Brain Day - No Regrets
... receptors must send the signal through a special area of the skull called the cribriform plate, which has many tiny holes for cell extensions (axons) to pass through. Olfactory areas of the brain work closely with structures involved in producing emotions. The limbic system is an example of a relate ...
... receptors must send the signal through a special area of the skull called the cribriform plate, which has many tiny holes for cell extensions (axons) to pass through. Olfactory areas of the brain work closely with structures involved in producing emotions. The limbic system is an example of a relate ...
levels of the neurotransmitter GABA, which
... neurotransmitter that is deficient in Alzheimer's disease, releases a neurotransmitter that is important for reinforcing learning (among other things), and helps neurons form new connections with each other. Taken together these suggest that uridine monophosphate exerts several cognitive benefits. N ...
... neurotransmitter that is deficient in Alzheimer's disease, releases a neurotransmitter that is important for reinforcing learning (among other things), and helps neurons form new connections with each other. Taken together these suggest that uridine monophosphate exerts several cognitive benefits. N ...
Unit 3A Notes
... morphine that our bodies produce. They improve our moods and reduce pain. They’re released either in times of pain or heavy exercise. 1. When a person uses drugs like cocaine, heroine, or morphine, the body will produce less endorphins of its own. 2. Drugs that act like neurotransmitters and bridge ...
... morphine that our bodies produce. They improve our moods and reduce pain. They’re released either in times of pain or heavy exercise. 1. When a person uses drugs like cocaine, heroine, or morphine, the body will produce less endorphins of its own. 2. Drugs that act like neurotransmitters and bridge ...
Nervous System (1)
... 3. Stroke - caused by a cerebral hemorrhage or a blood clot in a cerebral vessel which may result in brain damage 4. Polio - viral disease of the CNS which may result in paralysis, and is preventable through ...
... 3. Stroke - caused by a cerebral hemorrhage or a blood clot in a cerebral vessel which may result in brain damage 4. Polio - viral disease of the CNS which may result in paralysis, and is preventable through ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... improve our moods and reduce pain. They’re released either in times of pain or heavy exercise. 1. When a person uses drugs like cocaine, heroine, or morphine, the body will produce less endorphins of its own. 2. Drugs that act like neurotransmitters and bridge the synaptic gap are called agonist mol ...
... improve our moods and reduce pain. They’re released either in times of pain or heavy exercise. 1. When a person uses drugs like cocaine, heroine, or morphine, the body will produce less endorphins of its own. 2. Drugs that act like neurotransmitters and bridge the synaptic gap are called agonist mol ...
Laboratory Exercise 12: Sensory Physiology
... relatively high density of touch receptors and have great sensitivity, compared to the back. The back is not as sensitive, because of a relative low number of touch receptors per unit area of skin. C. Adaptation of Receptors When a receptor is excited a stimulus causes some change of its structure. ...
... relatively high density of touch receptors and have great sensitivity, compared to the back. The back is not as sensitive, because of a relative low number of touch receptors per unit area of skin. C. Adaptation of Receptors When a receptor is excited a stimulus causes some change of its structure. ...
CHAPTER 3
... cortex also contains areas important for language function and some networks of mirror neurons which facilitate learning from watching and copying others. c) The Forebrain: Subcortical Areas: Several structures below the cortex mediate information entering and exiting the forebrain. The thalamus pro ...
... cortex also contains areas important for language function and some networks of mirror neurons which facilitate learning from watching and copying others. c) The Forebrain: Subcortical Areas: Several structures below the cortex mediate information entering and exiting the forebrain. The thalamus pro ...
seminario - Instituto Cajal
... recordings. Hcrt in dRPO increased wakefulness and decreased both NREM and REM sleep. In contrast, Hcrt in vRPO suppressed REM sleep as the only significant effect on sleep. To determine the cellular mechanisms underlying such effects in dRPO and vRPO, we examined in urethane-anesthetized rats the e ...
... recordings. Hcrt in dRPO increased wakefulness and decreased both NREM and REM sleep. In contrast, Hcrt in vRPO suppressed REM sleep as the only significant effect on sleep. To determine the cellular mechanisms underlying such effects in dRPO and vRPO, we examined in urethane-anesthetized rats the e ...
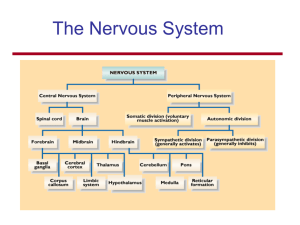
the nervous system
... the neuron membranes • The space between neurons is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters carry impulses across the synapse ...
... the neuron membranes • The space between neurons is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters carry impulses across the synapse ...
Nervous System
... – Neurons only possess one – mm to m in length. Where could an axon a meter in length be found? ...
... – Neurons only possess one – mm to m in length. Where could an axon a meter in length be found? ...
Purines/Pyrimidines LIGAND-SET™ (L2538)
... of each ligand per well. Stock solutions can be readily prepared by adding 1 ml of DMSO to each well. The set also comes with a diskette containing a structural database, or SD file and a Microsoft Excel file containing the catalog number, name, rack position and pharmacological characteristics of e ...
... of each ligand per well. Stock solutions can be readily prepared by adding 1 ml of DMSO to each well. The set also comes with a diskette containing a structural database, or SD file and a Microsoft Excel file containing the catalog number, name, rack position and pharmacological characteristics of e ...
John Ferguson MacDonald John Ferguson MacDonald, who died
... John Ferguson MacDonald, who died on April 22 in Toronto at the early age of 65, was an outstanding Canadian neuroscientist, whose career was rich in many achievements across a wide variety of research topics, ranging from the mechanisms of action of amino acid transmitters to the role of Ca ions in ...
... John Ferguson MacDonald, who died on April 22 in Toronto at the early age of 65, was an outstanding Canadian neuroscientist, whose career was rich in many achievements across a wide variety of research topics, ranging from the mechanisms of action of amino acid transmitters to the role of Ca ions in ...
Part 1: The Strange Tale of Phineas Gage
... messages across the synapses. Neurotransmitters do one of two things: excite or inhibit ...
... messages across the synapses. Neurotransmitters do one of two things: excite or inhibit ...
John Ferguson MacDonald
... John Ferguson MacDonald, who died on April 22 in Toronto at the early age of 65, was an outstanding Canadian neuroscientist, whose career was rich in many achievements across a wide variety of research topics, ranging from the mechanisms of action of amino acid transmitters to the role of Ca ions in ...
... John Ferguson MacDonald, who died on April 22 in Toronto at the early age of 65, was an outstanding Canadian neuroscientist, whose career was rich in many achievements across a wide variety of research topics, ranging from the mechanisms of action of amino acid transmitters to the role of Ca ions in ...
Blockade of NMDA receptors in the developing cortex and
... several studies reported neuroprotective effects of NMDA antagonists. However, there is more and more evidence indicating that, in the developing brain, glutamate exerts trophic effects on migrating GABAergic interneurons and that NMDA antagonists would present neurodevelopmental side effects. Thus, ...
... several studies reported neuroprotective effects of NMDA antagonists. However, there is more and more evidence indicating that, in the developing brain, glutamate exerts trophic effects on migrating GABAergic interneurons and that NMDA antagonists would present neurodevelopmental side effects. Thus, ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... FIGURE 22.4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the s ...
... FIGURE 22.4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the s ...
I. The Nervous System
... b. myelin sheath- lipids that cover part of some axons, conducts signal faster c. nodes of Ranvier- breaks in myelin sheath, leave cell exposed to access ions needed for impulse ...
... b. myelin sheath- lipids that cover part of some axons, conducts signal faster c. nodes of Ranvier- breaks in myelin sheath, leave cell exposed to access ions needed for impulse ...
What is the Nervous System?
... Myelin Sheath – insulates the axon, speeds up transmission 5. Terminal Button – end of axon, secretes neurotransmitters at the synapse 6. Synapse – junction where info is sent from one neuron to another ...
... Myelin Sheath – insulates the axon, speeds up transmission 5. Terminal Button – end of axon, secretes neurotransmitters at the synapse 6. Synapse – junction where info is sent from one neuron to another ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
Chapter 7
... active head rotation into an increase or decrease in neurotransmitter release • synapse with bipolar neurons ...
... active head rotation into an increase or decrease in neurotransmitter release • synapse with bipolar neurons ...
Chapter 18: Senses - Johnston Community College
... aorta respond to the pH of the blood and communicate with the medulla oblongata to change breathing rate. For example, when blood pH drops, these chemoreceptors signal the medulla respiratory center that triggers breathing rate to increase; expiration of CO2 raises the pH of the blood to normal. Tas ...
... aorta respond to the pH of the blood and communicate with the medulla oblongata to change breathing rate. For example, when blood pH drops, these chemoreceptors signal the medulla respiratory center that triggers breathing rate to increase; expiration of CO2 raises the pH of the blood to normal. Tas ...