Nervous System
... - formed by gap junctions between cells **chemical synapses: use chemicals to transfer impulses when action potentials are not transmitted from one neuron to the next, directly…needs a “communicator” = neurotransmitter (NT) - Located in vesicles of neuron - Binds to receptor portion of gated chann ...
... - formed by gap junctions between cells **chemical synapses: use chemicals to transfer impulses when action potentials are not transmitted from one neuron to the next, directly…needs a “communicator” = neurotransmitter (NT) - Located in vesicles of neuron - Binds to receptor portion of gated chann ...
PPT File - Holden R
... Responses of Sensory Receptors • Receptor: Interaction of stimulus with sensory receptor produces a local potential – Primary: Have axons that conduct action potential in response to receptor potential – Secondary: Have no axons and receptor potentials produced do not result in action potentials bu ...
... Responses of Sensory Receptors • Receptor: Interaction of stimulus with sensory receptor produces a local potential – Primary: Have axons that conduct action potential in response to receptor potential – Secondary: Have no axons and receptor potentials produced do not result in action potentials bu ...
Chapter 14
... Responses of Sensory Receptors • Receptor: Interaction of stimulus with sensory receptor produces a local potential – Primary: Have axons that conduct action potential in response to receptor potential – Secondary: Have no axons and receptor potentials produced do not result in action potentials bu ...
... Responses of Sensory Receptors • Receptor: Interaction of stimulus with sensory receptor produces a local potential – Primary: Have axons that conduct action potential in response to receptor potential – Secondary: Have no axons and receptor potentials produced do not result in action potentials bu ...
Chapter 14
... Area of skin whose stimulation results in changes in the firing rate of the neuron. Area of each receptor field varies inversely with the density of receptors in the region. Back and legs have few sensory endings. ...
... Area of skin whose stimulation results in changes in the firing rate of the neuron. Area of each receptor field varies inversely with the density of receptors in the region. Back and legs have few sensory endings. ...
1. Receptor cells
... 1- Sensory neurons: carry information form sense organs to the brain & spinal cord. 2-Motor neurons: carry signals from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands . 3-Inter-neurons: connect neuron to other neurons . ...
... 1- Sensory neurons: carry information form sense organs to the brain & spinal cord. 2-Motor neurons: carry signals from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands . 3-Inter-neurons: connect neuron to other neurons . ...
Monoclonal Antibody To Human GPR50
... UniProt: Q13585 GPR50 or melatonin-related receptor is a 617 amino acid protein that belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, containing one disulfide bond. GPR50 does not bind melatonin and its endogenous ligand is still unknown. Nevertheless, this receptor has been shown to behave as an ...
... UniProt: Q13585 GPR50 or melatonin-related receptor is a 617 amino acid protein that belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, containing one disulfide bond. GPR50 does not bind melatonin and its endogenous ligand is still unknown. Nevertheless, this receptor has been shown to behave as an ...
Neurons and how they communicate
... Serotonin – while involved in many behaviors, especially important for emotional states, impulse control, and dreaming Low levels lead to sadness, anxiety, aggression, and food cravings LSD bears a close structural resemblance, when it binds to serotonin receptors involved in dreaming, hallucination ...
... Serotonin – while involved in many behaviors, especially important for emotional states, impulse control, and dreaming Low levels lead to sadness, anxiety, aggression, and food cravings LSD bears a close structural resemblance, when it binds to serotonin receptors involved in dreaming, hallucination ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Neural Impulse – What are the steps taken when a neuron “fires”? ...
... Neural Impulse – What are the steps taken when a neuron “fires”? ...
These review questions are for the Bio 1 signal transduction topic
... 17) If you wish to alter a G protein-linked receptor such that it still could bind its signal molecule but it was unable to carry out any signal transduction, you should change which region of the receptor? A) the exterior (extracellular) end of the receptor B) the binding site for signal molecule ...
... 17) If you wish to alter a G protein-linked receptor such that it still could bind its signal molecule but it was unable to carry out any signal transduction, you should change which region of the receptor? A) the exterior (extracellular) end of the receptor B) the binding site for signal molecule ...
Chapter 18 - Austin Community College
... • Exposure to UV light, diabetes, heavy alcohol consumption,and smoking are all risk factors ...
... • Exposure to UV light, diabetes, heavy alcohol consumption,and smoking are all risk factors ...
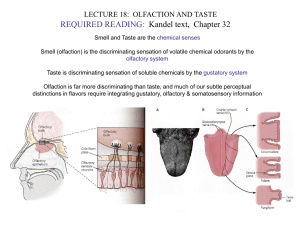
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
... SWEET-sensing taste cells use 7-TM receptor coupled to Gs. Sugars act through Gs to produce cAMP, and PKA phosphorylates and closes potassium leak channels, causing depolarization Alternatively, some substances (artificial sweeteners) bind receptors coupled to Gq which activates PLC to increase Ca+2 ...
... SWEET-sensing taste cells use 7-TM receptor coupled to Gs. Sugars act through Gs to produce cAMP, and PKA phosphorylates and closes potassium leak channels, causing depolarization Alternatively, some substances (artificial sweeteners) bind receptors coupled to Gq which activates PLC to increase Ca+2 ...
The Human Nervous System
... diagnosis and management of central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous system disorders using a combination of clinical evaluation and electrophysiologic testing such as electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), and nerve conduction studies (NCS), among others. Pain Medicine - provides a ...
... diagnosis and management of central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous system disorders using a combination of clinical evaluation and electrophysiologic testing such as electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), and nerve conduction studies (NCS), among others. Pain Medicine - provides a ...
test - Scioly.org
... d. the enzymatic behavior of the signal molecule e. binding to the intracellular receptors 33. Since water-soluble hormones are unable to pass through the plasma membrane, the cellular action they initiate results from _____. a. steroids are bigger, slower molecules b. steroids must usually be carri ...
... d. the enzymatic behavior of the signal molecule e. binding to the intracellular receptors 33. Since water-soluble hormones are unable to pass through the plasma membrane, the cellular action they initiate results from _____. a. steroids are bigger, slower molecules b. steroids must usually be carri ...
The Nervous System
... 1. A nerve impulse begins with a stimulus- usually this is a neurotransmitter released by other neurons, pain receptors, light excites receptors in the eye, etc. 2. Once the neuron is stimulated the “sodium gates” of the neuron open and sodium ions begin flowing across the cell membrane. This is cal ...
... 1. A nerve impulse begins with a stimulus- usually this is a neurotransmitter released by other neurons, pain receptors, light excites receptors in the eye, etc. 2. Once the neuron is stimulated the “sodium gates” of the neuron open and sodium ions begin flowing across the cell membrane. This is cal ...
Chemistry of Psychology - Point Loma High School
... Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hundreds of chemicals act as Neurotransmitters Discovered in 1970s while investiga ...
... Too much Glutamate = causes neurons to die Plays a role in allowing and supporting synaptic connections allows messages to cross synapse efficiently Important for learning & memory (p98) Peptides= Endorphins Hundreds of chemicals act as Neurotransmitters Discovered in 1970s while investiga ...
Outline14 Efferent NS
... - axon terminals secrete ACh into the synaptic cleft nicotinic cholinergic receptors at the motor end plate binding of ACh open cation channels → strong EPSP → exceeds threshold → muscle AP B. Autonomic Division (ANS) - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc. ...
... - axon terminals secrete ACh into the synaptic cleft nicotinic cholinergic receptors at the motor end plate binding of ACh open cation channels → strong EPSP → exceeds threshold → muscle AP B. Autonomic Division (ANS) - involuntary control of autonomic effectors (visceral organs, blood vessels, etc. ...
B6 Brain and Mind revised - Blackpool Aspire Academy
... are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
The Nervous System WS-11A Review Quest
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
Chapter 24
... both sensory and motor axons. only motor axons. both sensory and motor dendrites. only motor dendrites. only sensory axons. ...
... both sensory and motor axons. only motor axons. both sensory and motor dendrites. only motor dendrites. only sensory axons. ...
bio 342 human physiology
... e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
... e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
The nervous system
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
Nervous System
... Synapses serve as the means to allow neurons to pass signals to another cell. When a cell has a voltage disturbance, (one side more positively charged than the other) this is known as an action potential, in which an electrical current is released. An action potential is the local voltage change acr ...
... Synapses serve as the means to allow neurons to pass signals to another cell. When a cell has a voltage disturbance, (one side more positively charged than the other) this is known as an action potential, in which an electrical current is released. An action potential is the local voltage change acr ...
PowerPoint Slides
... substances at the synapse. •The neurotransmitters cause excitation or inhibition in the dendrite of the post-synaptic neuron. •The integration of the excitatory and inhibitory signals may produce spikes in the post-synaptic neuron. ...
... substances at the synapse. •The neurotransmitters cause excitation or inhibition in the dendrite of the post-synaptic neuron. •The integration of the excitatory and inhibitory signals may produce spikes in the post-synaptic neuron. ...
Biopsychology 2012 – sec 002
... They are proteins that are inserted into the membrane and contain binding sites for neurotransmitters. How do receptors recognize neurotransmitters? Receptors recognize specific neurotransmitters much like a lock and key arrangement; neurotransmitters are the keys that fit into specific locks (recep ...
... They are proteins that are inserted into the membrane and contain binding sites for neurotransmitters. How do receptors recognize neurotransmitters? Receptors recognize specific neurotransmitters much like a lock and key arrangement; neurotransmitters are the keys that fit into specific locks (recep ...
chapter38
... The action potential is a “all or none” response to a stimulus. A stimulus has to be of enough strength to cause an action potential to occur. The critical point at which a stimulus causes an action potential is called the threshold. ...
... The action potential is a “all or none” response to a stimulus. A stimulus has to be of enough strength to cause an action potential to occur. The critical point at which a stimulus causes an action potential is called the threshold. ...