AMP activate distinct but overlapping sets of target processes in skeletal muscle cells. ...
... FIGURE 15.5. Calcium and cyclic AMP activate distinct but overlapping sets of target processes in skeletal muscle cells. ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... • About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
... • About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
Slide ()
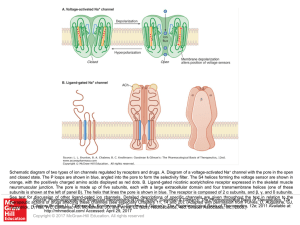
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
Brain Neurotransmitters
... Alcohol acts at many sites, including the reticular formation, spinal cord, cerebellum and cerebral cortex, and on many neurotransmitter systems. ...
... Alcohol acts at many sites, including the reticular formation, spinal cord, cerebellum and cerebral cortex, and on many neurotransmitter systems. ...
Somatosensory 2
... Pain (Nociception) The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimu ...
... Pain (Nociception) The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimu ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
Neurotransmitters
... o People with too little GABA tend to suffer from anxiety disorders, and drugs like Valium work by enhancing (binding to the GABA receptor sites) the effects of GABA. o Lots of other drugs influence GABA receptors, including alcohol and barbiturates. o If GABA is lacking in certain parts of the brai ...
... o People with too little GABA tend to suffer from anxiety disorders, and drugs like Valium work by enhancing (binding to the GABA receptor sites) the effects of GABA. o Lots of other drugs influence GABA receptors, including alcohol and barbiturates. o If GABA is lacking in certain parts of the brai ...